MatrineCAS No.:519-02-8
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0928 |
| Formula: | C15H24N2O |
| Mol Weight: | 248.37 |
Product name: Matrine
Synonym name: Sophoridine
Catalogue No.: BP0928
Cas No.: 519-02-8
Formula: C15H24N2O
Mol Weight: 248.37
Botanical Source: Alkaloid from Sophora alopecuroides, Sophora flavescens, Sophora microphylla, Sophora pachycarpa, Sophora tetraptera, many other Sophora spp., Vexibia pachycarpa (preferred genus name Sophora) and Euchresta horsfeldii (Leguminosae)
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Alkaloids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Matrine, an alkaloid purified from the chinese herb Sophora flavescens Ait, is well known to possess activities including anti-inflammation, anti-fibrotic and anticancer, it could inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis of SGC-7901 cells in vitro by up-regulating Fas/FasL expression and activating caspase-3 enzyme.[1]
Matrine upregulates the cell cycle protein E2F-1 and triggers apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway in K562 cells, it is a potential anti-drug.[2]
Matrine suppresses PMA-induced MMP-1 expression through inhibition of the AP-1 signaling pathway and also may be beneficial for treatment of some inflammatory skin disorders.[3]
Matrine can induce gastric cancer MKN45 cells apoptosis via increasing pro-apoptotic molecules of Bcl-2 family, also inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.[4,5]
Matrine can improve 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis in mice and the therapeutic mechanism might be related to the reduction of up-regulated colonic TNF-α production caused by TNBS.[6]
Matrine seems to be a novel autophagy inhibitor that can modulate the maturation process of lysosomal proteases.[7]
Matrine can reduce the mortality of acetaminophen overdosed mice more effectively, attenuate acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity, and reduces the number and area of γ-GT positive foci, thus protecting liver function and preventing HCC from occurring; it
also has a protective effect on immunosuppression, a strong non-specific anti-inflammatory effect, and an effect of reducing the incidence of sodium and water retention.[8]
References:
[1] Dai Z J, Gao J, Ji Z Z, et al.J Ethnopharmacol 2009, 123(1):91-6.
[2] Hua J, Hou C H, Zhang S B, et al. Eur J Pharmacol, 2007, 559(2-3):98-108.
[3] Eunsun Jung ?, Jongsung Lee ?, Huh S, et al.Biofactors, 2008, 33(2):121–8.
[4] Luo C, Zhu Y, Jiang T, et al. Toxicol, 2007, 229(3):245-52.
[5] Yu H B, Zhang H F, Li D Y, et al. J Asian Nat Prod Res, 2011, 13(3):242-50.
[6] Hong C, Bing X, Lin Z, et al. Pharmacol Res, 2006, 53(3):202-8.
[7] Wang Z, Zhang J, Wang Y, et al. Carcinogenesis, 2012, 34(1):128-38.
[8] Wan X Y, Luo M, Li X D, et al. Chem-Biol Interact, 2009, 181(1):15-9.
[9] Jiang Y L, Zhang S Y. Lishizhen Medicine & Materia Medica Research, 2006, 17(11):2204-5.
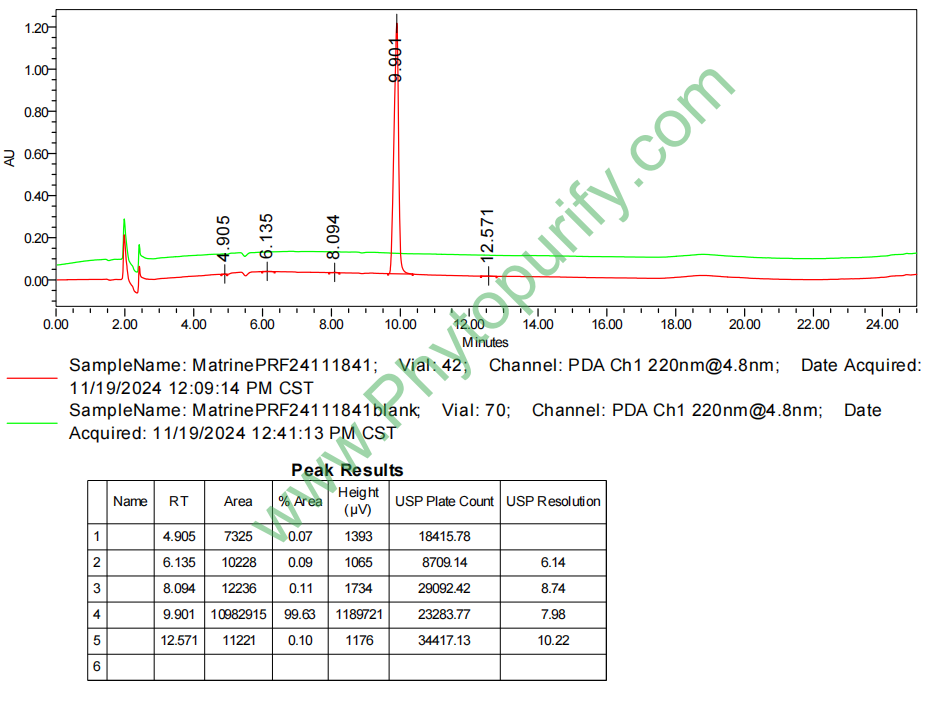
HPLC of Matrine