Polygalasaponin FCAS No.:882664-74-6
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1122 |
| Formula: | C53H86O23 |
| Mol Weight: | 1091.25 |
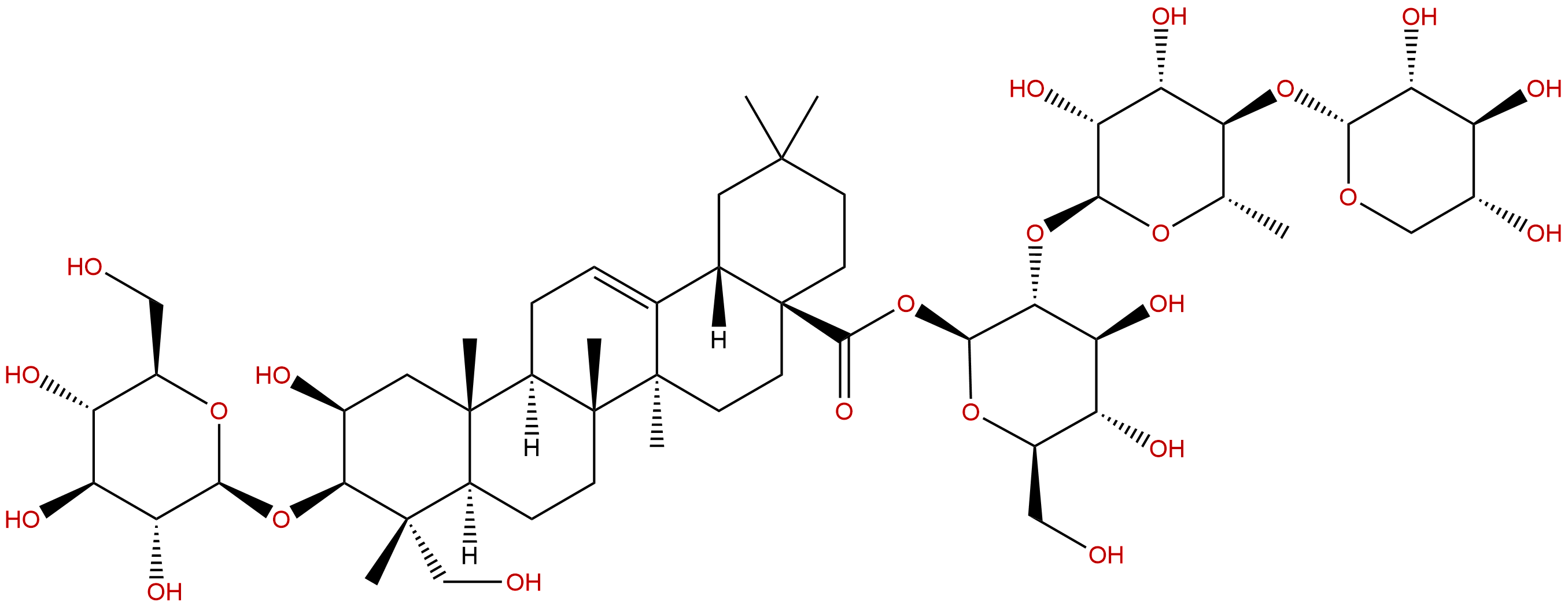
Product name: Polygalasaponin F
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP1122
Cas No.: 882664-74-6
Formula: C53H86O23
Mol Weight: 1091.25
Botanical Source: Polygala japonica
Physical Description: White powder
Type of Compound: Triterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Polygalasaponin F (PG-F), a triterpenoid saponin isolated from Polygala japonica, can induce long-term potentiation in adult rat hippocampus via NMDA receptor activation.[1]
Polygalasaponin F can increase the viability of rotenone-induced PC12 cells, decrease rotenone-induced apoptosis, restore rotenone-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, and suppress rotenone-induced protein expression; PS-F protects PC12 cells against rotenone-induced apoptosis via ameliorating the mitochondrial dysfunction, thus, PS-F may be a potential bioactive compound for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.[2]
Polygalasaponin F can inhibit NF-κB nuclear translocation in a dose-dependent manner, and significantly inhibit the cytotoxicity of conditioned medium prepared by LPS-stimulated BV-2 microglia to neuronal PC12 cells and improve cell viability, it inhibits the secretions of neuroinflammatory cytokines by the regulation of NF-κB-signaling pathway.[3]
Polygalasaponin F has protective effects on PC12 cells injuried by serum deprivation, oxidative stress or oxygen-glucose deprivation.[4]
References:
[1] Sun F, Sun J D, Nan N, et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2012, 33(4):431-7.
[2] Wu M M, Yuan Y H, Chen J, et al. J Asian Nat Prod Res, 2014, 16(1):59-69.
[3] Wei W, Yuan Y H, Gao Y N, et al. J Asian Nat Prod Res,, 2014, 16(8):865-75.
[4] Shi R L, Hu J F, Chen N H. International Conference For Physiological Sciences , 2012.
[5] Jiao Q Q, Wang W Y, Juan S U, et al. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice, 2010, 28(2):137-9
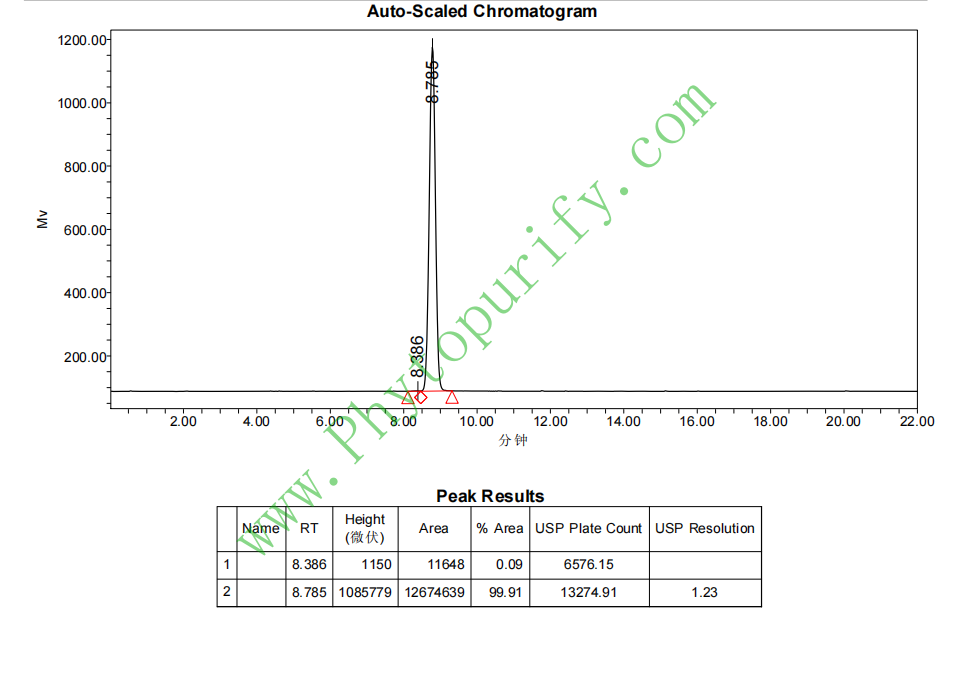
HPLC of Polygalasaponin F