+86-28-82633987sales@biopurify.com

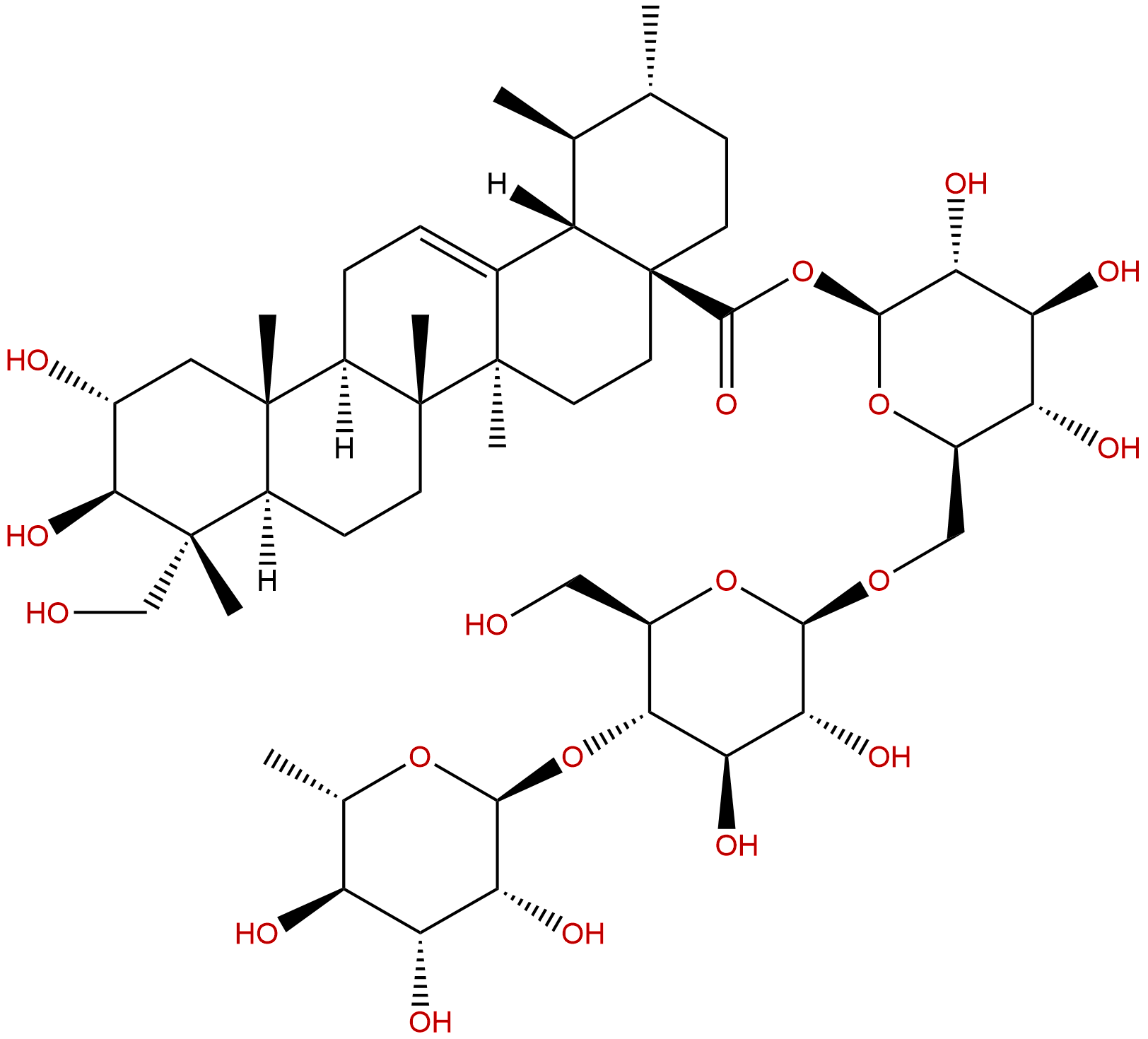
AsiaticosideCAS No.:16830-15-2
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0204 |
| Formula: | C48H78O19 |
| Mol Weight: | 959.133 |
Synonym name: Madecassol; Blastostimulina; Centelase; Emdecassol; Marticassol
Catalogue No.: BP0204
Cas No.: 16830-15-2
Formula: C48H78O19
Mol Weight: 959.133
Botanical Source: Centella asiatica (Asiatic pennywort) and Hydrocotyle asiatica
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Inquire for bulk scale.
