Platycodin DCAS No.:58479-68-8
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1111 |
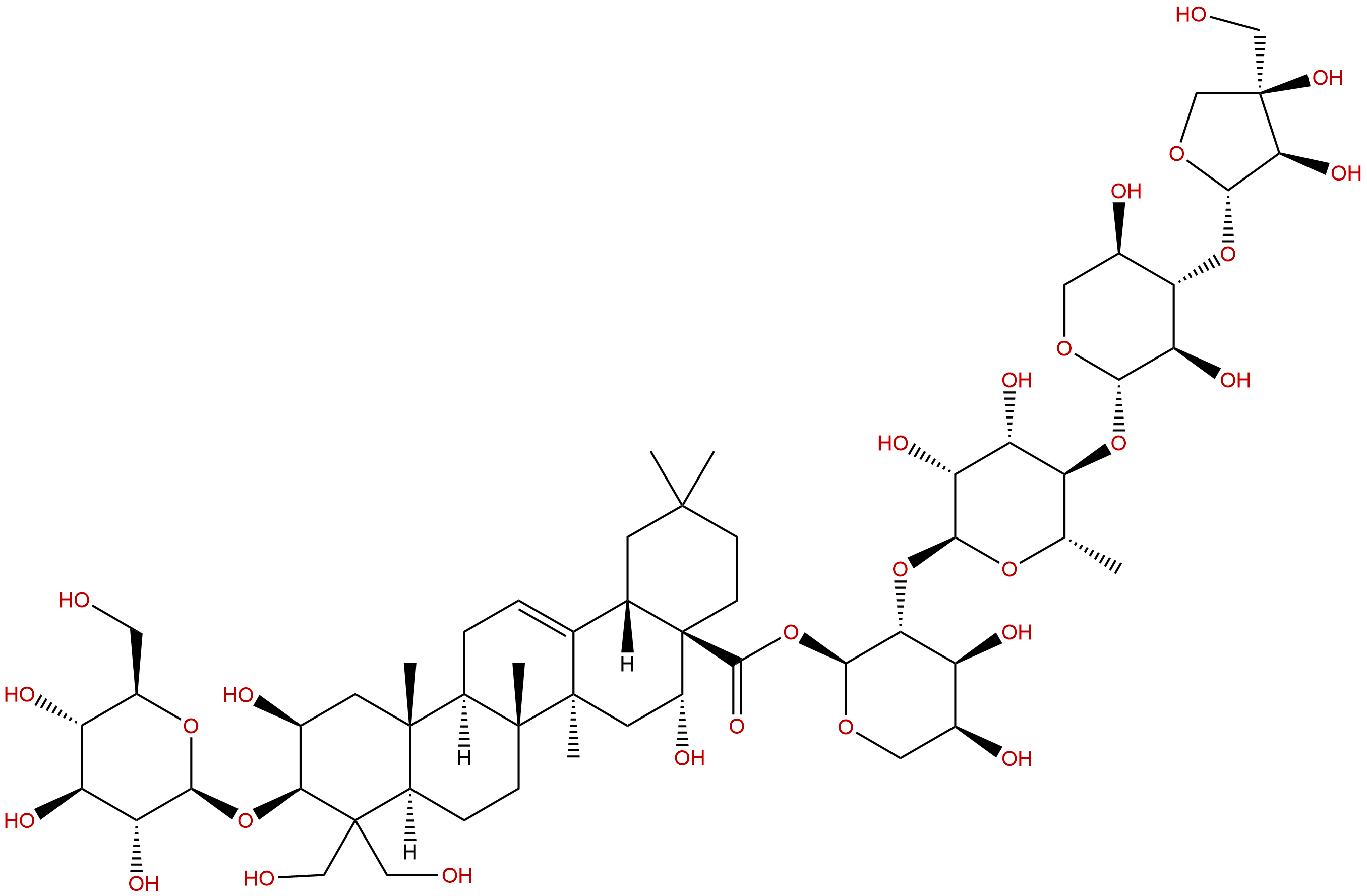
| Formula: | C57H92O28 |
| Mol Weight: | 1225.34 |
Product name: Platycodin D
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP1111
Cas No.: 58479-68-8
Formula: C57H92O28
Mol Weight: 1225.34
Botanical Source: Platycodon grandiflorum
Physical Description: White powder
Type of Compound: Triterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Platycodon D (PD) and D3 (PD3) isolated from Platycodon grandiflorum has been previously reported to show anti-inflammatory activities in rats, PD may stimulate TNF-α synthesis or inhibit degradation of TNF-α mRNA, suggest a dichotomous regulation of these important proinflammatory mediators by PD and PD3.[1]
Platycodin D suppresses prostaglandin E2 production at 10 and 30 uM in rat peritoneal macrophages stimulated by the protein kinase C activator 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA).[2]
Platycodin D has the ability to induce apoptosis in HaCaT cells through the upregulation of Fas receptor and FasL expression via to NF-κB activation in the transcriptional level, suggests that the NF-κB activation plays a crucial role in the induction of apoptosis in human HaCaT cells on treatment with platycodin D.[3]
Platycodin D (PD) significantly promotes the production of Th1 (IL-2 and IFN-gamma) and Th2 (IL-10) cytokines and up-regulates the mRNA expression of Th1 cytokines (IL-2 and IFN-gamma) in splenocytes from the mice immunized with HBsAg, also increases the killing activities of natural killer (NK) cells and CTLs from splenocytes in the HBsAg-immunized mice, which may have important implications for vaccination against hepatitis B virus,suggests that PD may be the candidates as adjuvants for use in prophylactic and therapeutic hepatitis B vaccine.[4]
Platycodin-D(PD) can induce autophagy in NCI-H460 and A549 cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and activating JNK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways.[5]
Platycodin D has showed an antinociceptive effect .[6]
Platycodin D can inhibit migration, invasion, and growth of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells via suppression of EGFR-mediated Akt and MAPK pathways.[7]
References:
[1] Wang C, Levis G B S, Lee E B, et al. Int Immunopharmacol, 2004, 4(8):1039-49.
[2] Kim Y P, Lee E B, Kim S Y, et al. Planta Medica, 2001, 67(4):362-4.
[3] Ahn K S, Hahn B S, Kwack K B, et al. Eur J Pharmacoly, 2006, 537(1-3):1-11.
[4] Xie Y, Sun H X, Li D. Vaccine, 2009, 27(5):757764.
[5] Zhao R, Chen M, Jiang Z, et al. J Cancer, 2015, 6(7):623-31.
[6] SeongSoo Choi, EunJung Han, TaeHee Lee, et al. Am J Chinese Med, 2004, 32(2):257-68.
[7] Chun J, Kim Y S. Chem-Biol Interact, 2013, 205(3):212-21.
[8] Chen G, Tai S, Huang L. China Pharm, 014(18):51-3.
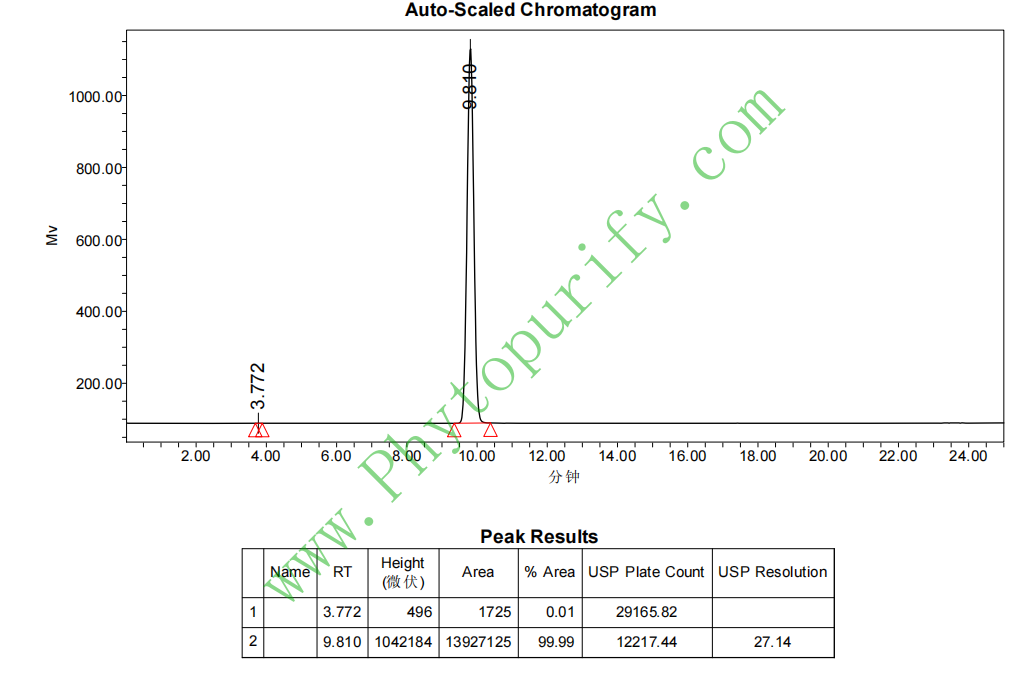
HPLC of Platycodin D