
Oroxin ACAS No.:57396-78-8
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1043 |
| Formula: | C21H20O10 |
| Mol Weight: | 432.381 |
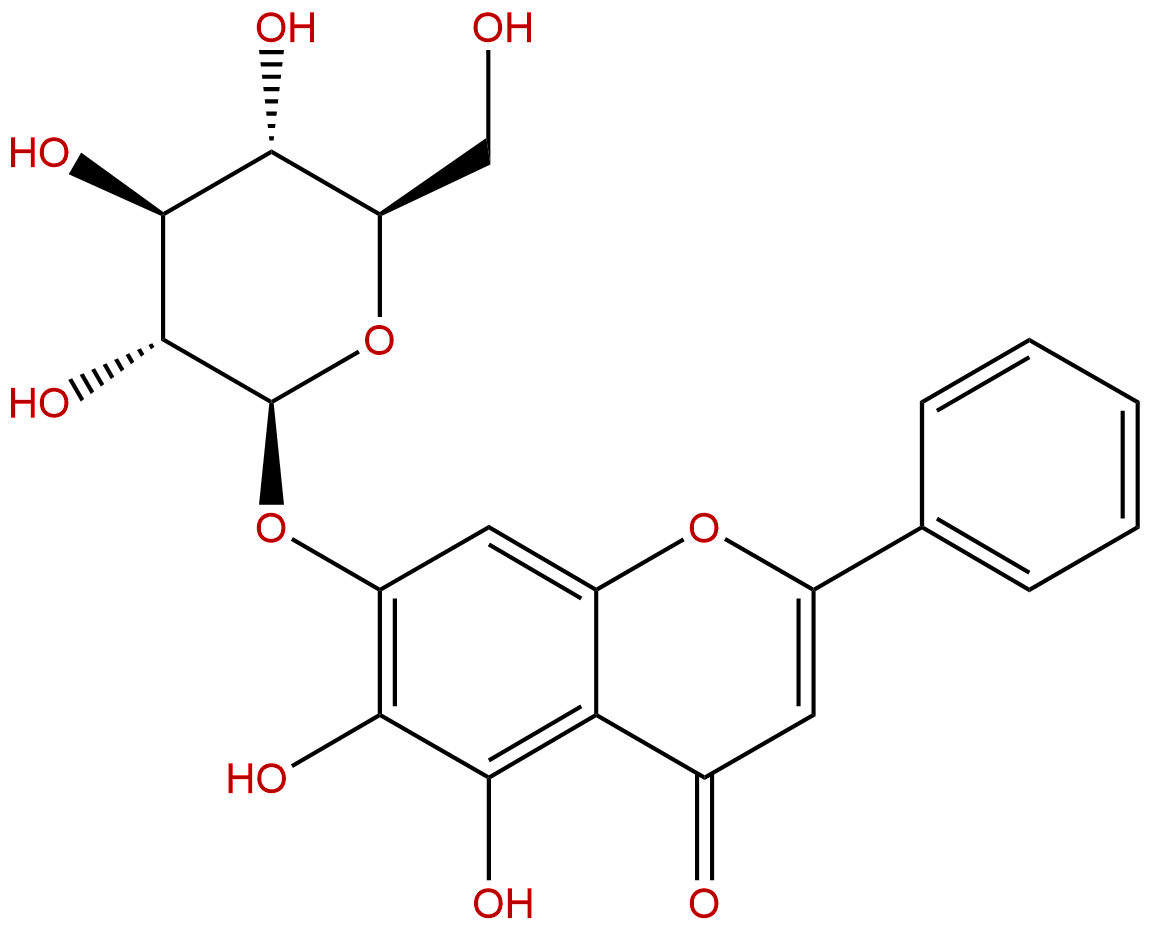
Product name: Oroxin A
Synonym name: Baicalein-7-O-glucoside
Catalogue No.: BP1043
Cas No.: 57396-78-8
Formula: C21H20O10
Mol Weight: 432.381
Botanical Source: Oroxylum indicum(L.)Vent.
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Flavonoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Oroxin A is a xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibitor, it exerts its antibreast cancer effects by inducing ER stress-mediated senescence, activating the key stress signaling pathway, and increasing key ER stress genes and expression levels.
References:
Anticancer Drugs. 2016 Mar;27(3):204-15.
Oroxin A inhibits breast cancer cell growth by inducing robust endoplasmic reticulum stress and senescence.
Breast cancer is a major cause of cancer death among women. Although various anticancer drugs have been used in clinics, drugs that are effective against advanced and metastatic breast cancer are still lacking and in great demand.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we found that Oroxin A, an active component isolated from the herb Oroxylum indicum (L.) Kurz, effectively inhibited the growth of human breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231 and MCF7 by inducing endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-mediated senescence. Oroxin A caused breast cancer cell cycle arrest at the G2/M stage, and reorganization of microtubules and actin cytoskeleton accompanied by a decrease in cellular mitosis. ER-specific probe ER-Tracker Red and confocal microscope imaging showed that ER-Tracker Red-positive cells increased in an Oroxin A dosage-dependent manner. In addition, Oroxin A increased cell population with high β-Gal activity and SAHF-positive staining; these data suggest that Oroxin A induces breast cancer cell ER stress and senescence. Mechanistic studies showed that Oroxin A led to a significant increase in intracellular reactive oxygen species levels, promoted expression of ER stress markers ATF4 and GRP78, and increased the phosphorylation of a key stress-response signaling protein p38, resulting in an ER stress-mediated senescence.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our data indicate that Oroxin A exerts its antibreast cancer effects by inducing ER stress-mediated senescence, activating the key stress p38 signaling pathway, and increasing key ER stress genes ATF4 and GRP78 expression levels.