NodakeninCAS No.:495-31-8
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1002 |
| Formula: | C20H24O9 |
| Mol Weight: | 408.403 |
Product name: Nodakenin
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP1002
Cas No.: 495-31-8
Formula: C20H24O9
Mol Weight: 408.403
Botanical Source: Peucedanum decursivum roots
Physical Description: White powder
Type of Compound: Coumarins
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Nodakenin, a coumarin isolated from the roots of Angelica biserrata (Shan et Yuan) Yuan etShan, possesses neuroprotective, antiaggregatory, antibacterial, and memory
-enhancing effects; down-regulates the expression of the proinflammatory iNOS, COX-2, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β genes in macrophages by interfering with the activation of TRAF6, thus preventing NF-κB activation.[1]
Nodakenin can inhibit acetylcholinesterase activity in a dose-dependent manner (IC(50)=84.7 microM), nodakenin may be a useful for the treatment of cognitive impairment, and that its beneficial effects are mediated, in part, via the enhancement of cholinergic signaling.[2]
Nodakenin efficiently inhibits antigen-induced airway inflammation in asthmatic mouse, by reducing levels of IL-4,IL-5 and IL-13 in BALF,and IgE in serum,decreasing levels of nuclear P65 and p-P65 protein,increasing cytoplasmic P65 and IκBα protein,and NF-κB DNA binding activity. [3]
Nodakenin can inhibit mast cell degranulation through the inhibition of IL-4 and TNF-α mRNA expression, and that nodakenin may potentially serve as an anti-allergic agent.[4]
Nodakenin may be a potential therapeutic resource for AD as well as an adjunctive agent to control associated with AD, by suppressing the increase of AD-like skin lesions in ICR.[5]
References:
[1] Rim H K, Cho W, Sung S H, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2012, 342(3):654-64.
[2] Dong H K, Kim D Y, Kim Y C, et al. Life Sci?, 2007, 80(21):1944-50.
[3] Xiong Y Y, Shi W J, Hao Y U, et al. Basic & Clinical Medicine, 2014.
[4] Kim Y J, Park S J, Kim T J. ??????, 2011, 21:1721-1725.
[5] Park S J, Cha H S, Lee Y H, et al. Biosci BiotechI Bioch, 2014, 78(9):1568-71.
[6] Zhang P, Yang X W. J Asian Nat Prod Res, 2009, 11(4):371-9.
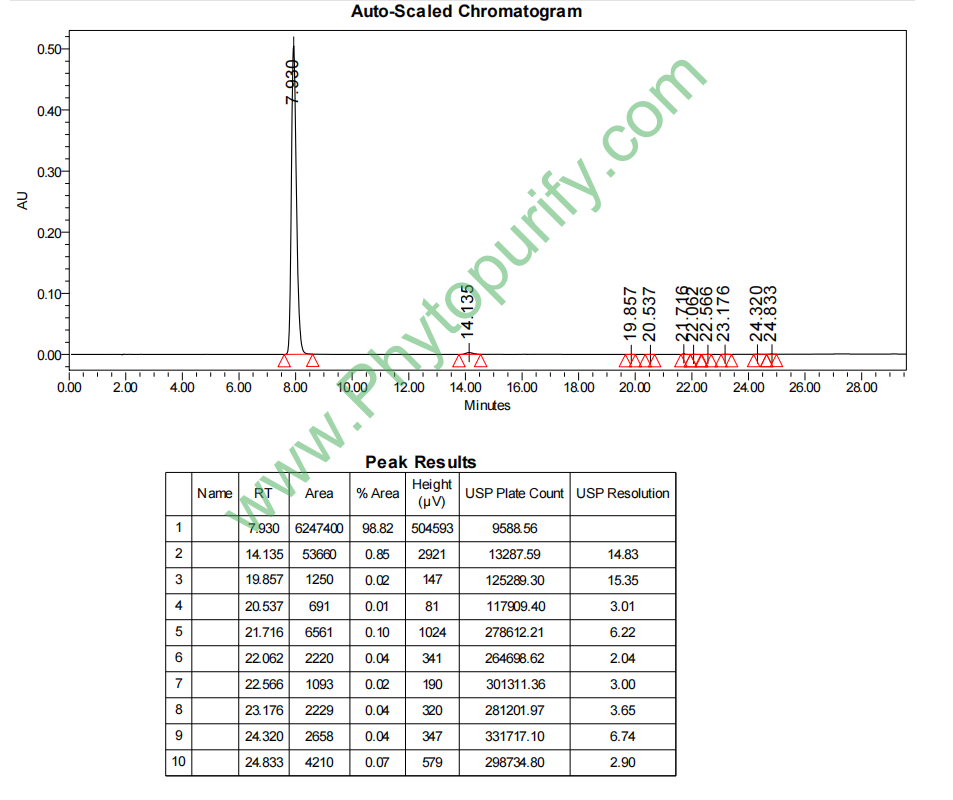
HPLC of Nodakenin
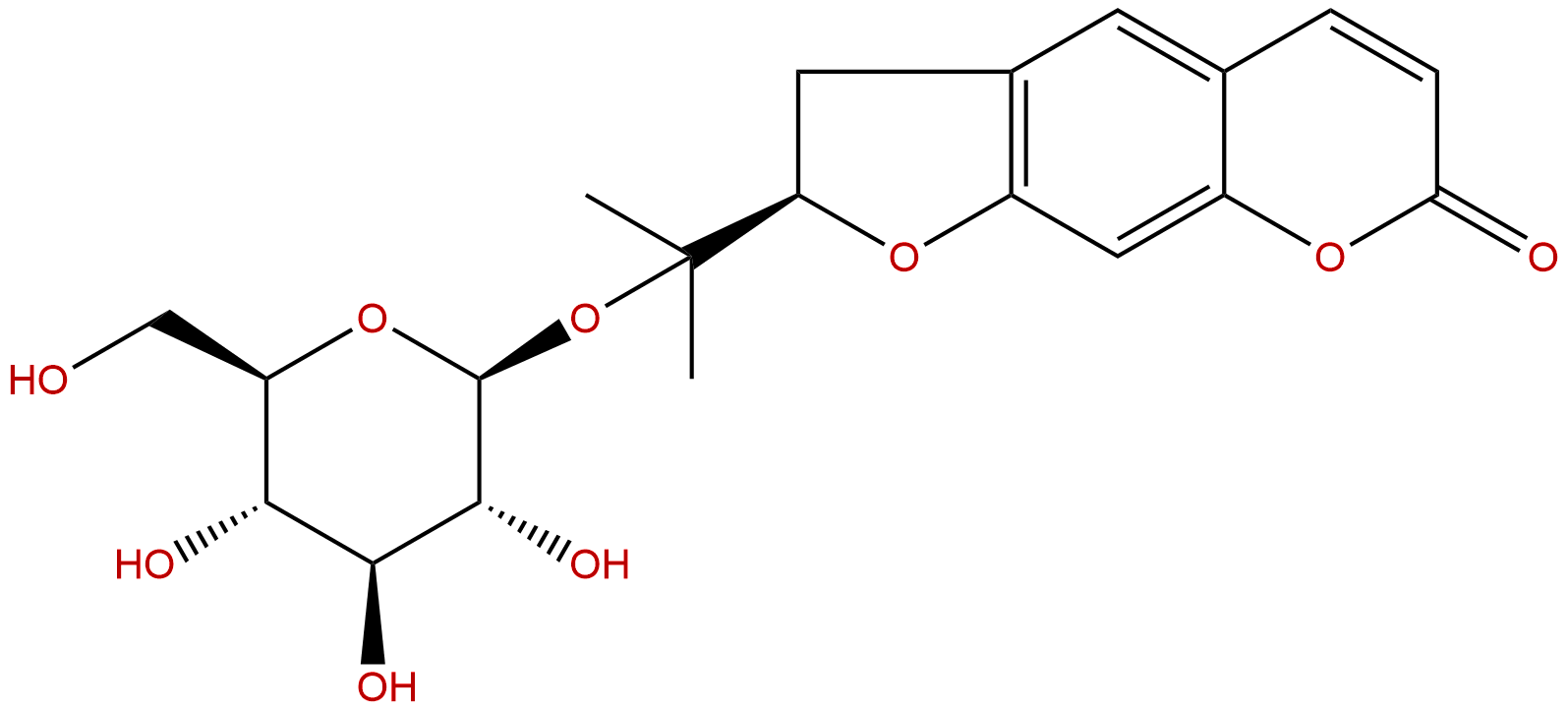
HNMR of Nodakenin