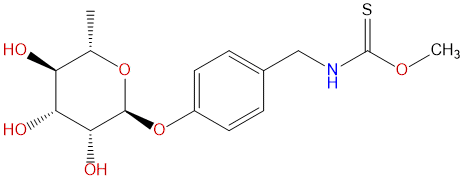
NiazininCAS No.:147821-57-6
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP2162 |
| Formula: | C15H21NO6S |
| Mol Weight: | 343.394 |
Product name: Niazinin
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP2162
Cas No.: 147821-57-6
Formula: C15H21NO6S
Mol Weight: 343.394
Botanical Source: Moringa Seeds.
Type of Compound:
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
References:
Isolation and structure elucidation of novel hypotensive agents, niazinin A, niazinin B, niazimicin and niaziminin A + B from Moringa oleifera: the first naturally occurring thiocarbamates
Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 1 Pub Date : 1992 , DOI: 10.1039/p19920003237
Abstract
Novel hypotensive principles, niazinin A 1, niazinin B 2, niazimicin 4 and niaziminin A and B 6+7, have been obtained from the ethanolic extract of the fresh leaves of Moringa oleifera, employing a bioassay-guided isolation procedure. Their structures have been elucidated through spectroscopic (including 2D NMR techniques) and chemical methods. These compounds are mustard oil glycosides which are very rare in Nature and are also the first examples of naturally occurring thiocarbamates.
Pharmacological studies on hypotensive and spasmolytic activities of pure compounds from Moringa oleifera
Phytotherapy Research Volume8, Issue2 March 1994 Pages 87-91
Abstract
Bioassay directed fractionation of an ethanolic extract of Moringa oleifera (MO) leaves resulted in the isolation of four pure compounds, niazinin A (1), niazinin B (2), niazimicin (3) and niaziminin A + B (4 + 5). Intravenous administration of either one of the compounds (1–10 mg/kg) produced hypotensive and bradycardiac effects in anaesthetized rats. Pretreatment of the animals with atropine (1 mg/kg) completely abolished the hypotensive and bradycardiac effects of acetylcholine (ACh), whereas cardiovascular responses to the test compounds remained unaltered, ruling out the possible involvement of muscarinic receptor activation. In isolated guinea‐pig atria all the compounds (50–150 μg/mL) produced negative inotropic and chronotropic effects. Each compound inhibited K+ ‐induced contractions in rabbit aorta as well as ileal contractions induced by ACh or histamine at similar concentrations. Spontaneous contractions of rat uterus were also inhibited equally by all compounds. These data indicate that the direct depressant action of these compounds exhibited on all the isolated preparations tested is probably responsible for its hypotensive and bradycardiac effects observed in vivo. Moreover, spasmolytic activity exhibited by the constituents of the plant provides a scientific basis for the traditional uses of the plant in gastrointestinal motility disorders.
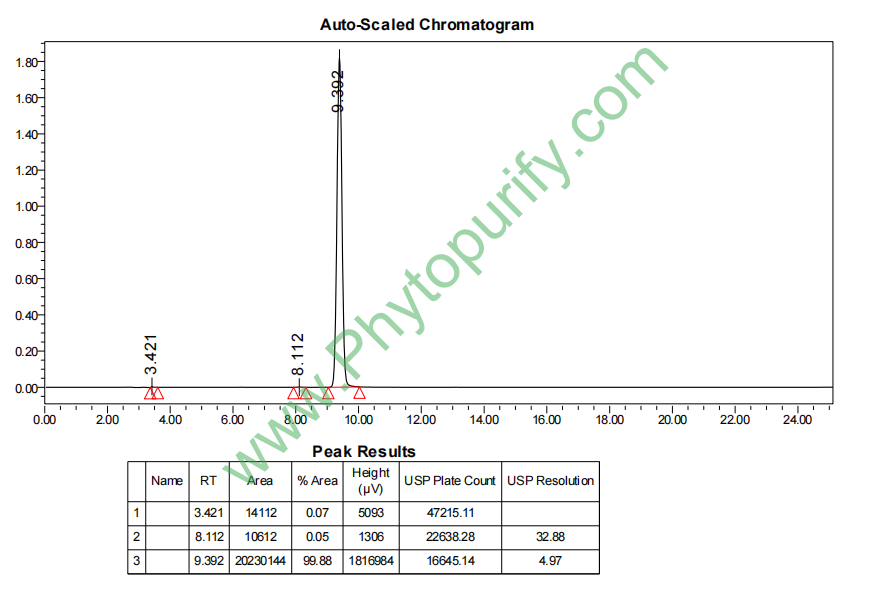
HPLC of Niazinin