Sennoside CCAS No.:37271-16-2
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1294 |
| Formula: | C42H40O19 |
| Mol Weight: | 848.763 |
Product name: Sennoside C
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP1294
Cas No.: 37271-16-2
Formula: C42H40O19
Mol Weight: 848.763
Botanical Source: Sennae Folium
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Anthraquinones
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Sennoside C , aloe-emodin anthrone and rhein anthrone which formed mainly by intraluminal bacterial action, synergistically exert their purgative effects on mice.
References:
Comput Biol Chem. 2011 Oct 12;35(5):293-7.
Drug-target network and polypharmacology studies of a Traditional Chinese Medicine for type II diabetes mellitus.
Many Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs) are effective to relieve complicated diseases such as type II diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this work, molecular docking and network analysis were employed to elucidate the action mechanism of a medical composition which had clinical efficacy for T2DM. We found that multiple active compounds contained in this medical composition would target multiple proteins related to T2DM and the biological network would be shifted. We predicted the key players in the medical composition and some of them have been reported in literature. Meanwhile, several compounds such as Rheidin A, Rheidin C, Sennoside C, procyanidin C1 and Dihydrobaicalin were notable although no one have reported their pharmacological activity against T2DM.
CONCLUSIONS:
The association between active compounds, target proteins and other diseases was also discussed.
J Pharm Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;44(12):973-6.
Metabolic activation of sennoside C in mice: synergistic action of anthrones.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Sennosides A and C directly injected into the caecum of mice showed equal purgative activity. Intracaecal administration reduced time to onset of diarrhoea induced by Sennoside C from about 3 h after oral administration to about 24 min. At 2.3 h after oral administration of Sennoside C, nearly equimolar amounts of aloe-emodin anthrone and rhein anthrone were detected in the large intestine of mice. The purgative effect of oral Sennoside C could be reduced by pretreating mice with chloramphenicol. This was observed as a decreased formation of total anthrones in the large intestine. Both anthrones and an equimolar mixture of both anthrones directly injected into the caecum exerted a purgative effect, although the activity was lower for aloe-emodin anthrone. The intracaecal ED50 values were 54.5 (24.1-89.6), 11.4 (5.0-15.7) and 11.2 (6.1-14.6) mumol kg-1 for aloe-emodin anthrone, rhein anthrone and an equimolar mixture of both anthrones, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
We concluded that aloe-emodin anthrone and rhein anthrone, formed mainly by intraluminal bacterial action, are the true active metabolites of Sennoside C in mice and that both anthrones synergistically exert their purgative effects on mice.
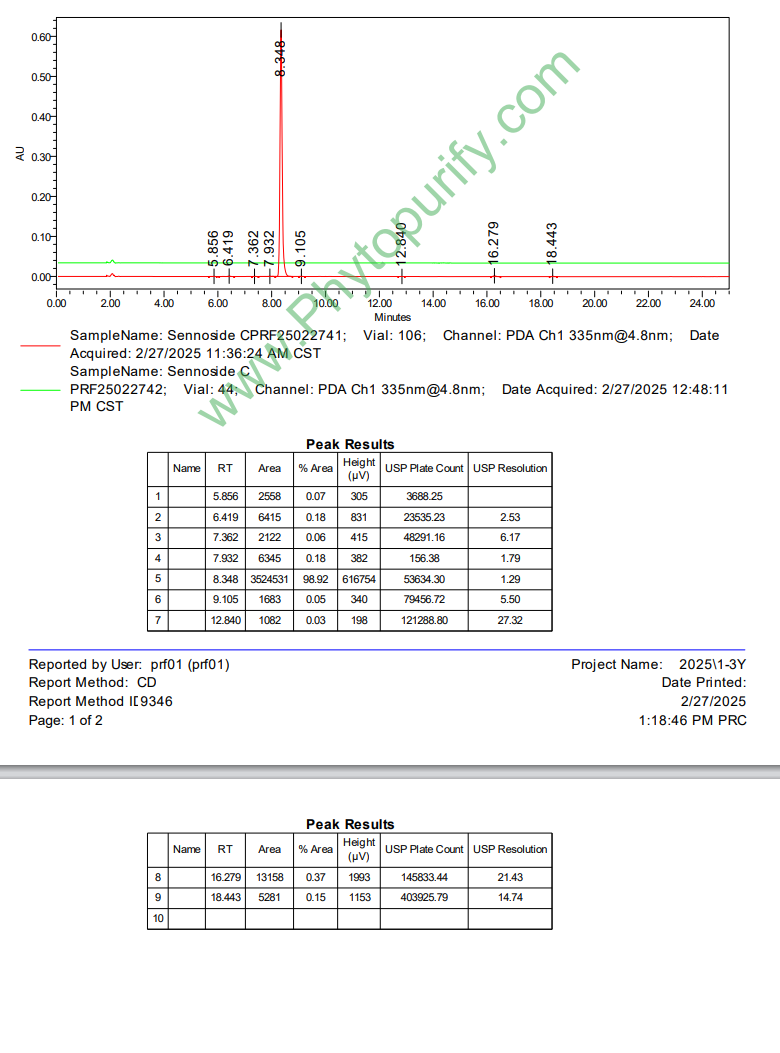
HPLC of Sennoside C