
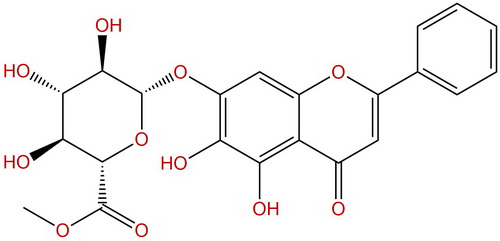
Baicalin methyl esterCAS No.:82475-03-4
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP2026 |
| Formula: | C22H20O11 |
| Mol Weight: | 460.391 |
Product name: Baicalin methyl ester
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP2026
Cas No.: 82475-03-4
Formula: C22H20O11
Mol Weight: 460.391
Botanical Source: Scutellaria spp.
Physical Description:
Type of Compound:
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Description:
Baicalin methyl ester shows inhibitory effects on the Avian Myeloblastosis Virus reverse transcriptase (AMV-RT).
References:
Japanese Journal of Pharmacognosy , 1991 , 45 (3) :240-254.
Effects of Flavonoids and Alkaloids on Reverse Transcriptase
METHODS AND RESULTS:
One hundred-ninety flavonoids and 75 alkaloids were studied for their inhibitory effects on the Avian Myeloblastosis Virus reverse transcriptase (AMV-RT) by using (rA)_n-p(dT)_<12-18> or (rC)_n-p(dG)_<12-18> as a template-primer. Of the flavonoids tested, 6-hydroxyluteolin (50), pedalitin (52), 6-hydroxykaempferol (109) and quercetagetin (129), were the most potent inhibitors with IC_<50>≦10 μM. Five other flavonoids, baicalein (19), Baicalin methyl ester (23), scutellarein (33), myricetin (126) and gossypetin (130), gave IC_<50> between 35 and 200 μM. The kinetic studies on 50, 126 and 130 gave the inhibitory constants (K_i) of 10, 94 and 90 μM, respectively, with respect to the substrate and 5, 200 and 100 μM, respectively, with respect to the template-primer. Structurally different alkaloids such as isoquinoline, indol, steroidal, quinolizidine, pyrrolizidine, pyridine and imidazole alkaloids were also investigated for the activity and berberine type alkaloids were shown to have a strong inhibitory activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
Flavonoids or alkaloids that inhibited AMV-RT did not show any significant effect on DNA-polymerase I.