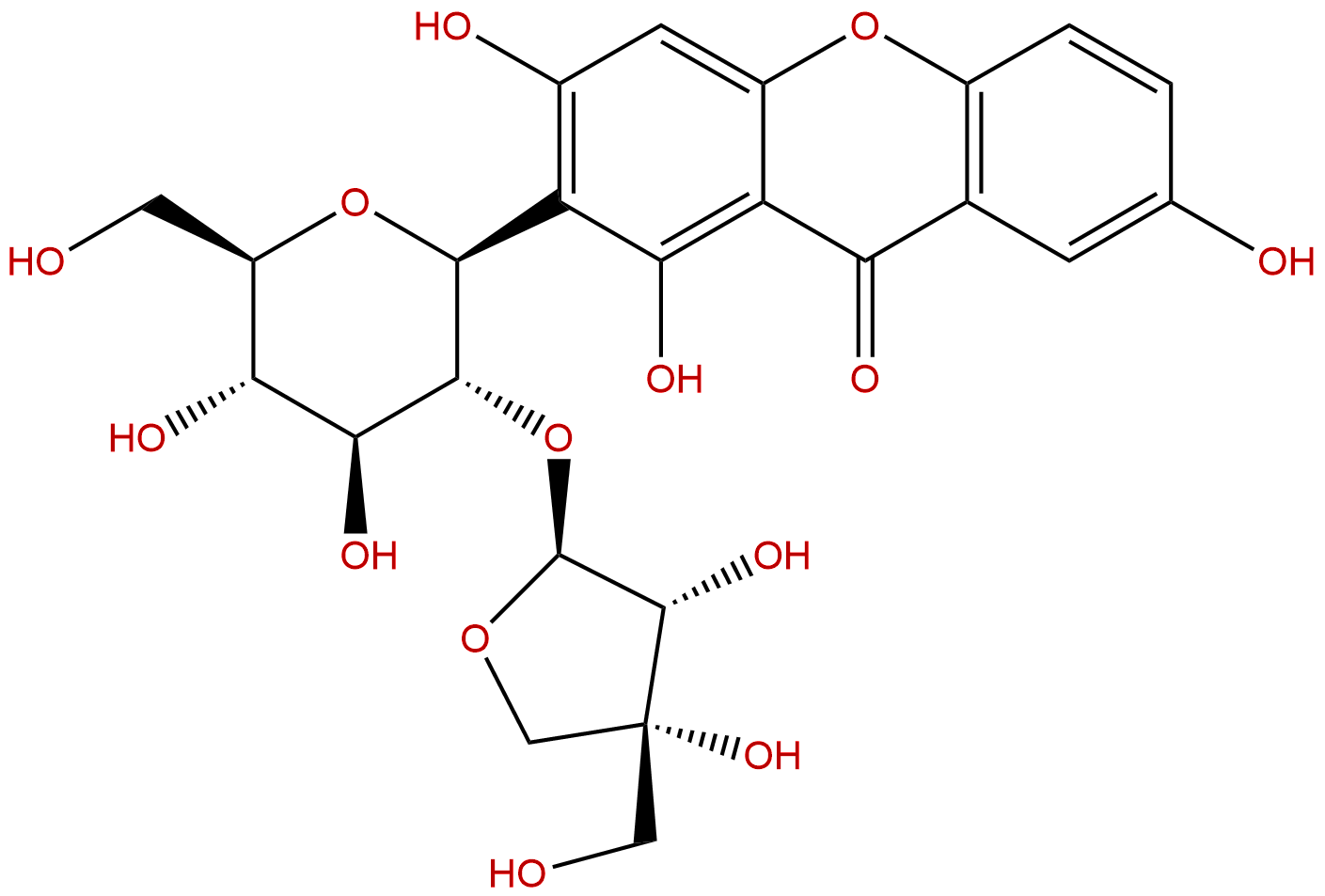
sibiricaxanthone BCAS No.:241125-81-5
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP3366 |
| Formula: | C24H26O14 |
| Mol Weight: | 538.458 |
Product name: sibiricaxanthone B
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP3366
Cas No.: 241125-81-5
Formula: C24H26O14
Mol Weight: 538.458
Botanical Source:
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Xanthones
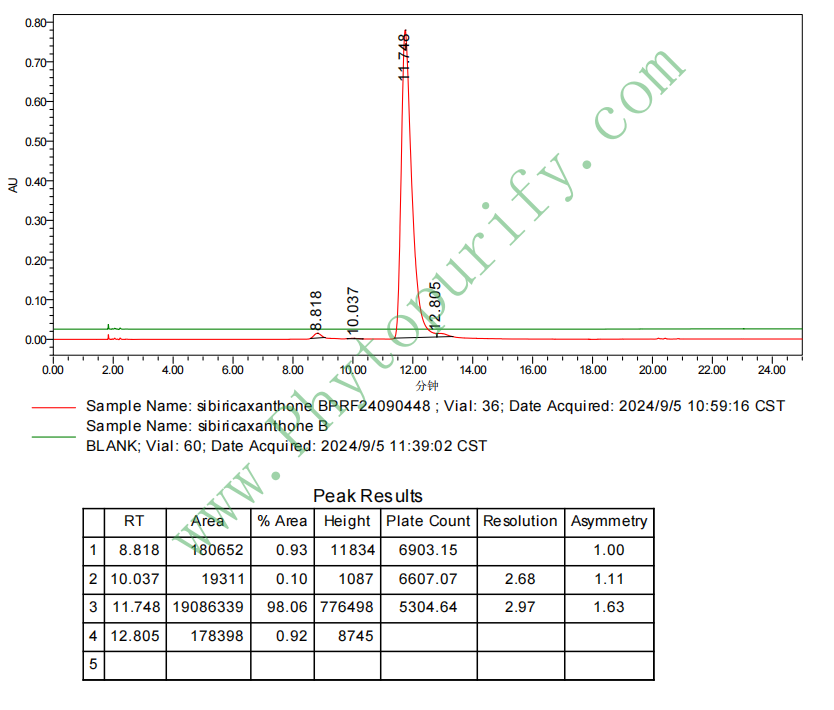
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams. Inquire for bulk scale.
We provide solution to improve the water-solubility of compounds, thereby facilitating the variety of activity tests and clinic uses.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Description:
Sibiricaxanthone B is a natural product from Polygala tenuifolia.
References:
J Sep Sci. 2017 May;40(10):2131-2140.
Ultra-fast liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry determination of eight bioactive components of Kai-Xin-San in rat plasma and its application to a comparative pharmacokinetic study in normal and Alzheimer's disease rats.
A method of ultra-fast liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry was developed and validated for the simultaneous quantitation of eight bioactive components, including polygalaxanthone III, Sibiricaxanthone B, tenuifolin, sibiricose A5, sibiricose A6, tenuifoliside A, ginsenoside Re and ginsenoside Rb1 in rat plasma after oral administration of Kai-Xin-San.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The plasma samples were extracted by liquid-liquid extraction using digoxin as an internal standard. Chromatographic separation was performed on a Venusil MP C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm, 3 μm) with methanol and 0.05% acetic acid in water as mobile phase. The tandem mass spectrometric detection was performed in the multiple reaction monitoring with turbo ion spray source in the negative ionization. Validation parameters were within acceptable ranges. The established method has been successfully applied to compare the pharmacokinetic profiles of the analytes between normal and Alzheimer's disease rats.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results indicated that there were significant differences in pharmacokinetic parameters of some components between two groups, which may be due to the mechanisms of Alzheimer's disease and pharmacological effects of the analytes. The pharmacokinetic research in the pathological state might provide more useful information to guide the clinical usage of herbal medicine.
HPLC of sibiricaxanthone B