
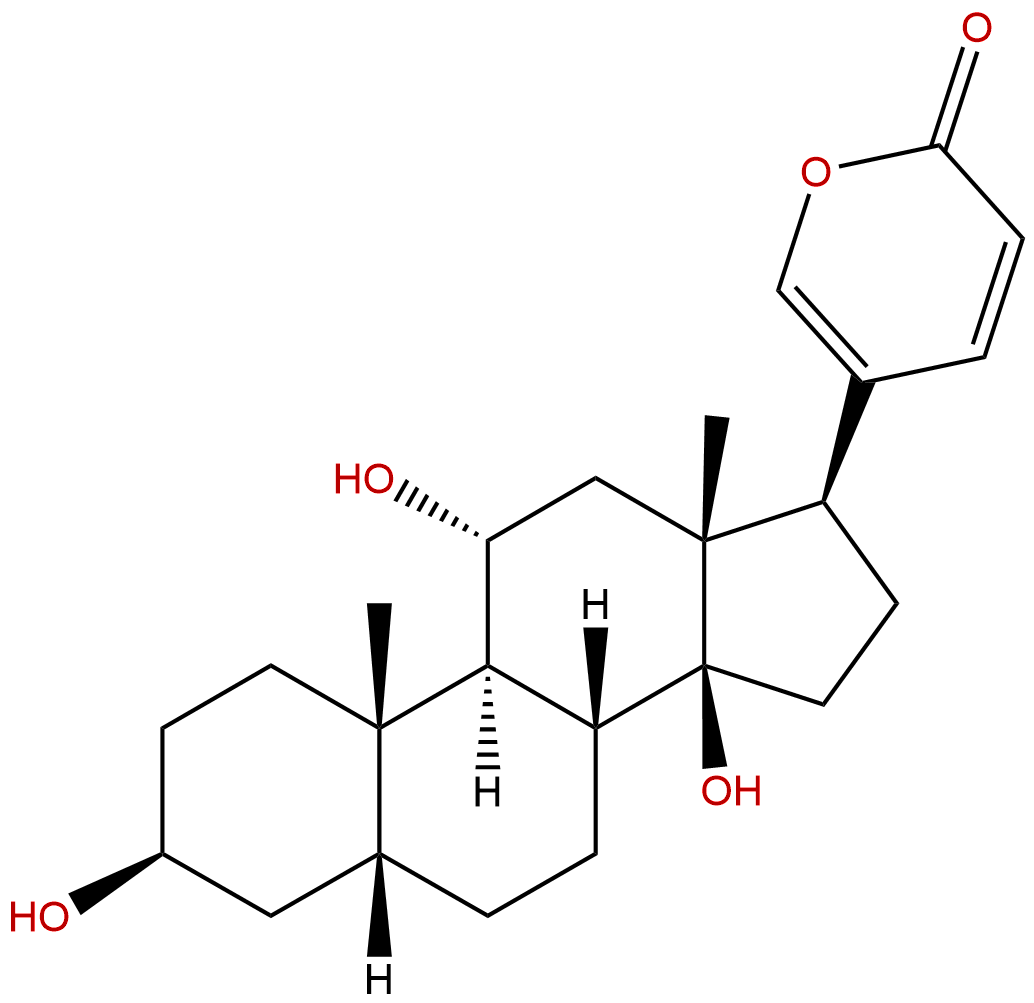
GamabufotalinCAS No.:465-11-2
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0612 |
| Formula: | C24H34O5 |
| Mol Weight: | 402.531 |
Product name: Gamabufotalin
Synonym name: Gamabufagin; Gamabufogenin
Catalogue No.: BP0612
Cas No.: 465-11-2
Formula: C24H34O5
Mol Weight: 402.531
Botanical Source: poisonous secretion of toads Bufo vulgaris formosus and Bufo bufo gargarizans, and toad poison Ch'an Su. Rhabdophis tigrinus
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Steroids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Gamabufotalin(CS-6), a bufadienolide compound from toad venom, suppresses COX-2 expression through targeting IKKβ/NF-κB signaling pathway in lung cancer cells, suggests that CS-6 exhibits potential use in the treatment of COX-2-mediated diseases such as lung cancer.[1]
Gamabufotalin has been shown to strongly inhibit cancer cell growth and inflammatory response, CS-6 inhibits angiogenesis by inhibiting the activation of VEGFR-2 signaling pathways and CS-6 could be a potential candidate in angiogenesis-related disease therapy.[2]
Gamabufotalin triggers c-Myc degradation via induction of WWP2 in multiple myeloma(MM) cells, it may be as a promising therapeutic agent in the treatment of MM.[3]
References:
[1] Yu Z, Guo W, Ma X, et al. Mol Cancer, 2014, 13(1):1-14.
[2] Tang N, Shi L, Yu Z, et al. Oncotarget, 2015, 7(3):3533-47.
[3] Yu Z, Li T, Wang C, et al. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(13):15725-37.
[4] Ma X C, Zhang B J, Xin X L, et al. Nat Prod Commun, 2009, 4(4):179-84.
HPLC of Gamabufotalin
