PhyscionCAS No.:521-61-9
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1092 |
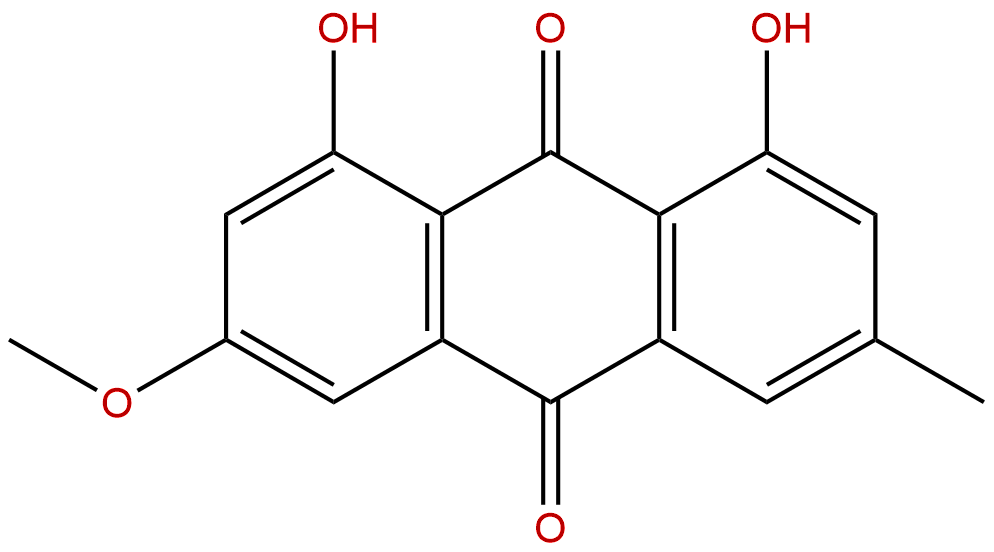
| Formula: | C16H12O5 |
| Mol Weight: | 284.267 |
Product name: Physcion
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP1092
Cas No.: 521-61-9
Formula: C16H12O5
Mol Weight: 284.267
Botanical Source: Widely distributed in lichens, e.g. Parmelia spp., higher plants, e.g. Rumex spp. and prod. by Aspergillus and Penicillium spp. Also the marine annelid Urechis unicintus
Physical Description: Yellow powder
Type of Compound: Anthraquinones
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Physcion is an anthraquinone from rhubarb (rhizomes of Rheum tanguticum), has anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, antifungal, and anti-cancer activities; Physcion has anti-proliferative activity might via the induction of G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human breast cancer cells.[1]
Physcion is the extract of the plant Baill, is highly active against plant powdery mildew.[2]
Physcion could be a potential candidate in the field of anticancer drug discovery against human cervical cancer, could significantly induce cell apoptosis through down-regulating of Bcl-2 expression, up-regulating of Bax expression, and activating the caspase-3 pathway. [3]
References:
[1] Hong J Y, Chung H J, Song Y B, et al. Asian Pac J Cancer P, 2014, 19(4):273-8.
[2] Yang X, Yang L, Wang S, et al. Pest Manag Sci?, 2007, 63(5):511–515.
[3] Wijesekara I, Zhang C, Ta Q V, et al. Microbiol Res?, 2014, 169(4):255-261.
[4] Zhu L, Song Y. Asia-Pacific Traditional Medicine, 2013, 9(4):28-30.
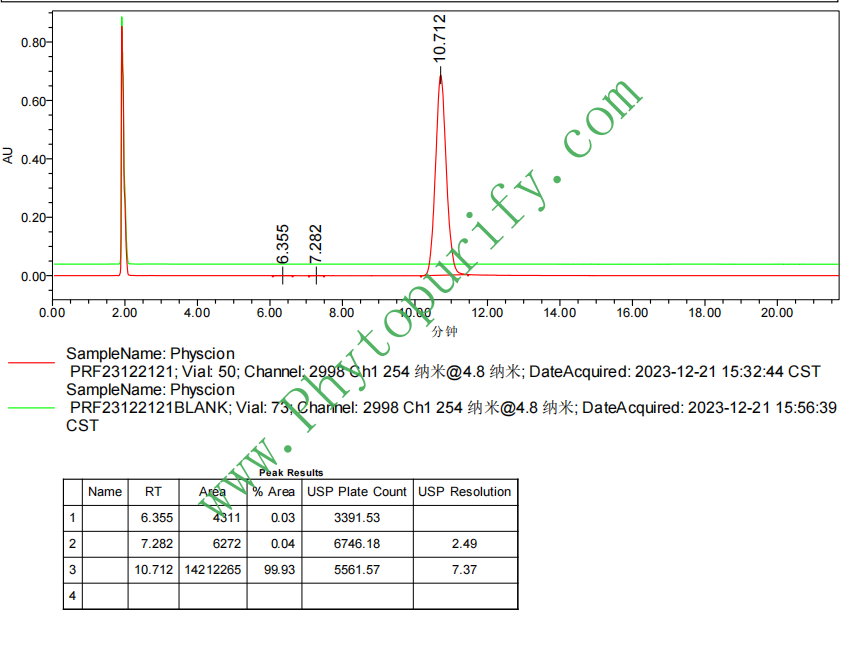
HPLC of Physcion