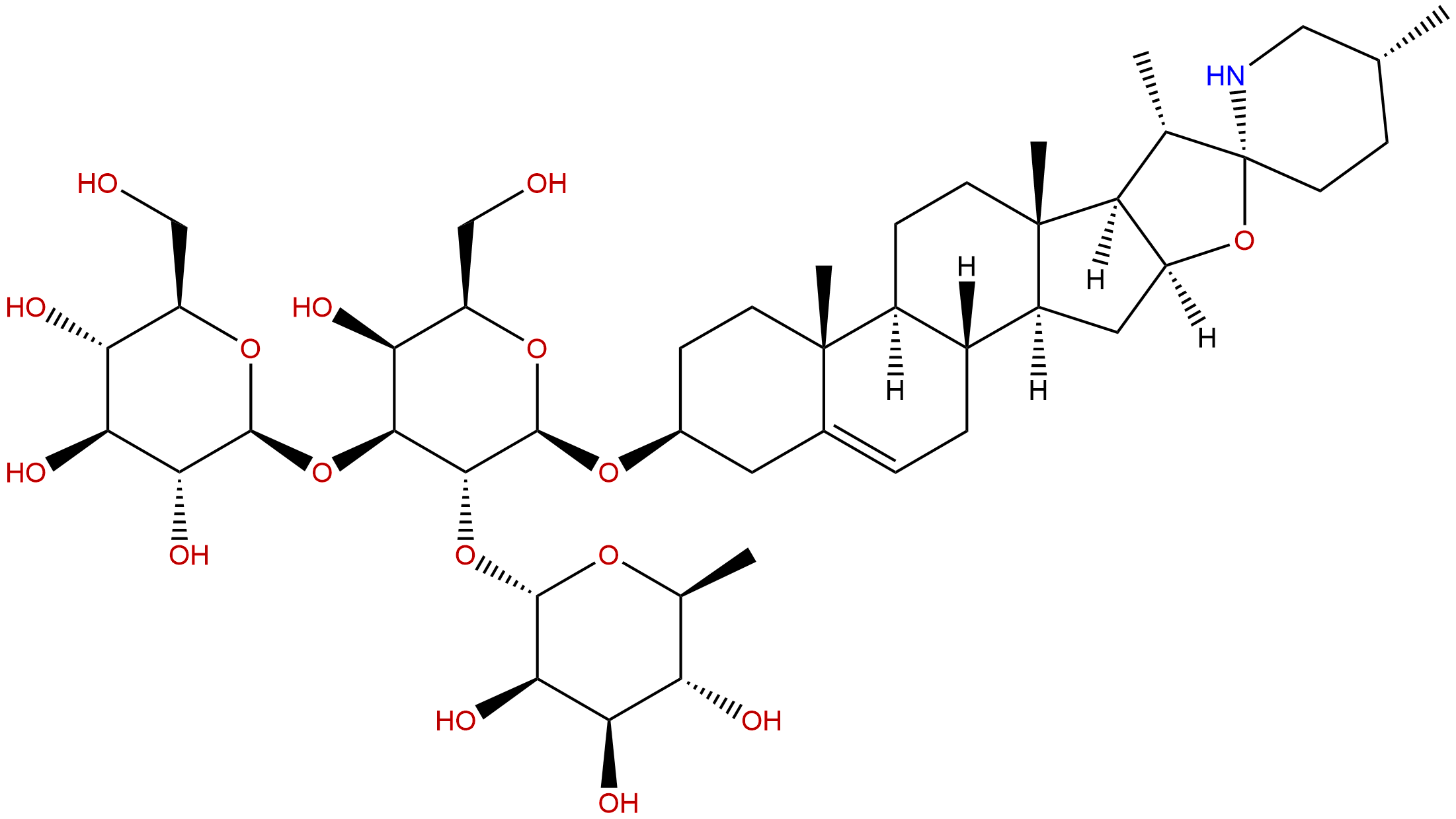
Solasonine Descrtption
Product name: Solasonine
Synonym name: Solasodamine
Catalogue No.: BP1323
Cas No.: 19121-58-5
Formula: C45H73NO16
Mol Weight: 884.07
Botanical Source: Solanum nigrum L.
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Alkaloids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Solasonine displays leishmanicidal activity against promastigote forms of L. amazonensis.
References:
Phytochemistry. 1994 Nov;37(4):1007-11.
Interactions between the glycoalkaloids solasonine and solamargine in relation to inhibition of fungal growth.
Inhibition of mycelium development in Phoma medicaginis and Rhizoctonia solani by solamargine and Solasonine generally increased with increasing pH. P. medicaginis was the more susceptible species and solamargine the more potent compound.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Solasonine was inactive against R. solani over the tested pH range (5-8). Dose-response curves confirmed these differential effects. Solamargine caused 50% growth inhibition in P. medicaginis at 60 microM (at pH 7) whereas no other treatment achieved this effect at 100 microM. Combinations of 50 microM of each glycoalkaloid produced synergistic effects against both fungi, especially R. solani which was essentially unaffected by either compound, by significantly inhibited by a 1:1 mixture of the two. The magnitude of the synergism was not affected by a pH change between 6 and 7. Spore germination in Alternaria brassicicola was markedly inhibited by 100 microM solamargine but unaffected by 100 microM Solasonine or either compound at 50 microM. In P. medicaginis, neither glycoalkaloid was inhibitory up to 150 microM.
CONCLUSIONS:
In combination, the two compounds caused synergistic effects in both species, but to a much greater extent in A. brassicicola.
HPLC of Solasonine