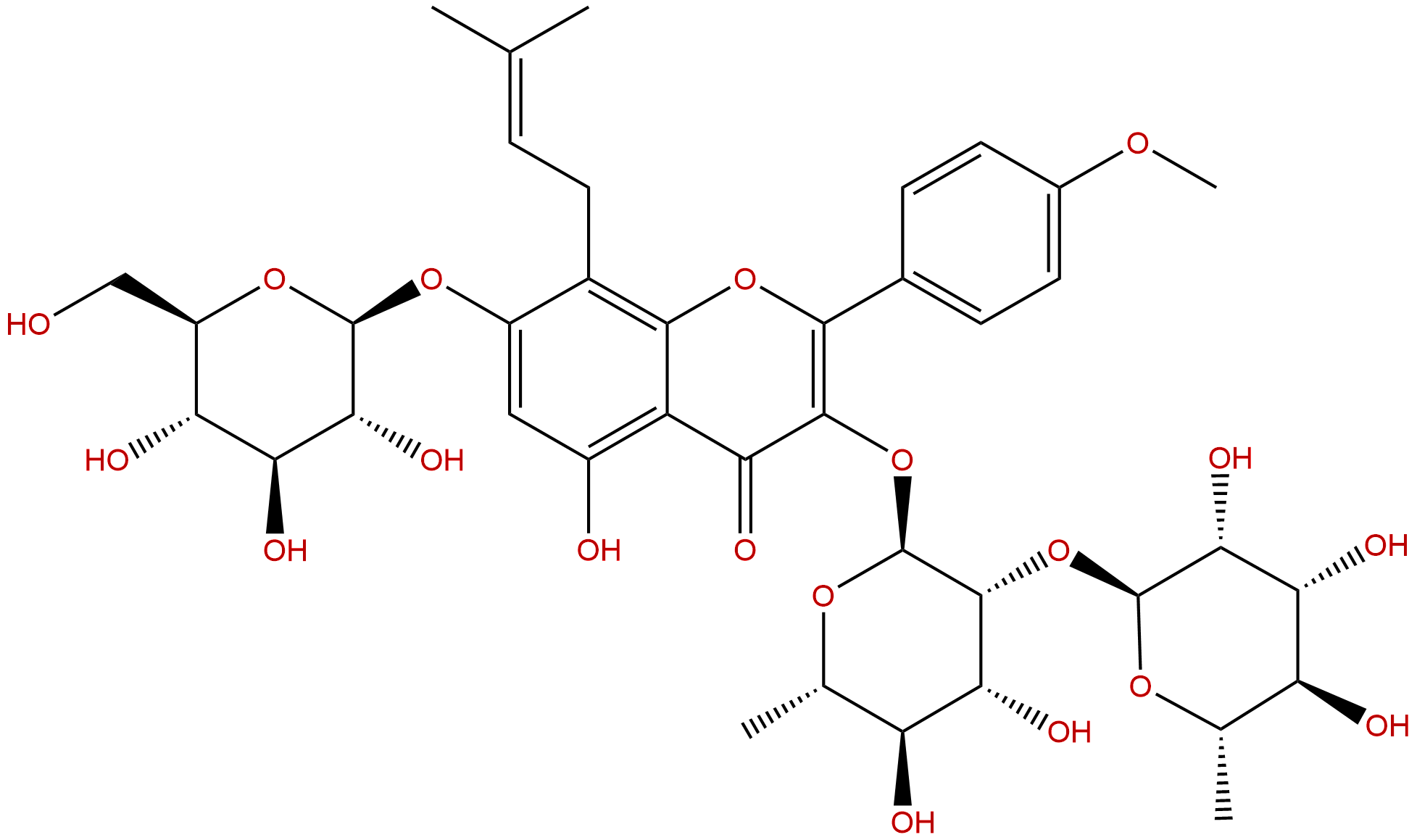
Epimedin CCAS No.:110642-44-9
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0547 |
| Formula: | C39H50O19 |
| Mol Weight: | 822.81 |
Product name: Epimedin C
Synonym name: Baohuoside VI
Catalogue No.: BP0547
Cas No.: 110642-44-9
Formula: C39H50O19
Mol Weight: 822.81
Botanical Source: Epimedii folium
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Flavonoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Epimedin C and diphylloside A have antiinflammation effect, can reduce the swelling of the rats foot induced by egg. The accumulation of epimedinsA, B, C, and icariin in a traditional medicinal plant could be suppressed by light stress.
References:
Acta Physiol Plant, 2013, 35(11):3271-5.
Light stress suppresses the accumulation of epimedins A, B, C, and icariin in Epimedium, a traditional medicinal plant.
Epimedium is well-known in China and East Asia due to high content of flavonoid derivatives, including icariin, Epimedin A, epimedin B, and Epimedin C, hereafter designated as bioactive components, which have been extensively utilized to cure many diseases. So far, the molecular mechanism of the bioactive components biosynthesis remains unclear.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, the effect of light stress (24 h illumination) on the accumulation of bioactive components and the expression of flavonoid genes in Epimedium was investigated. Under light stress, the structural genes CHS1, CHI1, F3H, FLS, DFR1, DFR2, and ANS were remarkably up-regulated while CHS2 and F3′H were significantly down-regulated. For transcription factors, the expression of Epimedium MYB7 and TT8 were increased while Epimedium GL3, MYBF, and TTG1 expression were depressed. Additionally, the content of bioactive components was significantly decreased under light stress.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results suggested that the decrease of bioactive compounds may be attributed to transcripts of late genes (DFRs and ANS) increased to a higher level than that of early genes (FLS and CHS1).
Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy, 2012(3):198-201.
Antiinflammatory Effect of Epimedin C and Diphylloside A of Epimedium Wushanense T.S.Ying.s.
To study the antiinflammatory effect of Epimedin C and diphylloside A of Epimedium wushanense T.S.Ying.s on rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Effect of Epimedin C and diphylloside A on swelling foot of rats induced by egg was assayed,degree of swelling was calculated,and compared with distilled water or indomethacin. Swelling of the rats foot induced by egg was reduced by Epimedin C and diphylloside A,and there was significant difference,compared with distilled water;and there was significant difference of Epimedin C in high dosage,compared with indomethacin,but there was no significant difference of Epimedin C in low dosage.
CONCLUSIONS:
Epimedin C and diphylloside A have antiinflammation effect.
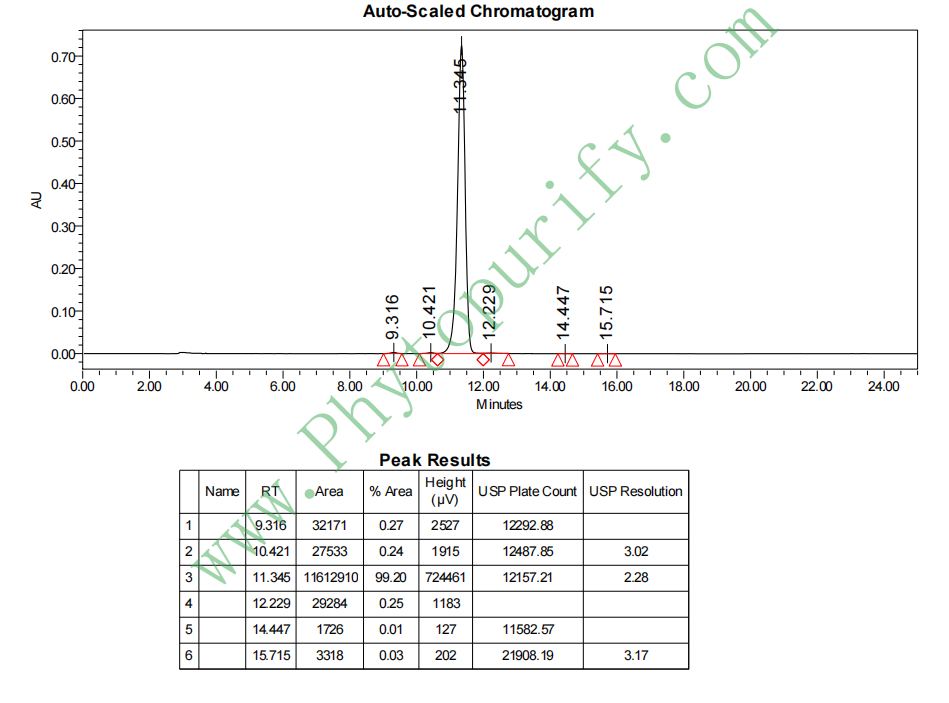
HPLC of Epimedin C
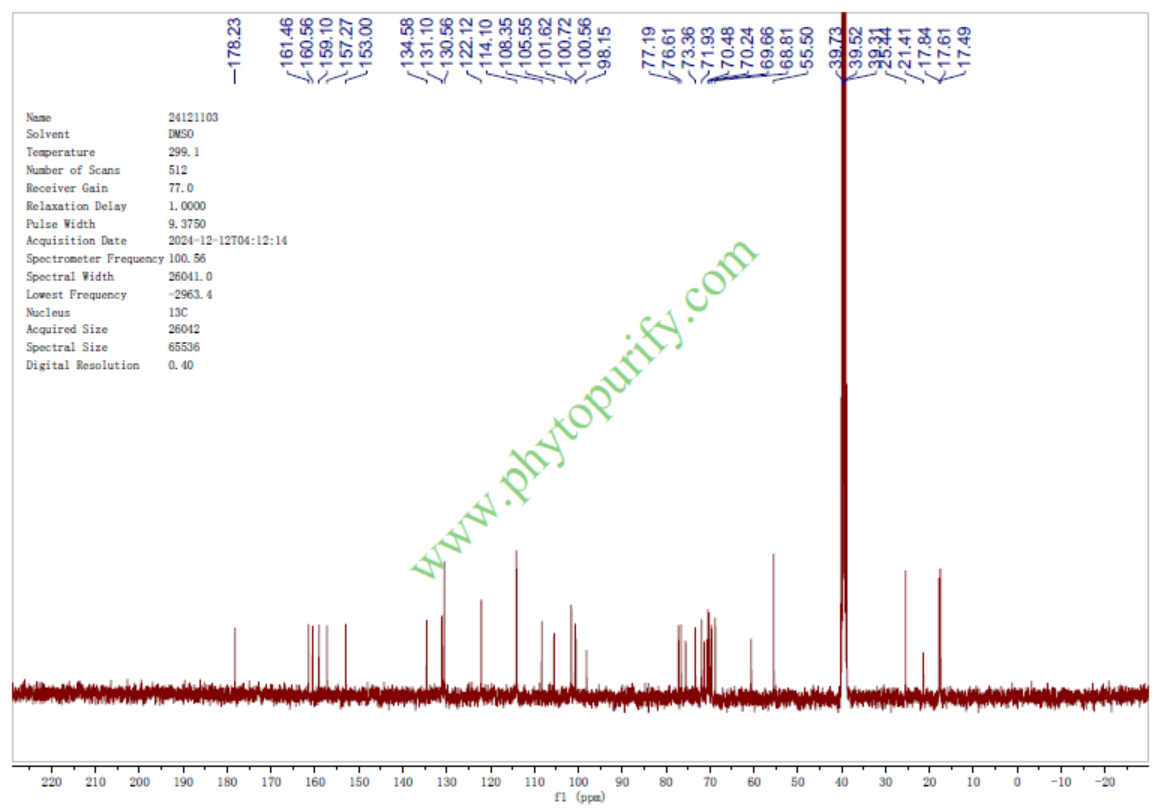
NMR of Epimedin C