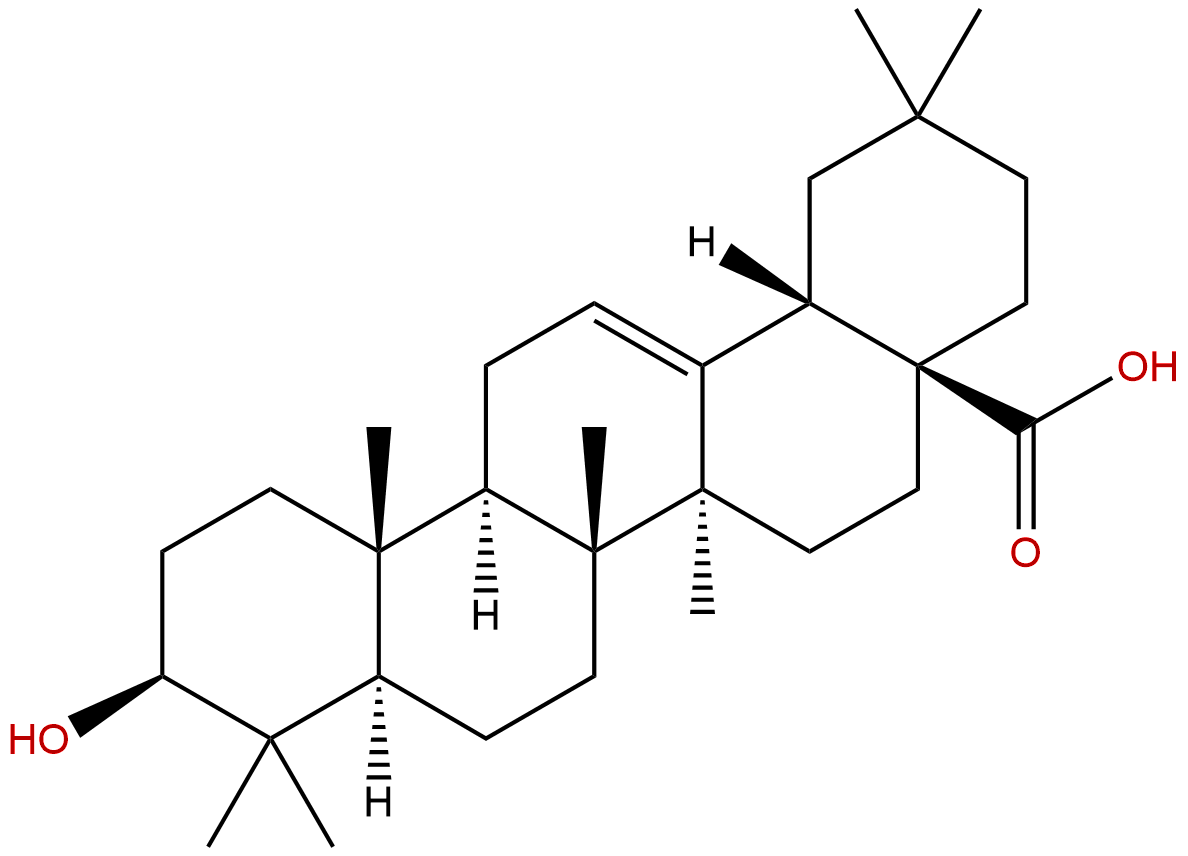
Oleanolic acidCAS No.:508-02-1
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1026 |
| Formula: | C30H48O3 |
| Mol Weight: | 456.711 |
Product name: Oleanolic acid
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP1026
Cas No.: 508-02-1
Formula: C30H48O3
Mol Weight: 456.711
Botanical Source: Occurs as glycosides in mistletoe, cloves (Syzygium aromaticum), sugar beet (Beta vulgaris), olive leaves, etc. Very widely distributed aglycone. a Black Sea alga, family Cladophoraceae and from Ulva fasciata
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Triterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Oleanolic acid is a pentacyclic triterpenoid compound with a widespread occurrence throughout the plant kingdom. In nature, the compound exists either as a free acid or as an aglycone precursor for triterpenoid saponins, in which it can be linked to one or more sugar chains. Oleanolic acid and its derivatives possess hepatoprotective effects, and anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, or anticancer activities. [1]
Oleanolic acid may be a promising agent to disturb adipocyte differentiation and suppress obesity-associated inflammation, 25mol/L oleanolic acid-treated adipocytes can significantly repress visfatin production possibly through blocking PPAR activation.[2]
Oleanolic acid and ursolic acid exhibit anti-HCV activity at least partly through suppressing HCV NS5B RdRp activity as noncompetitive inhibitors,could be used as potential HCV antivirals that can be applied to clinic trials either as monotherapy or in combination with other HCV antivirals.[3]
Oleanolic acid may be a possible bioactive agent that blunts adipogenesis and adipokine inflammation, can suppress adipocyte differentiation-associated resistin and adipogenesis production by disturbing the Tyk2-STAT1/3 signaling pathway and promoting SOCS3 expression. [4]
References:
[1] Pollier J, Goossens A. Phytochemistry, 2012, 77(5):10-15.
[2] Sung H Y, Kang S W, Kim J L, et al. Nutr Res, 2010, 30(12):831–39.
[3] Kong L, Li S, Liao Q, et al. Antivir Res,2013, 98(1):44-53.
[4] Kim H S, Sung H Y, Kim M S, et al. Nutr Res, 2013, 33(2):144-53.
[5] Zhou C, Chen K, Sun C, et al. Biomed Chromatogr, 2007, 21(7):755-61.
HPLC of Oleanolic acid

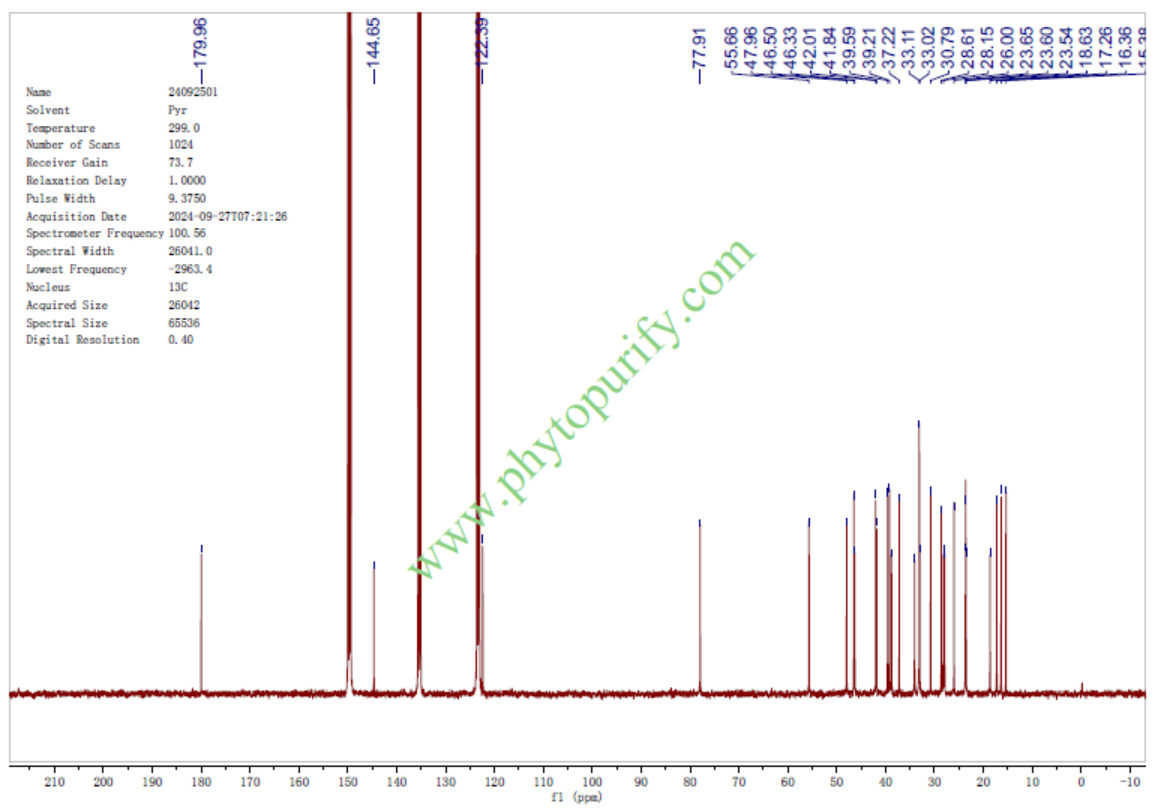
NMR of Oleanolic acid