PeriplocinCAS No.:13137-64-9
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1079 |
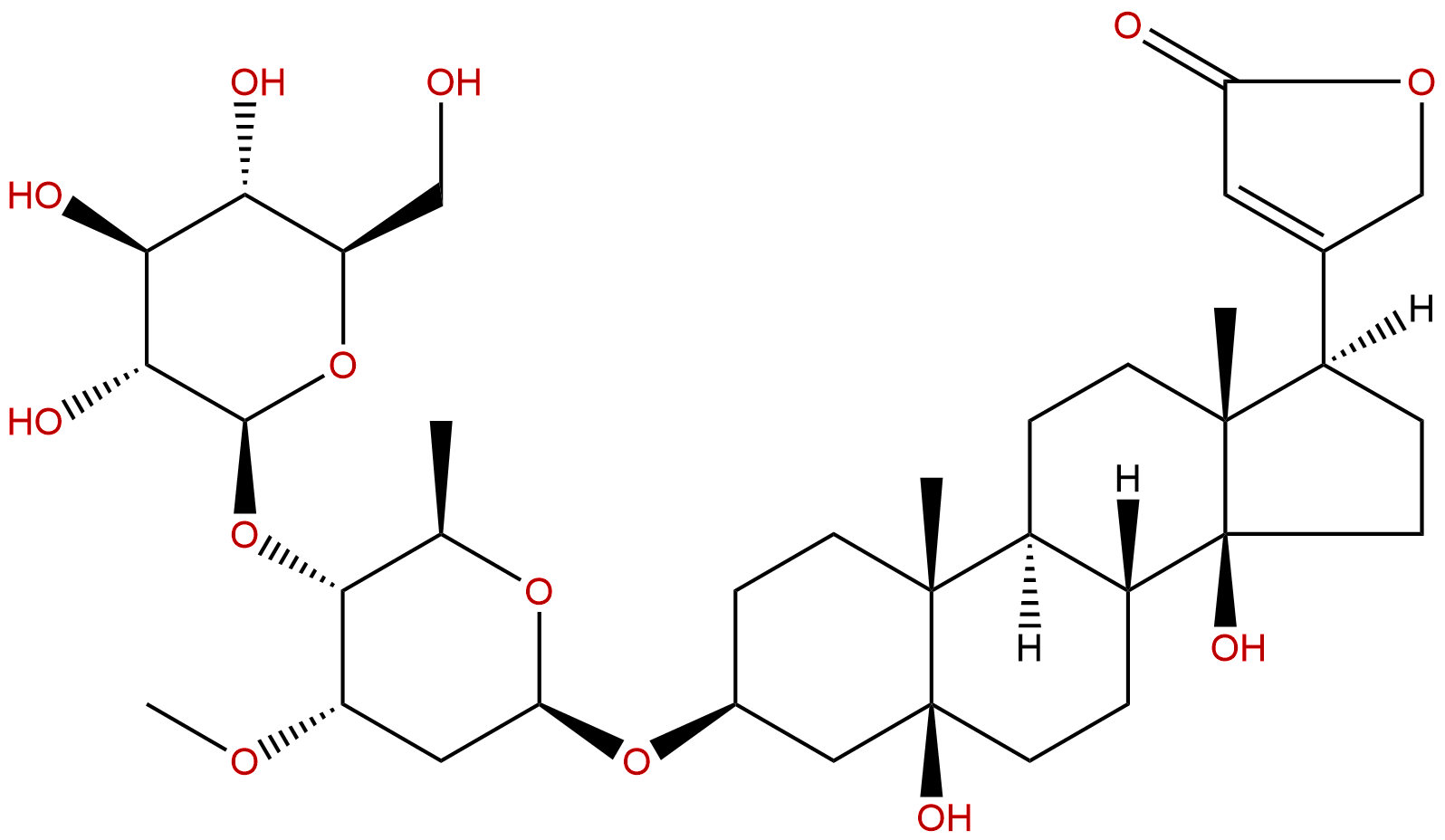
| Formula: | C36H56O13 |
| Mol Weight: | 696.831 |
Synonym name: Periplocoside
Catalogue No.: BP1079
Cas No.: 13137-64-9
Formula: C36H56O13
Mol Weight: 696.831
Botanical Source: Periploca graeca and Strophanthus preussii
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Periplocin has anti-cancer, and potent immunoregulatory effects, it induces apoptosis and inhibits growth of cancer cells by the beta-catenin/Tcf signaling pathway. Periplocin is used for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, reinforcement of bones and tendons, palpitations or shortness of breath and lower extremity edema in traditional medicine.
References:
Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;33(3):859-68.
Comparative proteomic analysis of anti-cancer mechanism by periplocin treatment in lung cancer cells.
Periplocin is used for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, reinforcement of bones and tendons, palpitations or shortness of breath and lower extremity edema in traditional medicine. Our previous findings suggested that Periplocin could inhibit the growth of lung cancer both in vitro and in vivo. But the biological processes and molecular pathways by which Periplocin induces these beneficial effects remain largely undefined.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To explore the molecular mechanisms of Periplocin involved in anti-cancer activity, in the present study the protein profile changes of human lung cancer cell lines A549 in response to Periplocintreatment were investigated using the proteomics approaches (2-DE combined with MS/MS). Western blot was employed to verify the changed proteins. Interactions between changed proteins were analyzed by STRING. 29 down-regulated protein species named GTP-binding nuclear protein Ran (RAN), Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor 1 (ARHGDIA), eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A-1 (EIF5A) and Profilin-1(PFN1), and 10 up-regulated protein species named Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein (HSPA8),10 kDa heat shock protein (HSPE1), and Cofilin-1(CFL-1) were identified. Among them, GTP-binding nuclear protein Ran (RAN) and Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor 1 (ARHGDIA) were the most significantly changed (over tenfold). The proteasome subunit beta type-6 (PSMB6), ATP synthase ecto-α-subunit (ATP5A1), Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 (ALDH1) and EIF5A were verified by immunoblot assays to be dramatically down-regulated. By STRING bioinformatics analysis revealing interactions and signaling networks it became apparent that the proteins changed they are primarily involved in transcription and proteolysis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Periplocin inhibited growth of lung cancer by down-regulating proteins, such as ATP5A1, EIF5A, ALDH1 and PSMB6. These findings may improve our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the anti-cancer effects of Periplocin on lung cancer cells.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:958025.
Antitumor Effect of Periplocin in TRAIL-Resistant Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through Downregulation of IAPs.
Cortex periplocae is the dried root bark of Periploca sepium Bge., a traditional Chinese herb medicine. It contains high amounts of cardiac glycosides. Several cardiac glycosides have been reported to inhibit tumor growth or induce tumor cell apoptosis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We extracted and purified cortex periplocae and identified Periplocin as the active ingredient that inhibited the growth of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-(TRAIL-) resistant hepatocellular carcinoma cells. The antitumor activity of Periplocin was further increased by TRAIL cotreatment. Periplocin sensitized TRAIL-resistant HCC through the following two mechanisms. First, Periplocin induced the expression of DR4 and FADD. Second, the cotreatment of TRAIL and Periplocin suppressed several inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs). Both mechanisms resulted in the activation of caspase 3, 8, and 9 and led to cell apoptosis. In addition, intraperitoneal injection (IP) of Periplocin repressed the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in xenograft tumor model in mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
In summary, Periplocin sensitized TRAIL-resistant HCC cells to TRAIL treatment and resulted in tumor cell apoptosis and the repression of tumor growth in vivo.
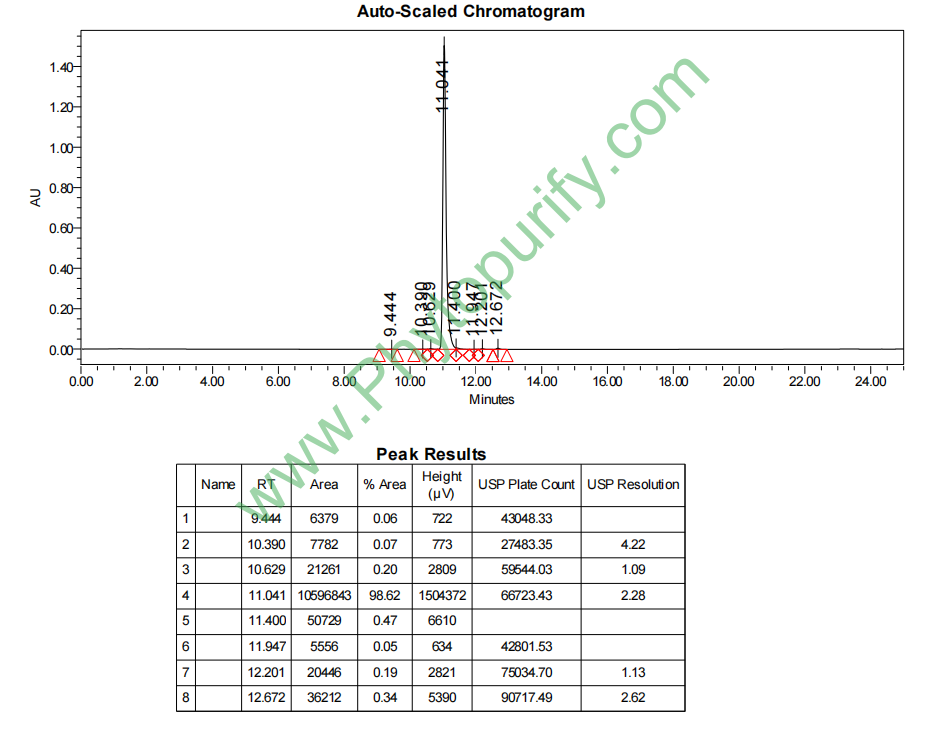
HPLC of Periplocin