
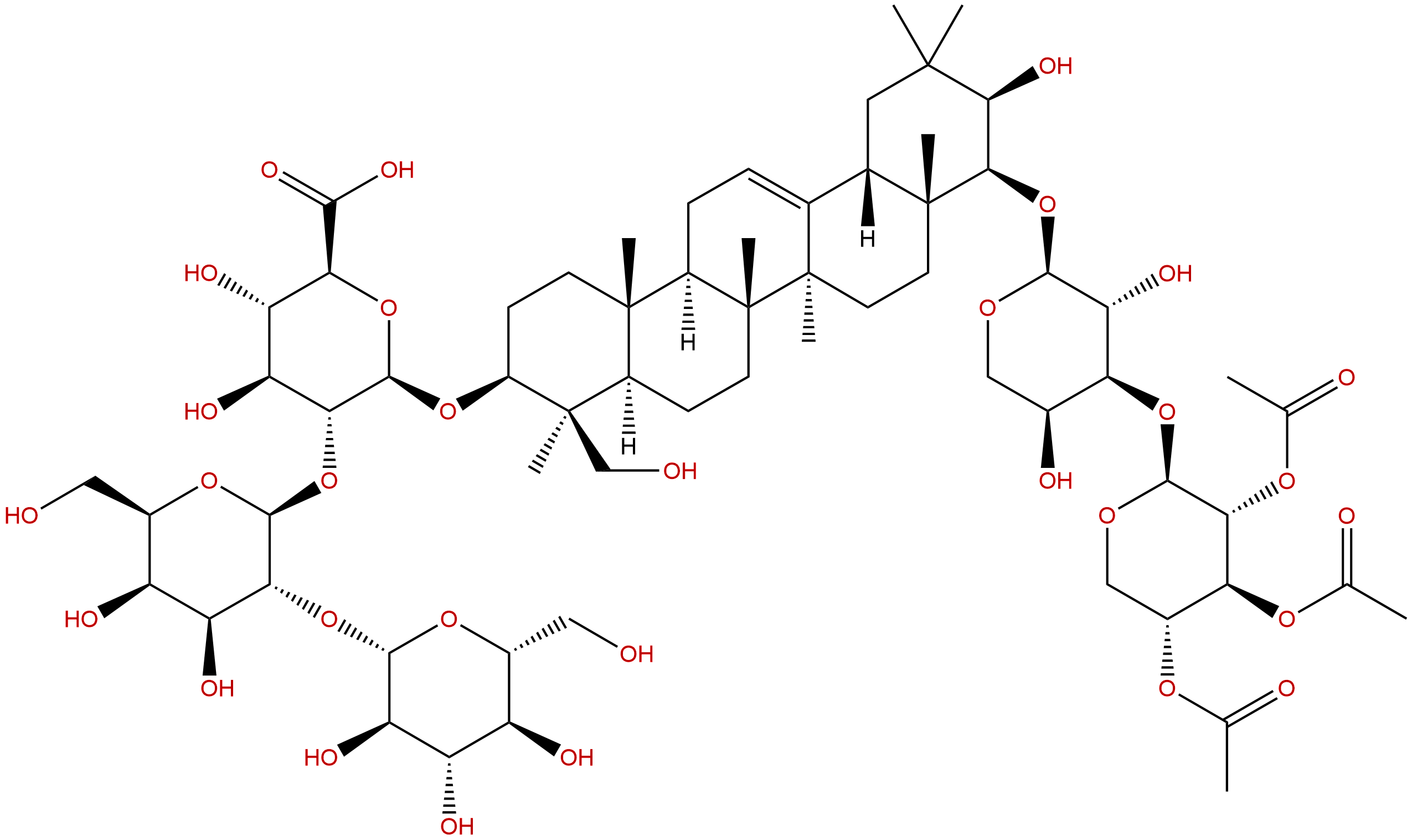
Soyasaponin AaCAS No.:117230-33-8
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1330 |
| Formula: | C64H100O31 |
| Mol Weight: | 1365.47 |
Product name: Soyasaponin Aa
Synonym name: Acetylsoyasaponin A4
Catalogue No.: BP1330
Cas No.: 117230-33-8
Formula: C64H100O31
Mol Weight: 1365.47
Botanical Source: Glycine max
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Triterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Soyasaponin Aa and soyasaponin Ab dose-dependently markedly inhibit adipocyte differentiation and expression of various adipogenic marker genes, through the downregulation of the adipogenesis-related transcription factors PPARγ and C/EBPα in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
References:
Phytother Res. 2015 Feb;29(2):281-7.
Soyasaponins Aa and Ab exert an anti-obesity effect in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through downregulation of PPARγ.
In this study, we investigated the effects and molecular mechanism of Soyasaponin Aa and soyasaponin Ab in regulating adipocyte differentiation and expression of adipogenic marker genes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Soyasaponin Aa and soyasaponin Ab dose-dependently inhibited the accumulation of lipids and the expression of adiponectin, adipocyte determination and differentiation factor 1/sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c, adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein 2, fatty acid synthase, and resistin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. In addition, Soyasaponin Aa and soyasaponin Ab suppressed the transcriptional activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) in HEK 293T cells. Furthermore, we confirmed that the expression of PPARγ and of CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein α (C/EBPα) was suppressed at both the mRNA and protein levels in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by treatment with Soyasaponin Aa and soyasaponin Ab.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these findings indicate that Soyasaponin Aa and soyasaponin Ab markedly inhibit adipocyte differentiation and expression of various adipogenic marker genes through the downregulation of the adipogenesis-related transcription factors PPARγ and C/EBPα in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.