
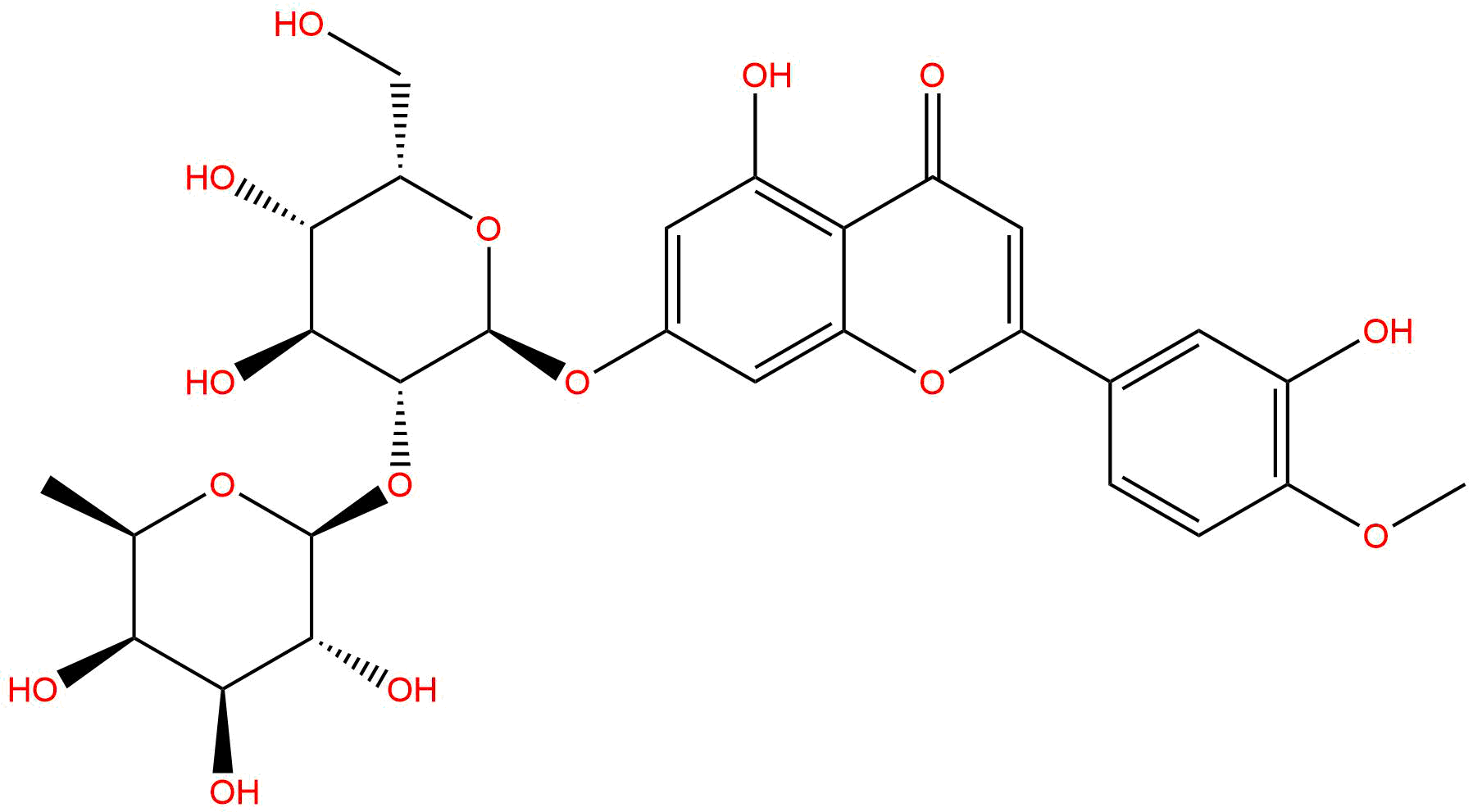
NeodiosminCAS No.:38665-01-9
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP3881 |
| Formula: | C28H32O15 |
| Mol Weight: | 608.549 |
Product name: Neodiosmin
Synonym name: Diosmetin 7-neohesperidoside
Catalogue No.: BP3881
Cas No.: 38665-01-9
Formula: C28H32O15
Mol Weight: 608.549
Botanical Source: Citrus aurantium
Physical Description:
Type of Compound:
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Description:
Neodiosmin has poor aqueous solubility but exerts a good debittering effect and is a strong antioxidant with potential applications in foods, beverages, and pharmaceutical preparations.
References:
J Agric Food Chem. 2013 Feb 27;61(8):1686-93.
HPLC-PDA-MS and NMR characterization of a hydroalcoholic extract of Citrus aurantium L. var. amara peel with antiedematogenic activity.
The phytochemical profile of a hydroalcoholic extract of Citrus aurantium var. amara L. peel, used as herbal medicine, was characterized by HPLC-PDA-MS.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Two di-C-glycosyl flavones (vincenin II and diosmetin 6,8-di-C-glucoside), a series of flavones (luteolin 7-O-neohesperidoside, rhoifolin, and Neodiosmin), and flavanone (neoeriocitrin, naringin, and neohesperidin) 7-O-neohesperidosides and two methoxyflavones (nobiletin and tangeretin), commonly present in Citrus, were identified. Furthermore, brutieridin and melitidin, two 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl flavanone glycosides, were also characterized along with rhoifolin 4'-glucoside and three coumarins (8,3'-β-D-glucopyranosyloxy-2'-hydroxy-3'-methylbutyl-7-methoxycoumarin, merazin hydrate, and isomerazin). A preparative isolation procedure followed by NMR spectroscopy confirmed the proposed structures of the major flavonoids and identified the coumarins.
CONCLUSIONS:
The phenolic content was found to be 14.8 mg mL(-1), and naringin and neohesperidin were the compounds present in the highest concentration (3.6 and 2.6 mg mL(-1)). The extract of C. aurantium peel inhibited significantly (p < 0.05) both histamine- and dextran-induced edema in rats in a concentration-dependent manner (IC(50) = 119.6 and 118.3 mg kg(-1), respectively), providing evidence for the therapeutic use of C. aurantium var. amara peel.
Starch -Stärke, 2016, 69(5-6):1-9.
Increased solubility and taste masking of a ternary system of neodiosmin with β -cyclodextrin and lysine: Ternary system for increasing solubility and masking bitter tastes
Neodiosmin has poor aqueous solubility but exerts a good debittering effect and is a strong antioxidant with potential applications in foods, beverages, and pharmaceutical preparations.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The water solubility of Neodiosmin was greatly enhanced by forming a Neodiosmin/β-cyclodextrin/lysine ternary inclusion complex. The inclusion type is described in detail in terms of its structural aspects using a phase diagram of solubility. The Neodiosmin/β-cyclodextrin/lysine ternary inclusion complex was synthesized and characterized by thermal analysis and powder X-ray diffractometry (XRD). The molecular and fractal structures of the ternary complexes were investigated using 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) spectroscopy and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. Additionally, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) revealed that Neodiosmin was embedded in a matrix of β-cyclodextrin with lysine.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results demonstrated that the inclusion complex was formed and that the solubility of Neodiosmin was greatly improved. Additionally, the bitterness-masking power of this system was evaluated by a panel test using a series of limonin concentrations as a reference scale. The Neodiosmin/β-cyclodextrin/lysine ternary inclusion complex showed the highest efficacy, and the bitterness attenuation was statistically significant.