RheinCAS No.:478-43-3
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1208 |
| Formula: | C15H8O6 |
| Mol Weight: | 284.223 |
Product name: Rhein
Synonym name: Monorhein; Cassic acid
Catalogue No.: BP1208
Cas No.: 478-43-3
Formula: C15H8O6
Mol Weight: 284.223
Botanical Source: Obt. from various Cassia spp. such as senna. Present in Rheum palmatum (Chinese rhubarb). Also Scrophularia nodosa, Kniphofia uvaria and other plants
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Anthraquinones
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Rhein, an anthraquinone compound isolated from rhubarb, has been proved effective in treatment of experimental diabetic nephropathy (DN), one of the mechanism is the Inhibition of the hexosamine pathway. [1]
Rhein can effectively inhibit the IL-1-activated pathway and the of NF-kappaB and factors in chondrocytes cultured in hypoxia, and can reduce the procatabolic effect of the cytokine, by reducing the synthesis, and enhance the synthesis of matrix components, such as type II and aggrecan. [2]
Rhein has been shown to induce apoptosis in several cancer cell lines, and induces apoptosis in A-549 cells via a Ca2+ -dependent mitochondrial pathway. [3]
Rhein has protective effect on liver injury and can inhibit liver flbrosis induced by CCl4/ethanol in rats,the mechanisms possibly contribute to its action of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity, also associated with its effect of inhibiting TGF-β1 and suppressing the activation of hepatic stellate cells.[4]
References:
[1] Zheng J M, Zhu J M, Li L S, et al. Brit J Pharmacol, 2008, 153(7):1456–1464.
[2] Durocher F, Labrie Y, Soucy P, et al. Inflammation, 2003, 27(4):233-246.
[3] Hsia T C, Yang J S, Chen G W, et al. Anticancer Res, 2009, 29(1):309-18.
[4] Guo M Z, Xiao-Sheng L I, Hai-Rong X U, et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2002, 23(8):739-44.
[5] Cui Y Q, Dong Z M, Men J Y, et al. Central South Pharmacy, 2009, 7(1):20-23.
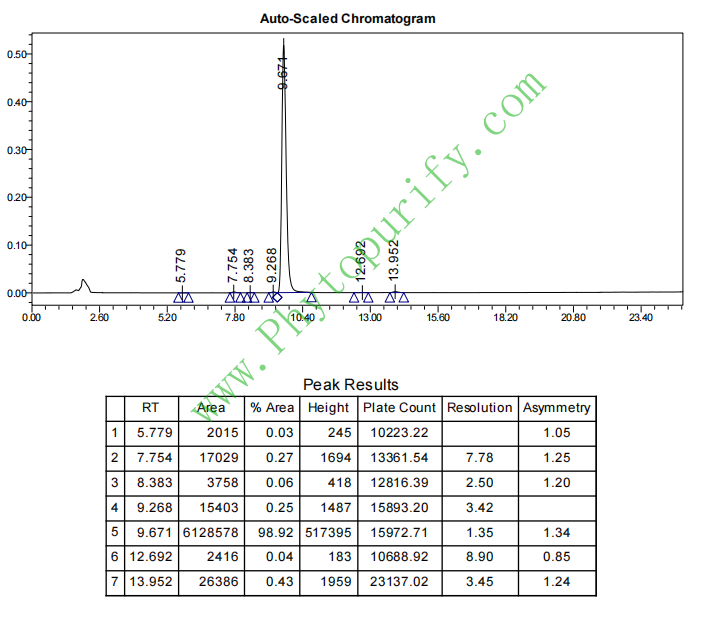
HPLC of Rhein
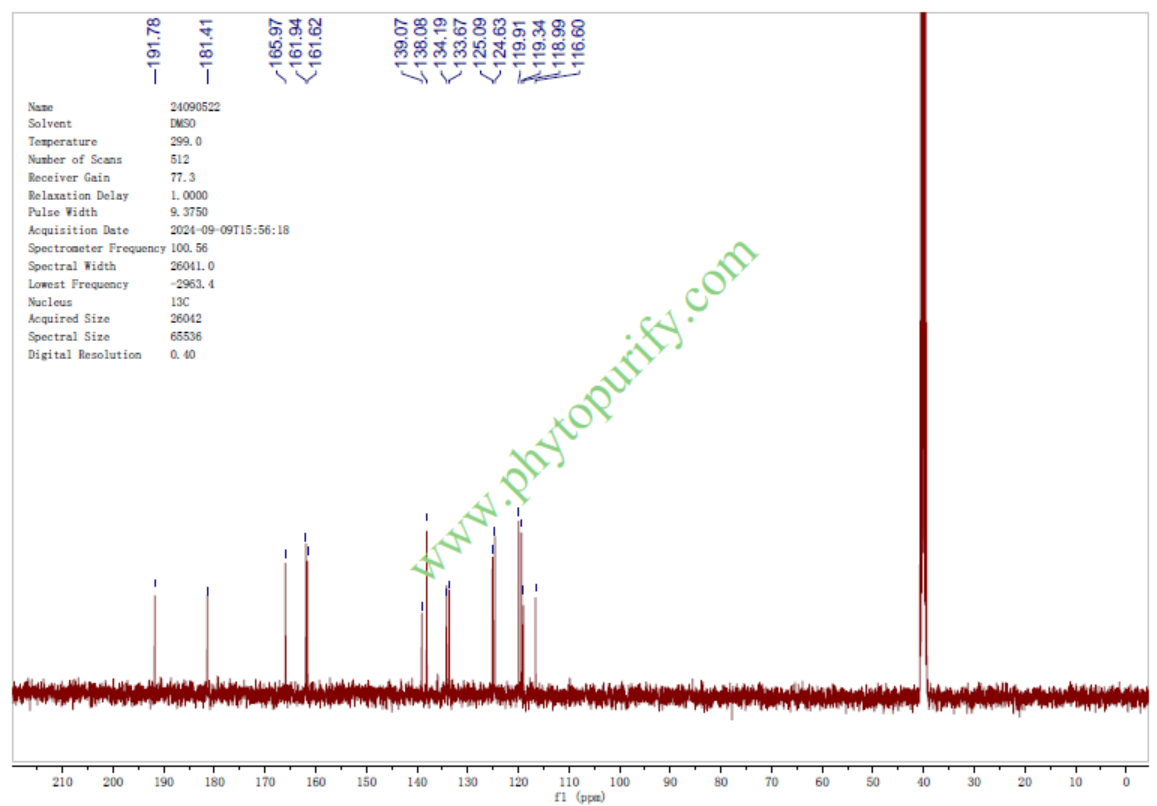
NMR of Rhein