
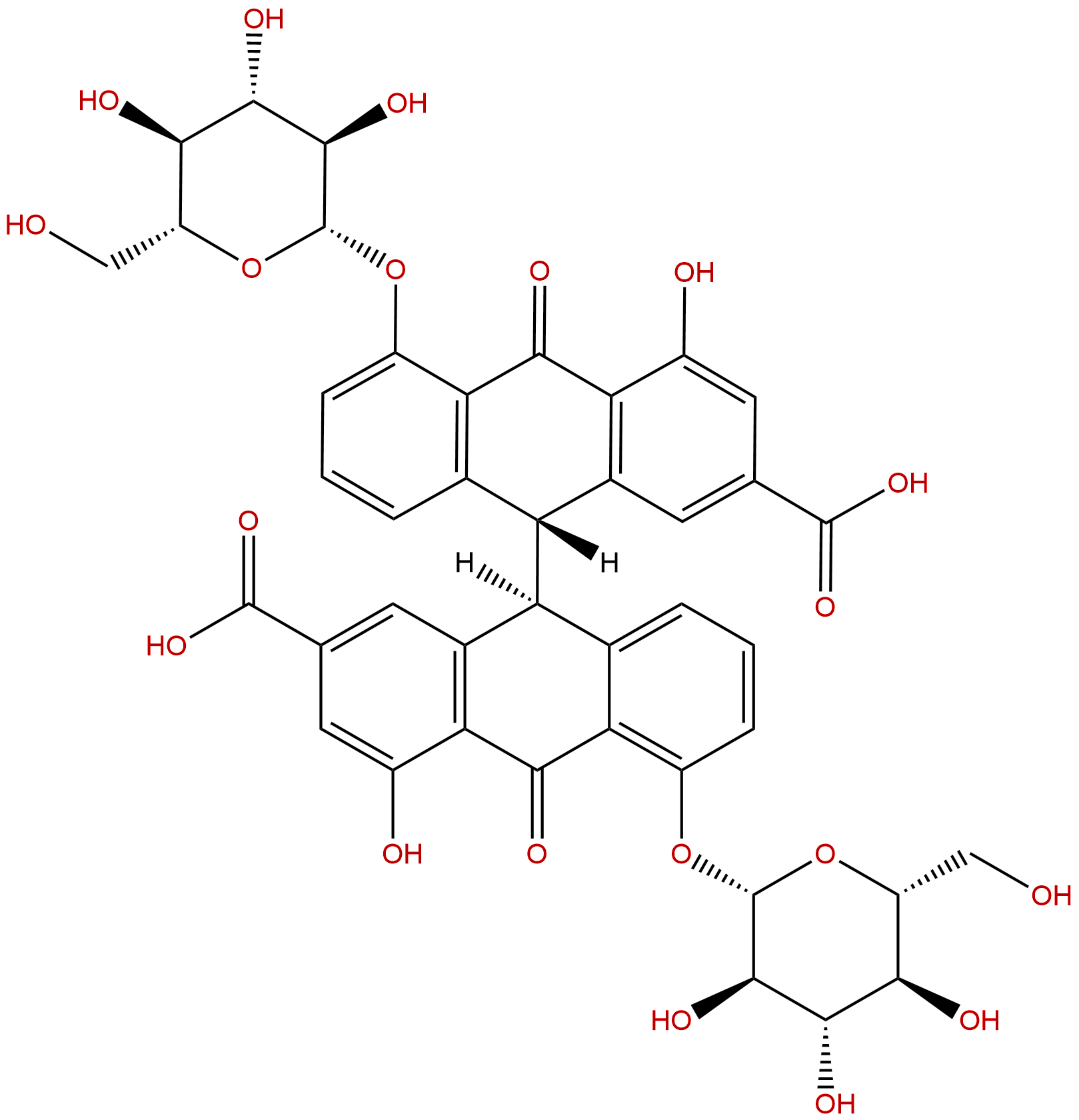
Sennoside BCAS No.:128-57-4
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1293 |
| Formula: | C42H38O20 |
| Mol Weight: | 862.746 |
Synonym name: Tisasen B
Catalogue No.: BP1293
Cas No.: 128-57-4
Formula: C42H38O20
Mol Weight: 862.746
Botanical Source: senna
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Sennoside B, a major purgative component, has a potential utility in the treatment of proliferative diseases, through inhibiting PDGF-stimulated cell proliferation by binding to PDGF-BB and its receptor and by down-regulating the PDGFR-beta signaling pathway. It and sennoside A also possess significant gastroprotective activities .
References:
Life Sci. 2009 Jun 19;84(25-26):915-22.
Sennoside B inhibits PDGF receptor signaling and cell proliferation induced by PDGF-BB in human osteosarcoma cells.
AIMS: To address the possibility that Sennoside B inhibition of cell proliferation is mediated via interference with platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) signaling. MAIN METHODS: Human osteosarcoma MG63 cells were treated with PDGF in the presence or absence of Sennoside B. Activation of the PDGF signaling pathway was monitored using western immunoblotting with specific antibodies against the PDGF receptor, phosphotyrosine and components of the downstream signaling cascade. Activation of cell metabolism and proliferation was assessed by chromogenic reduction of MTT. KEY FINDINGS: Sennoside B was found to inhibit PDGF-BB-induced phosphorylation of the PDGF receptor (PDGFR) in human MG63 osteosarcoma cells. Downstream signaling was also affected; pre-incubation of PDGF-BB with Sennoside B inhibited the phosphorylation of pathway components including Ak strain To address the possibility that Sennoside Binhibition of cell proliferation is mediated via interference with platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) signaling.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Human osteosarcoma MG63 cells were treated with PDGF in the presence or absence of Sennoside B. Activation of the PDGF signaling pathway was monitored using western immunoblotting with specific antibodies against the PDGF receptor, phosphotyrosine and components of the downstream signaling cascade. Activation of cell metabolism and proliferation was assessed by chromogenic reduction of MTT. Sennoside B was found to inhibit PDGF-BB-induced phosphorylation of the PDGF receptor (PDGFR) in human MG63 osteosarcoma cells. Downstream signaling was also affected; pre-incubation of PDGF-BB with Sennoside B inhibited the phosphorylation of pathway components including Ak strain transforming protein (AKT), signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT-5) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2). Further, we found that Sennoside B can bind directly to the extracellular domains of both PDGF-BB and the PDGF-beta receptor (PDGFR-beta). The effect was specific for Sennoside B; other similar compounds including aloe-emodin, rhein and the meso isomer (sennoside A) failed to inhibit PDGFR activation or downstream signaling. Sennoside B also inhibited PDGF-BB stimulation of MG63 cell proliferation.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that Sennoside B can inhibit PDGF-stimulated cell proliferation by binding to PDGF-BB and its receptor and by down-regulating the PDGFR-beta signaling pathway. Sennoside B is therefore of potential utility in the treatment of proliferative diseases in which PDGF signaling plays a central role.
HPLC of Sennoside B
