
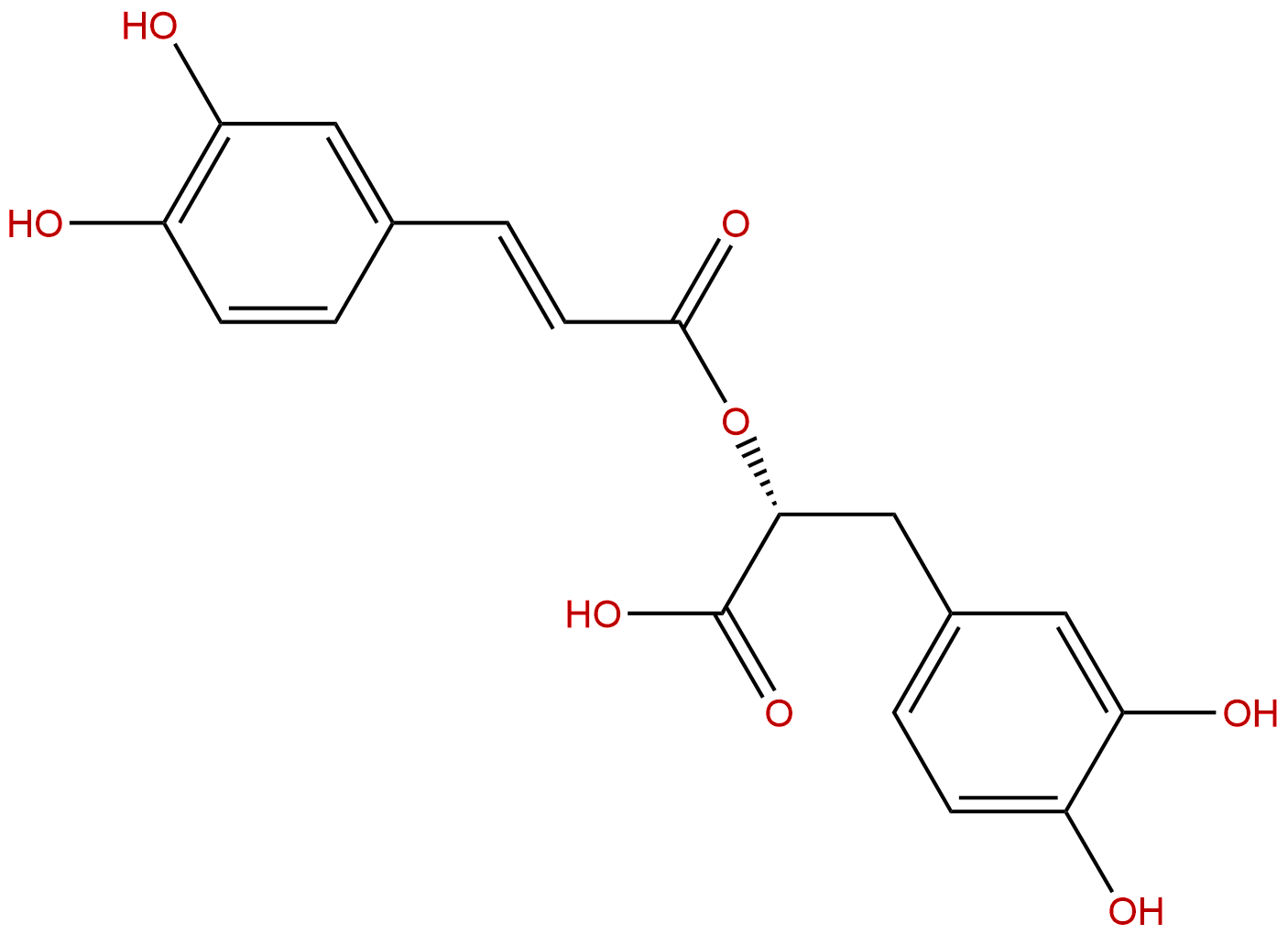
Rosmarinic acidCAS No.:20283-92-5
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1224 |
| Formula: | C18H16O8 |
| Mol Weight: | 360.318 |
Product name: Rosmarinic acid
Synonym name: Labiatenic acid
Catalogue No.: BP1224
Cas No.: 20283-92-5
Formula: C18H16O8
Mol Weight: 360.318
Botanical Source: Rosmarinus officinalis, Melissa officinalis, Momordica balsamina, Mentha piperita, Salvia officinalis, Teucrium scorodonia, Sanicula europaea, Coleus blumei, Thymus spp., Hyptis verticillata, Lithospermum erythrorhizon and other plant spp.
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Phenylpropanoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Rosmarinic acid is a naturally occurring hydroxylated compound, it is present in many plants, such as Artemisia capillaris , Calendulla officinalis; it shows antiviral, antibacterial, antiinflammatory and antioxidant activity, can produce anxiolytic-like effect without exerting locomotor alterations or DNA damage in brain tissue.[1]
Rosmarinic acid can inhibit complement activation in vivo as well as in vitro, the inhibition of complement activation by rosmarinic acid is due to the reaction of rosmarinic acid with the activated thioester of metastable C3b, resulting in covalent attachment of the inhibitor to the protein.[2]
Rosmarinic acid induces melanogenesis through protein kinase A activation signaling, which occurs downstream of cAMP production.[3
Rosmarinic acid has antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activities, can inhibit diesel exhaust particles (DEP)-induced lung injury by the reduction of proinflammatory molecule expression, and the antioxidative activities may also contribute to its protective effects.[4]
Rosmarinic acid inhibits the expression of CCL11 and CCR3 by suppressing the IKK- β activity in NF- κ B activation signaling, suggests that rosmarinic acid might inhibit the expression of NF- κ B promoter-related genes. [5]
Rosmarinic acid has potent anticancer, anti-lipid peroxidative and apoptotic effect in 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced skin carcinogenesis.[6]
Rosmarinic acid mediates neuroprotective effects against H2O2-induced neuronal cell damage in N2A cells, suggests that it may potentially serve as an agent for prevention of several human neurodegenerative diseases caused by oxidative stress.[7]
References:
[1] Pereira P, Tysca D P, Da S B L, et al. Pharmacol Res, 2005, 52(3):199-203.
[2] Sahu A, Rawal N, Pangburn M K. Biochem Pharmacol, 1999, 57(57):1439-46.
[3] Lee J, Kim Y S, Park D. Biochem Pharmacol, 2007, 74(7):960-8.
[4] Sanbongi C, Takano H, Osakabe N, et al.Free Radical Biol Med, 2003, 34(8):1060-9.
[5] Jongsung Lee, Eunsun Jung, Youngji Kim,et al. Brit J Pharmacol, 2006, 148(3):366-75.
[6] Sharmila R, Manoharan S. Indian J Exp Biol 2012, 50(3):187-94.
[7] Ghaffari H, Venkataramana M, Ghassam B J, et al. Life Sci, 2014, 113(1–2):7-13.
[8] Wang Z, Xu Y, Jiao R, et al. China Pharmacist, 2014(09):1473-5.
HPLC of Rosmarinic acid
