Luteolin Descrtption
Product name: Luteolin
Synonym name: Digitoflavone; Daphneflavonol; Flavopurpol; Luteolol
Catalogue No.: BP0896
Cas No.: 491-70-3
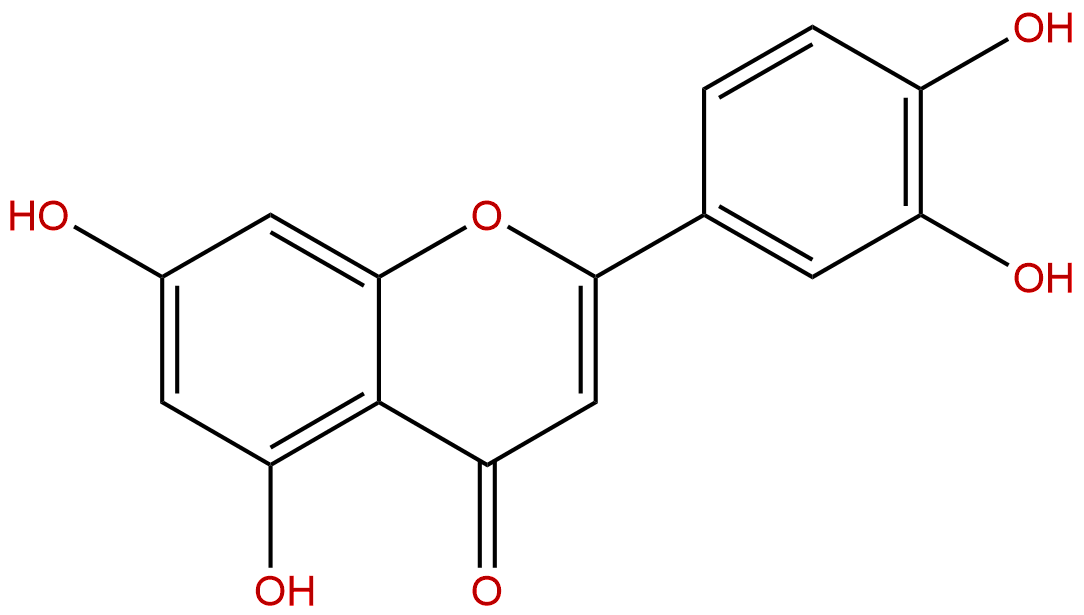
Formula: C15H10O6
Mol Weight: 286.239
Botanical Source: Occurs in many plants in Leguminosae, Resedaceae, Euphorbiaceae, Umbelliferae, Scrophulariaceae, Fabaceae, Asteraceae, Cistaceae, Passifloraceae, Yerbenaceae and Hepaticae. First isol. in 1832 from Reseda luteola
Physical Description: Yellow powder
Type of Compound: Flavonoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Luteolin, is a common flavonoid that exists in many types of plants including fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs, has anti-oxidant, anti-inflammation, anti-allergy and anticancer, has been used in Chinese traditional medicine for treating various diseases such as hypertension, inflammatory disorders, and cancer. [1]
Luteolin can reduce production of proinflammatory mediators and inhibit LPS-induced IL-6 production in the brain by inhibiting the JNK signaling pathway and activation of AP-1 in microglia, also shows potent anti-inflammatory activities by inhibiting nuclear factor kappa B (NFkB) signaling in immune cells, thus, could be a promising candidate to develop immuno-modulatory and neuroprotective therapies for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders.[2-3]
Luteolin induces apoptosis in various cancer cells, one mechanism through death receptor 5 (DR5) upregulation, treatment with luteolin might be promising as a new therapy against cancer. [4]
Luteolin attenuates TGF-β1-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition of lung cancer cells by interfering in the PI3K/Akt–NF-κB–Snail pathway, strengthen the anti-cancer effects of flavonoid compounds via the regulation of migration/invasion and EMT ability of various cancer cells.[5]
References:
[1] Lin Y, Shi R, Wang X, et al. Curr Cancer Drug Tar, 2008, 8(7):634-46(13).
[2] Jang S, Kelley K W, Johnson R W. P Natl Acad Sci USA, 2008, 105(21):7534-9.
[3] Dirscherl K, Karlstetter M, Ebert S, et al. J Neuroinflamm, 2010, 7(1):1-16.
[4] Horinaka M, Yoshida T, Shiraishi T, et al. Oncogene, 2005, 24(48):7180-9.
[5] Chen K C, Chen C Y, Lin C J, et al. Life Sci, 2013, 93(24):924-33.
[6] Chen X, Liu L, Sun Z, et al. Biomed Chromatogr, 2010, 24(8):826–32.