
RosarinCAS No.:84954-93-8
|
||||||||||
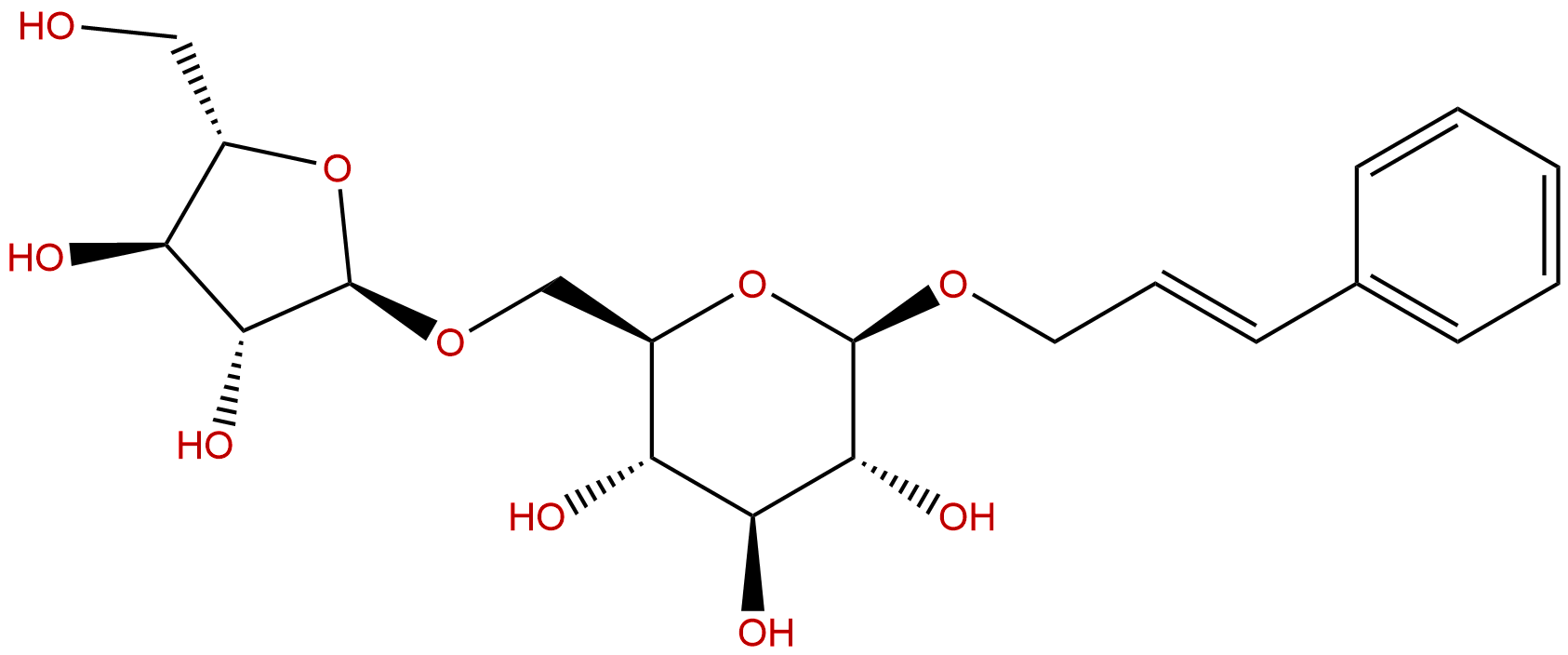 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1220 |
| Formula: | C20H28O10 |
| Mol Weight: | 428.434 |
Product name: Rosarin
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP1220
Cas No.: 84954-93-8
Formula: C20H28O10
Mol Weight: 428.434
Botanical Source: Rhodiolae Crenulatae Radixet Rhizoma
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Phenylpropanoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Rosarin is a natural product from Rhodiola rosea L.
References:
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:514049.
Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects of Constituents Isolated from Rhodiola rosea.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To determine the biological activity of Rhodiola rosea, the protein expression of iNOS and proinflammatory cytokines was measured after the activation of murine microglial BV2 cells by LPS under the exposure of constituents of Rhodiola rosea: crude extract, rosin, Rosarin, and salidroside (each 1-50 μ g/mL). The LPS-induced expression of iNOS and cytokines in BV2 cells was suppressed by the constituents of Rhodiola rosea in a concentration-dependent manner. Also the expression of the proinflammatory factors iNOS, IL-1 β , and TNF- α in the kidney and prefrontal cortex of brain in mice was suppressed by the oral administration of Rhodiola rosea crude extract (500 mg/kg). To determine the neuroprotective effect of constituents of Rhodiola rosea, neuronal cells were activated by L-glutamate, and neurotoxicity was analyzed. The L-glutamate-induced neurotoxicity was suppressed by the treatment with rosin but not by Rosarin. The level of phosphorylated MAPK, pJNK, and pp38 was increased by L-glutamate treatment but decreased by the treatment with rosin and salidroside.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that Rhodiola rosea may have therapeutic potential for the treatment of inflammation and neurodegenerative disease.