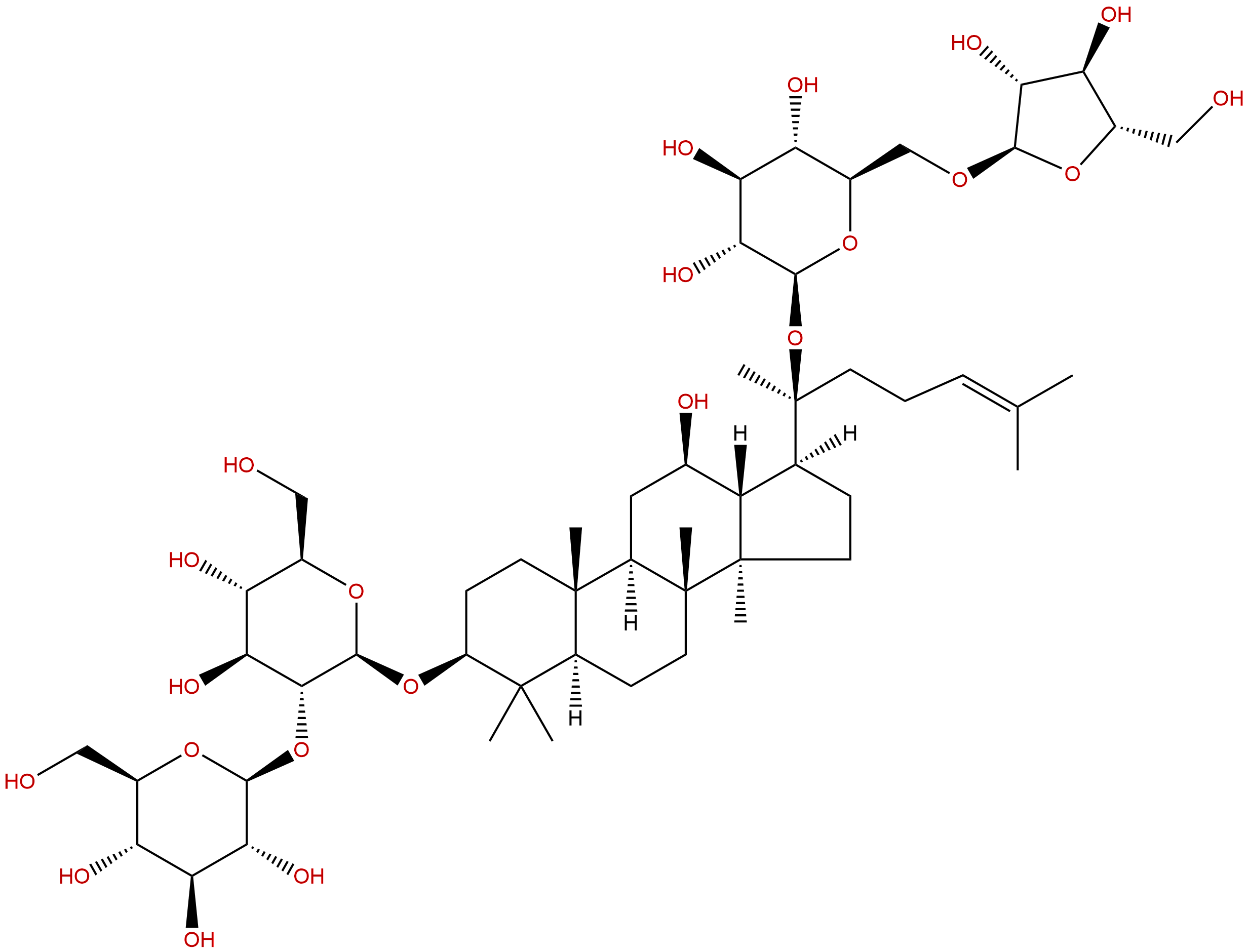
Ginsenoside RcCAS No.:11021-14-0
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0660 |
| Formula: | C53H90O22 |
| Mol Weight: | 1079.28 |
Product name: Ginsenoside Rc
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP0660
Cas No.: 11021-14-0
Formula: C53H90O22
Mol Weight: 1079.28
Botanical Source: Panax ginseng (ginseng)
Physical Description: White powder
Type of Compound: Triterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Ginsenoside Rc (Rc), a protopanaxadiol type ginsenoside, is the active component mainly responsible for the therapeutic and pharmacologic properties of ginseng, which are derived from its suppression of superoxide-induced free radicals, Rc can modulate Forkhead box O (FoxO1)phosphorylation through activation of PI3K/Akt and inhibition of AMPK and FoxO1 acetylation through interaction with CBP and SIRT1, and that this leads to upregulation of catalase under conditions of oxidative stress.[1]
Ginsenoside Rc from Korean Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) exhibits anticancer and anti-inflammatory activities, can attenuate inflammatory symptoms of gastritis, hepatitis and arthritis.[2]
Ginsenoside Rc and Re induce c-fos in MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells at both the mRNA and protein levels, they act via other transcription factors and not via estrogen receptor in c-Fos expression.[3]
Ginsenoside Rc significantly enhances glucose uptake by inducing ROS generation, which leads to AMPK and p38 MAPK activation.,consequently, it can be used as a potent natural anti-diabetic agent.[4]
Ginsenoside Rc can promote anti-adipogenic activity on 3T3-L1 adipocytes by down-regulating C/EBPα and PPARγ.[5]
References:
[1] Kim D H, Chan H P, Park D, et al. Arch Pharm Res, 2014, 37(6):813-20.
[2] Tao Y, Man H R, Lee J, et al. Am J Chinese Med, 2016:1-21.
[3] Lee Y J, Jin Y R, Lim W C, et al. Arch Pharm Res, 2003, 26(1):53-7.
[4] Lee M S, Hwang J T, Kim S H, et al. J Ethnopharmacol, 2010, 127(3):771-6.
[5] Yang J W, Kim S S. Molecules, 2015, 20(1):1293-303.
[6] Gao Y, Zang P, Hao J, et al. J Med Plants Res. 2012,6(15):3030-6.
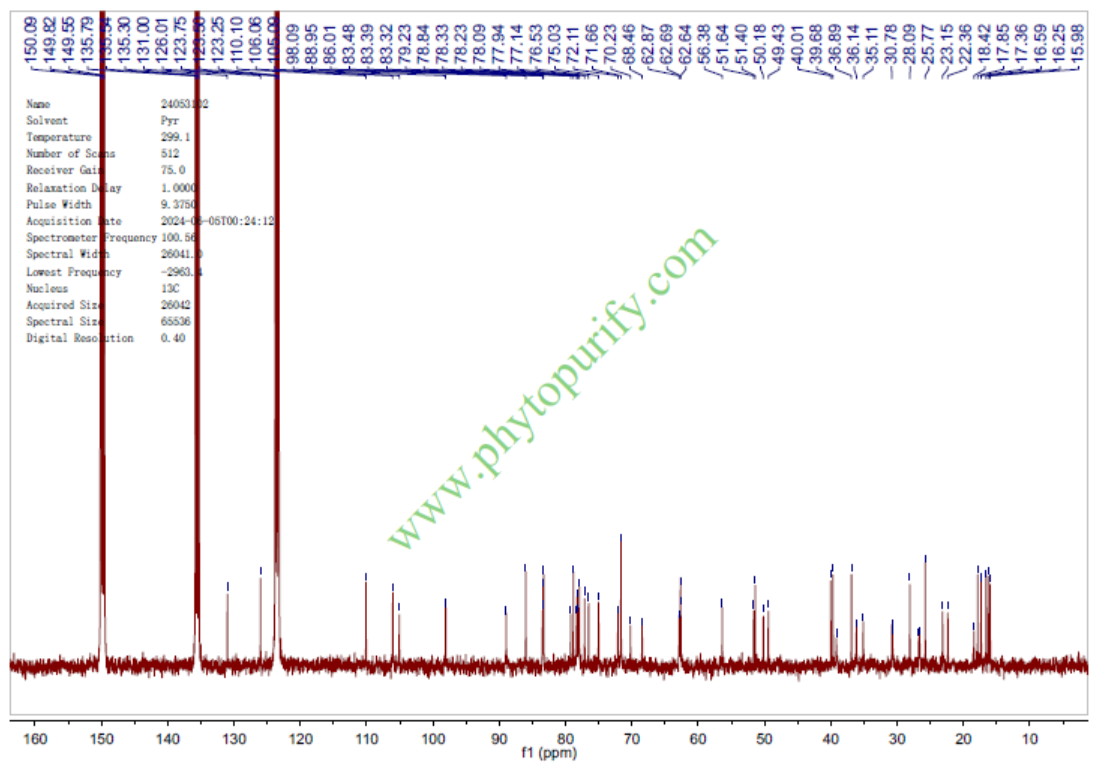
NMR of Ginsenoside Rc
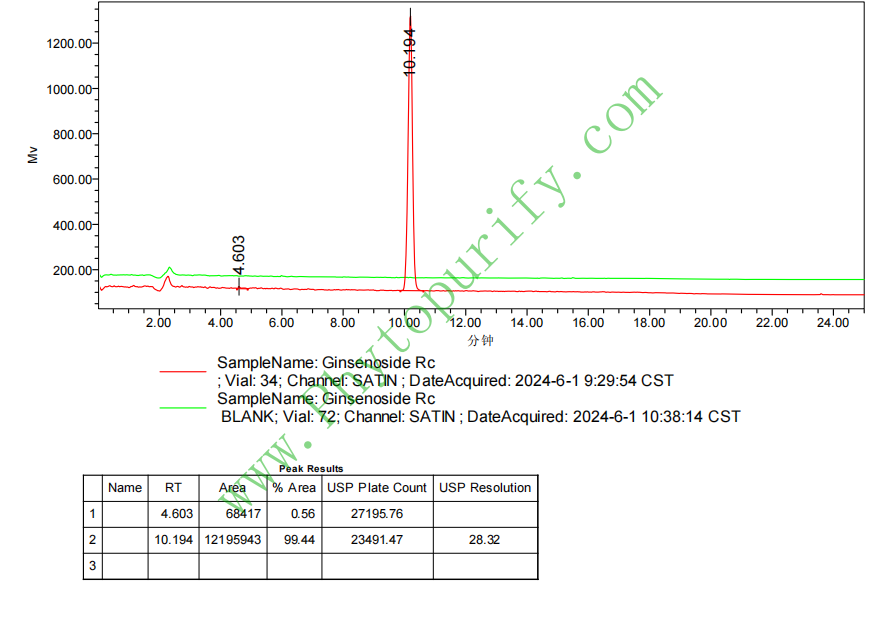
HPLC of Ginsenoside Rc