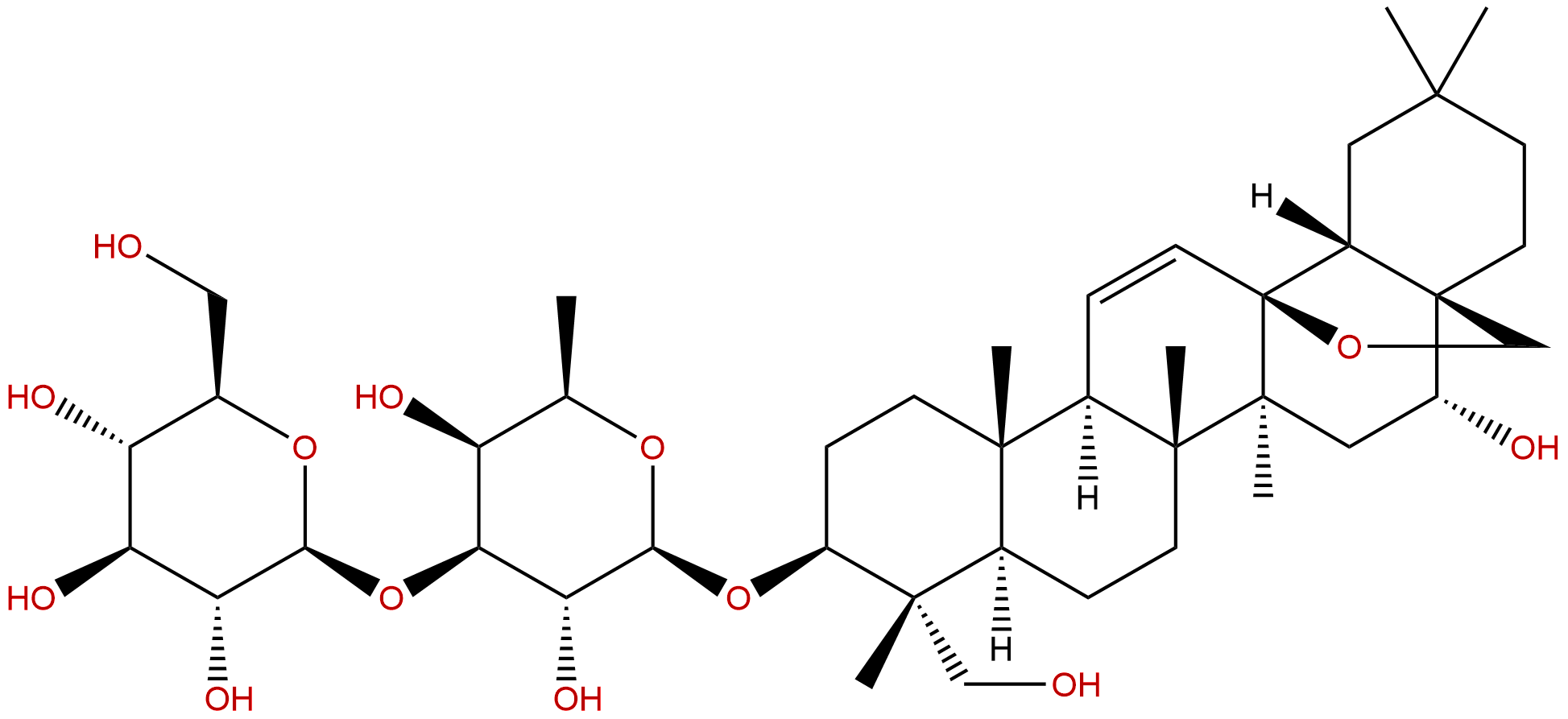
Saikosaponin D Descrtption
Product name: Saikosaponin D
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP1242
Cas No.: 20874-52-6
Formula: C42H68O13
Mol Weight: 780.993
Botanical Source: Bupleurum falcatum, Bupleurum kummingense and Bupleurum chinense
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Triterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
SaikosaponinD (SSd) is a major triterpenoid saponin derivative from Radix bupleuri, which has been long used in Chinese traditional medicine for treatment of various inflammation-related diseases; it shows potent anti-inflammatory activity through inhibitory effects on NF-κB activation and thereby on iNOS, COX-2 and pro-inflammatory cytokines.[1]
Saikosaponin D attenuates CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats, which may be related to its effects of hepato-protective and anti-inflammation properties,the down-regulation of liver TNF-α, IL-6 and NF-κBp65 expression and the increased I-κBα activity in liver.[2]
Saikosaponin D is an agonist of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), and it possesses neuroprotective effects in corticosterone-treated PC12 cells; SSD exhibits its anti-apoptotic effects via differential regulation of mitochondrial and nuclear GR translocation, partial reversal of mitochondrial dysfunction, inhibition of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, and selective activation of the GR-dependent survival pathway.[3]
Saikosaponin D is a novel autophagic inducer, can increase cytosolic calcium level via direct inhibition of sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) ATPase pump, leading to autophagy induction through the activation of the Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent kinase kinase-AMP-activated protein kinase-mammalian target of rapamycin pathway, which has the potential of being developed into an anti-cancer agent for targeting apoptosis-resistant cancer cells.[4]
References:
[1] Lu C N, Yuan Z G, Zhang X L, et al. Int Immun Pharmaco, 2012, 14(1):121-126.
[2] Dang S S, Wang B F, Cheng Y A, et al. World J Gastroentero, 2007, 13(4):557-63.
[3] Li Z Y, Jiang Y M, Liu Y M, et al. Prog neuro-psychoph, 2014, 53(1448):80-89.
[4] Wong V K, Li T, Law B Y, et al. Cell Death Dis, 2012, 4(7):e720-e720.
[5] Liu L Z, Xiao-Jun J I, Bang-Qin Y A. China Pharmacy, 2014, 25(23):2147-2149.