
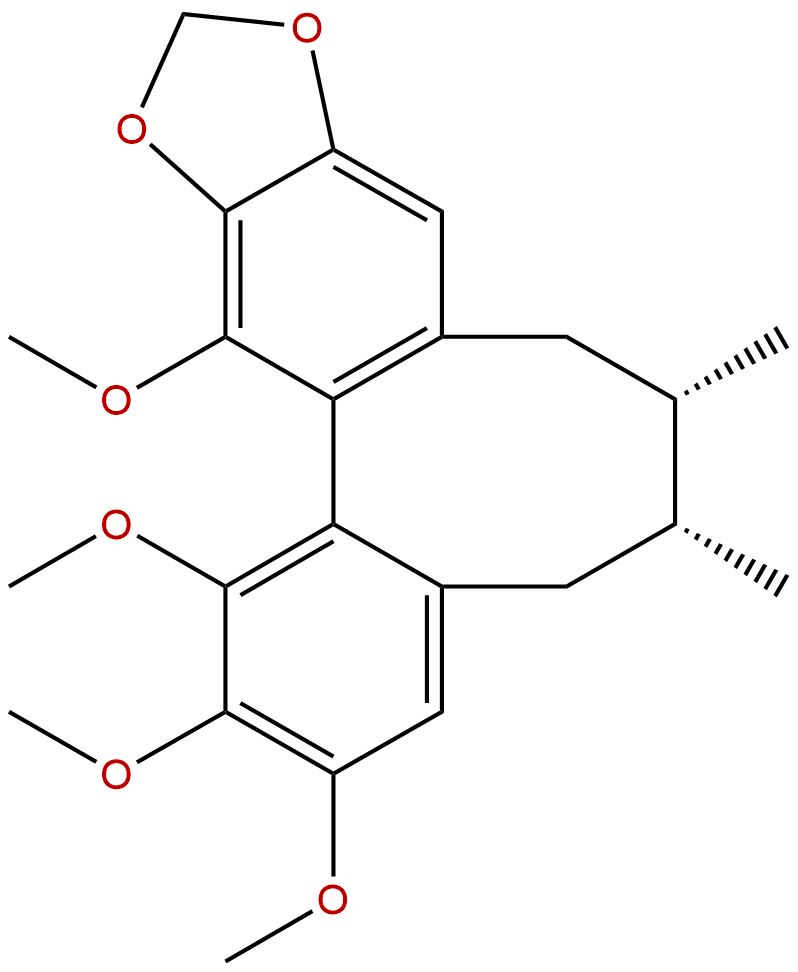
Schisandrin BCAS No.:61281-37-6
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1262 |
| Formula: | C23H28O6 |
| Mol Weight: | 400.471 |
Product name: Schisandrin B
Synonym name: Schizandrin B; Wuweizisu B; γ-Schisandrin
Catalogue No.: BP1262
Cas No.: 61281-37-6
Formula: C23H28O6
Mol Weight: 400.471
Botanical Source: Schisandra chinensis(Turcz.)Baill.
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Lignans
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Schisandrin B, a kind of ATR and P-gp inhibitor with high safety, has been shown to produce antioxidant effect on rodent liver and heart. It also has anti-photoaging, and presents promising activities for future development of protective agents against CisPt nephrotoxicity. Combination of schizandrin B and paclitaxel(PTX) can enhance anti-tumor effects and relieve side effects of PTX on rats with mammary carcinoma.
References:
J Appl Toxicol. 2014 Dec;34(12):1311-9.
Protective effects of schizandrin and schizandrin B towards cisplatin nephrotoxicity in vitro.
Renal proximal tubular epithelial cells are the main targets of toxic drugs such as cisplatin (CisPt), an alkylating agent indicated for the treatment of solid organ tumors. Current techniques aiming at reducing nephrotoxicity in patients receiving CisPt are still not satisfactory as they can only partially prevent acute kidney injury. New nephroprotective strategies remain to be developed.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present in vitro study, schizandrin (Schi) and Schizandrin B (Schi B), major phytochemicals from Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. fruits, were tested on HK-2 cells along four processes that could help alleviate CisPt toxicity. Results indicated that: (i) both Schi and Schi B enhanced cell survival via reducing apoptosis rate; (ii) only Schi showed moderate effects towards modulation of regeneration capacities of healthy cells; (iii) both Schi and Schi B limited extracellular matrix deposition; and (iv) both compounds could help preventing dedifferentiation processes via the β-catenin pathway.
CONCLUSIONS:
Schi and Schi B present promising activities for future development of protective agents against CisPt nephrotoxicity.
Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1989 Jul;10(4):353-6.
Action of schizandrin B, an antioxidant, on lipid peroxidation in primary cultured hepatocytes.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The action of Schizandrin B (Sin B) was observed in freshly isolated hepatocytes damaged by FeSO4/cysteine and CCl4. Two types of free radicals, .OH and .CCl3, generated from FeSO4/cysteine and CCl4, respectively, induced lipid peroxidation in hepatocytes. It was found that the speed of lipid peroxidation (MDA production) and the degree of alteration in hepatocyte morphology were closely related to the type of free radicals. MDA production and membrane protrusion of hepatocytes injuries by FeSO4/cysteine were faster and more severe than those observed with CCl4. Sin B was shown to decrease the production of MDA and the release of GPT and LDH, and to increase hepatocyte viability as well as maintaining the integrity of the hepatocyte membrane surface. These actions of Sin B were stronger than vitamin E at the same concentration. It was observed that no inhibitory effect of phenobarbital, a typical inducer of cytochrome P-450, as Sin B induced liver cytochrome P-450, on MDA production in hepatocytes damaged by FeSO4/cysteine.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results suggest that Sin B possesses antioxidant activity.
J. Pract. Med., 2012, 28(15):2506-9.
Experimental research on Schizandrin B enhancing sensitivity to paclitaxel on rats with mammary carcinoma.[Reference: WebLink]
To investigate the effects of Schizandrin B (Sch B) on enhancing sensitivity to paclitaxel (PTX) on rats with mammary carcinoma.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Fifty BALB/c rats were randomly divided into five groups, 10 animals of each group: a normal control (NC) group, model control (MC) group, PTX group, Sch B group and PTX + Sch B group. Sch B was administered to the rats by intraperitoneal injection at a dose of 10mg/kg once per day for 22 days. while PTX was every 2 days. The body weight, gross tumor volume, inhibition rate of tumor growth and organ index were observed. Compared with the MC group, the body weight in both the PTX group and Sch B + PTX group began to decrease since the 7th day of administration, the difference in weight was significant by statistics. Compared with the PTX group, the body weight in the Sch B + PTX group was elevated, but the difference was not significant. The inhibition rate in the PTX group was 15.7% and that in the Sch B + PTX group 25.9%. Compared with the MC group, the spleen index in PTX group and the Sch B + PTX group was significantly lower (P = 0.008 and 0.000, respectively). Compared with the PTX group, the spleen index in the Sch B + PTX group was lower, but the difference was not significant. Compared with the PTX group, the thyroid and adrenal gland index in the Sch B + PTX group was significantly elevated (P = 0.000 and 0.011, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS:
Combination of Sch B and PTX can enhance anti-tumor effects and relieve side effects of PTX on rats with mammary carcinoma.
HPLC of Schisandrin B
