
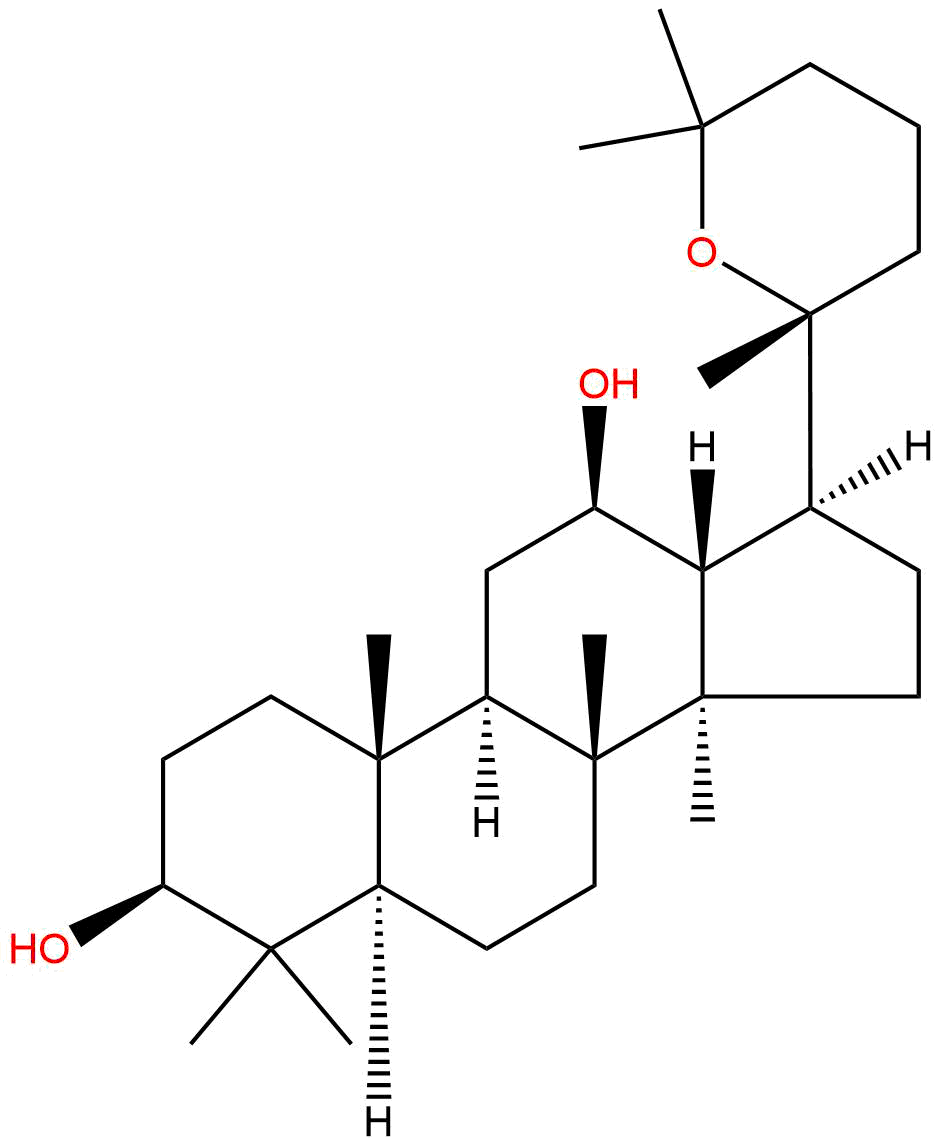
PanaxadiolCAS No.:19666-76-3
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1060 |
| Formula: | C30H52O3 |
| Mol Weight: | 460.743 |
Product name: Panaxadiol
Synonym name: (20R)-Panaxadiol
Catalogue No.: BP1060
Cas No.: 19666-76-3
Formula: C30H52O3
Mol Weight: 460.743
Botanical Source:
Physical Description: White powder
Type of Compound: Triterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Panaxadiol , a ginseng saponin with a dammarane skeleton, selectively interferes with the cell cycle in human cancer cell lines, it inhibits DNA synthesis in a dose-dependent manner with IC50 values ranging from 0.8 to 1.2 μM in SK-HEP-1 cells and HeLa cells, it selectively elevates p21WAF1/CIP1 levels and thereby arrests the cell cycle at G1/S phase by down-regulating Cyclin A–Cdk2 activity.[1]
Panaxadiol, a purified ginseng component, can enhance the anti-cancer effects of 5-fluorouracil in human colorectal cancer cells.[2]
Panaxadiol fraction and its ginsenosides can induce the antioxidant enzymes which are important for maintaining cell viability by lowering the level of oxygen radical generated from intracellular metabolism.[3]
Pretreatment with ginseng total saponin, especially panaxatriol, ameliorates I/R-induced myocardial damage and this protection is caused by reducing oxidative stress.[4]
References:
[1] Ying H J, Choi J S, Shin S, et al. Carcinogenesis, 2003, 24(11):1767-72.
[2] Li X L, Wang C Z, Mehendale S R, et al. Cancer Chemoth Pharm, 2009, 64(6):1097-104.
[3] Chang M S, Lee S G, Rho H M. Phytother Res, 1999, 13(8):641-4.
[4] Kim T H, Lee S M. Food Chem Toxicol , 2010, 48(6):1516-20.
[5] Shi L L, Qin W M, Zhu Z J, et al. Physical Testing & Chemical Analysis, 2010, 46(5):482-4.
HPLC of Panaxadiol

HNMR of Panaxadiol
