
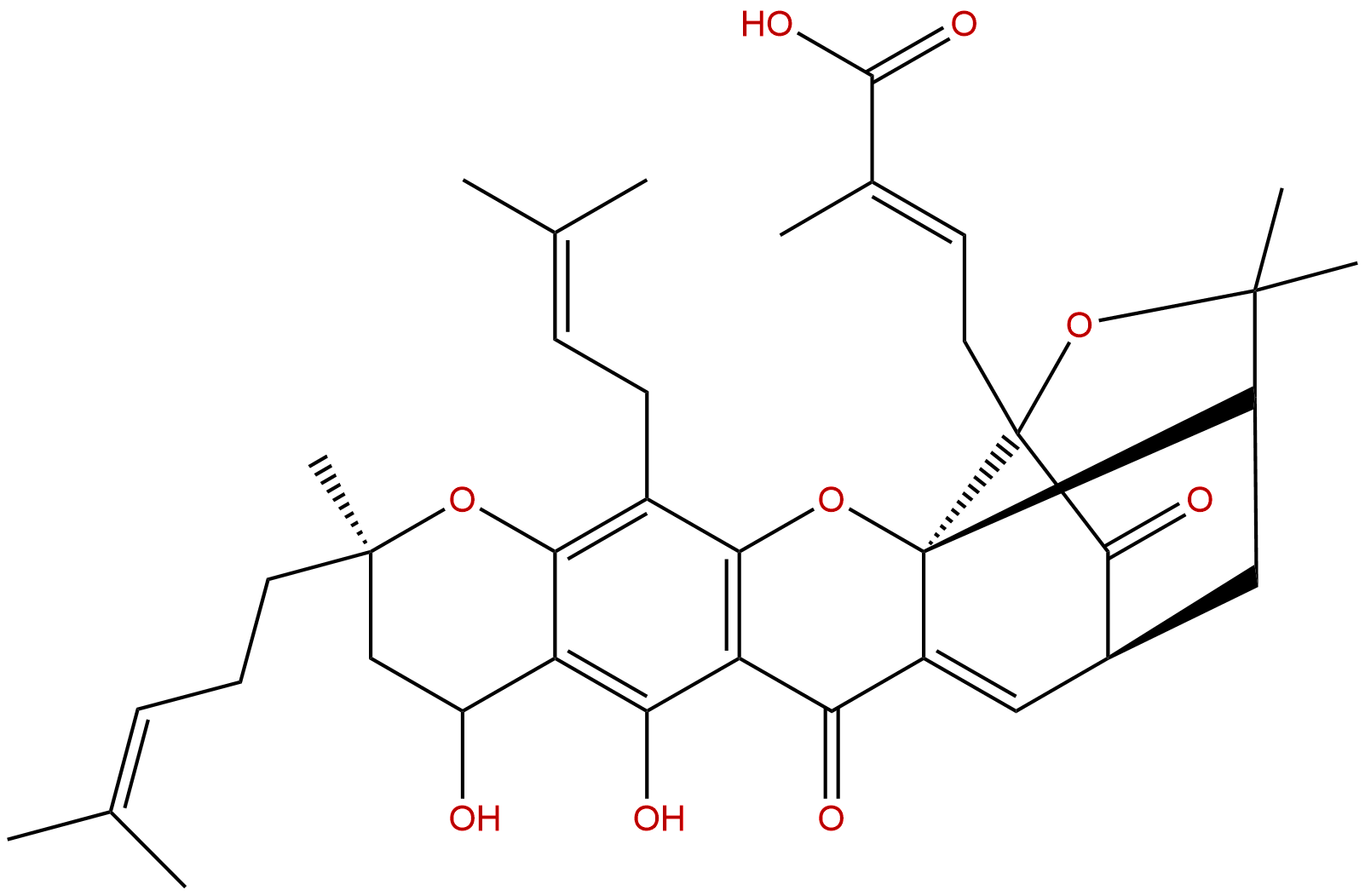
Neogambogic acidCAS No.:93772-31-7
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0990 |
| Formula: | C38H46O9 |
| Mol Weight: | 646.777 |
Product name: Neogambogic acid
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP0990
Cas No.: 93772-31-7
Formula: C38H46O9
Mol Weight: 646.777
Botanical Source: Garcinia hanburyi Hook.f.
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Miscellaneous
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Neogambogic acid , an active ingredient in garcinia, can inhibit the growth of some solid tumors and result in an anticancer effect, it may be responsible for the inhibition of proliferation of human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 cells.
References:
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2011 Sep;43(9):698-702.
The mechanism of neogambogic acid-induced apoptosis in human MCF-7 cells.
Neogambogic acid (NGA), an active ingredient in garcinia, can inhibit the growth of some solid tumors and result in an anticancer effect. We hypothesize that NGA may be responsible for the inhibition of proliferation of human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To investigate its anticancer mechanism in vitro, MCF-7 cells were treated with various concentrations of NGA. Results of MTT (methyl thiazolyl tetrazolum) assay showed that treatment with NGA significantly reduced the proliferation of MCF-7 cells in a dose-dependent manner. NGA could increase the expression of the apoptosis-related proteins FasL, caspase-3, caspase-8, caspase-9, and Bax and decrease the expression of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 accompanied by the mitochondrial transmembrane damage. The antiproliferative effect of NGA on MCF-7 cells is due to the G(0)/G(1) arrest, increased apoptosis and activation of Fas/FasL and cytochrome C pathway.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results provide an important insight into the cellular and molecular mechanisms through which NGA impairs the proliferation of breast cancer cells.