Momilacton ACAS No.:51415-07-7
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
||||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP5234 |
| Formula: | C20H26O3 |
| Mol Weight: | 314.425 |
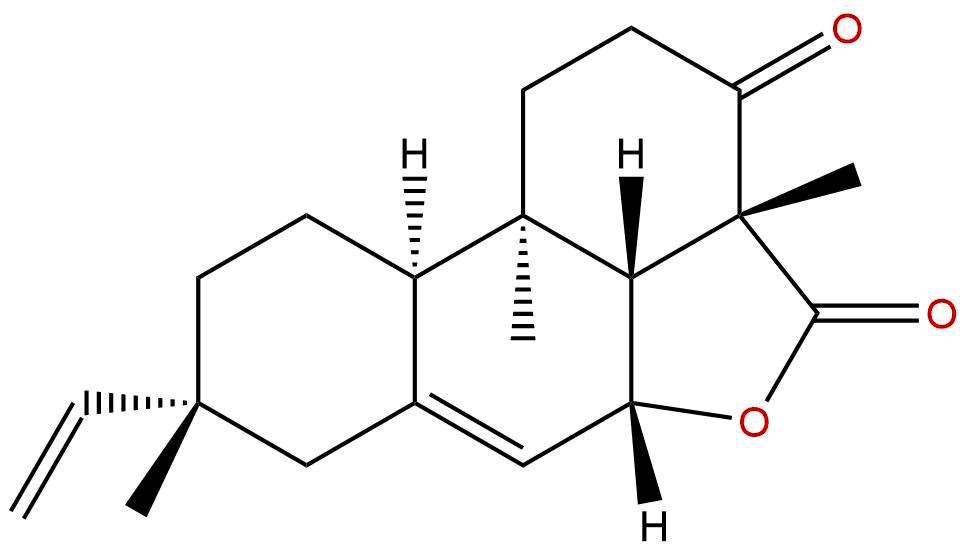
Product name: Momilacton A
Synonym name: Momilactone A
Catalogue No.: BP5234
Cas No.: 51415-07-7
Formula: C20H26O3
Mol Weight: 314.425
Botanical Source:
Type of Compound: Terpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Momilacton A and B are the main chemosensitizers for weed suppression in rice, and among them, Momilacton B is one of the most efficient natural herbicides found so far, and has good potential for application. Momilacton B can be released from the rice root system into the soil to inhibit the seed germination and growth of the surrounding barnyard grass and other plants. The concentration of Momilacton B greater than 3 nmol-mL-1 can inhibit the growth of roots and embryonic axes of watercress and lettuce, andMomilacton A and B are important phytochemicals for rice, which can effectively inhibit rice pathogens such as Magnaporthe grisea. In addition, M. grisea infection induced rice to synthesize more Momilactons.
Labdane-related diterpenoids, momilactones A and B were isolated and identified in rice husks in 1973 and later found in rice leaves, straws, roots, root exudate, other several Poaceae species and the moss species Calohypnum plumiforme. The functions of momilactones in rice are well documented. Momilactones in rice plants suppressed the growth of fungal pathogens, indicating the defense function against pathogen attacks. Rice plants also inhibited the growth of adjacent competitive plants through the root secretion of momilactones into their rhizosphere due to the potent growth-inhibitory activity of momilactones, indicating a function in allelopathy. Momilactone-deficient mutants of rice lost their tolerance to pathogens and allelopathic activity, which verifies the involvement of momilactones in both functions. Momilactones also showed pharmacological functions such as anti-leukemia and anti-diabetic activities. Momilactones are synthesized from geranylgeranyl diphosphate through cyclization steps, and the biosynthetic gene cluster is located on chromosome 4 of the rice genome.
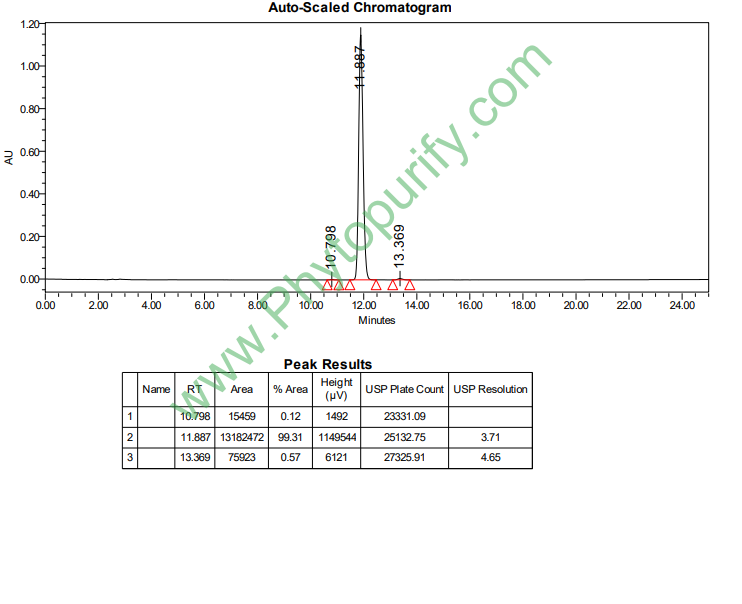
HPLC of Momilacton A