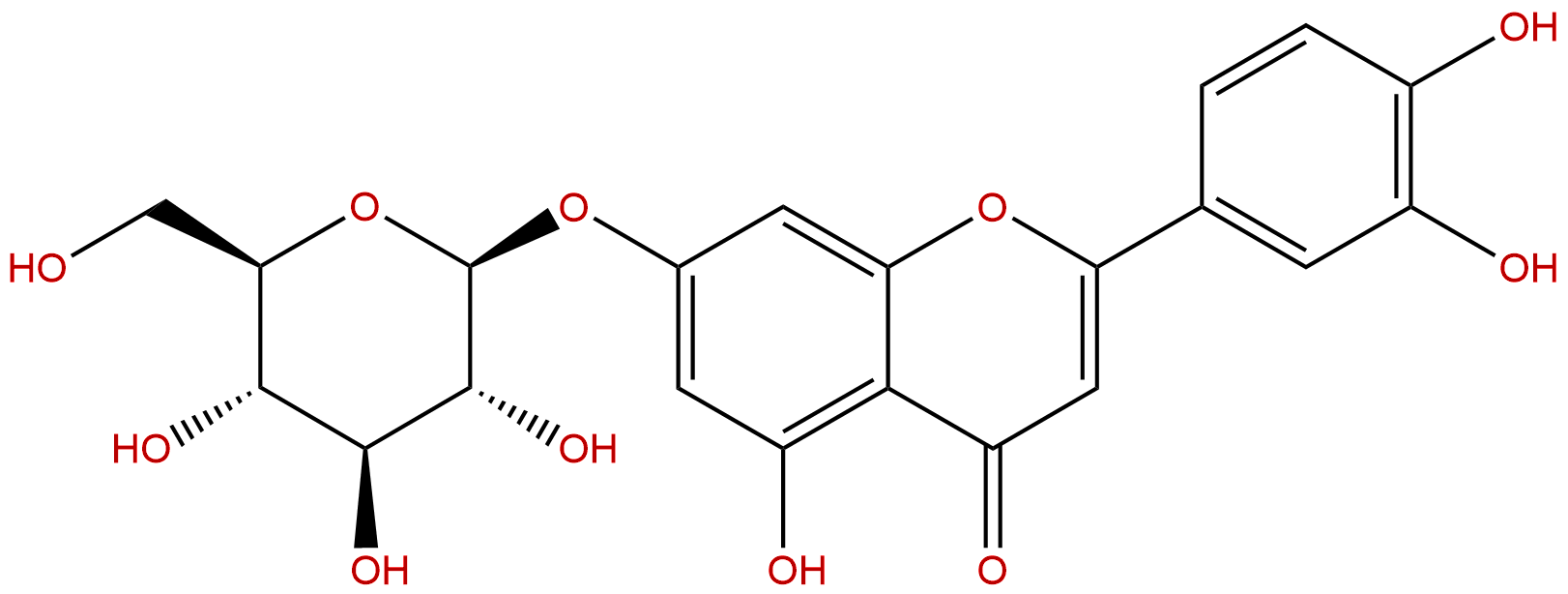
LuteolosideCAS No.:5373-11-5
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0899 |
| Formula: | C21H20O11 |
| Mol Weight: | 448.38 |
Product name: Luteoloside
Synonym name: Luteolin 7-glucoside; Glucoluteolin; Cinaroside; Cynaroside; Daphneflavonoloside; Flavopurposide
Catalogue No.: BP0899
Cas No.: 5373-11-5
Formula: C21H20O11
Mol Weight: 448.38
Botanical Source: Widespread in plants, e.g. in Salicaceae, Lamiaceae, Moraceae, Compositae, Leguminosae, Rosaceae, Gentianaceae. The commonest of all flavone glycosides
Physical Description: Yellow powder
Type of Compound: Flavonoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Luteolin-7-O-glucoside and luteolin at concentrations lower than 20 muM, significantly suppresses the productions of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E-2 (PGE(2)) in bacterial lipopolysaccharide activated-mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells without introducing cytotoxicity; the inhibitory effects were further attributed to the suppression of both inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) protein expression, and not reduced enzymatic activity.[1]
Luteolin-7-O-glucoside from Ailanthus altissima has antiasthmatic activity through the downregulation of T helper 2 cytokine expression and inhibition of prostaglandin E2 production in an ovalbumin-induced asthma model.[2]
Luteolin-7-O-Glucoside can induce apoptosis by scavenging ROS and suppressing the expression of β-catenin in COLO 320 DM cells and effectively inhibit ACF development in DMH-induced experimental carcinogenesis, Hence it can be a potent anticancer drug for colon carcinogenesis.[3]
Luteolin-7-O-glucoside and luteolin can inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses through modulation of NF-κB/AP-1/PI3K-Akt signaling cascades in RAW 264.7 cells.[4]
Luteolin-7-O-glucoside has anti-asthmatic activity, can suppress leukotriene C(4) production and degranulation by inhibiting the phosphorylation of mitogen activated protein kinases and phospholipase Cγ1 in activated mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells.[5]
References:
[1] Hu C, Kitts D. Mol Cellr Biochem, 2004, 265(1-2):107-13.
[2] Jin M, Yang J H, Lee E, et al. Biol Pharm Bull, 2009, 32(9):1500-3.
[3] Baskar A A, Ignacimuthu S, Michael G P, et al. Nut Cancer, 2011, 63(1):130-8.
[4] Chungmu P, Song Y S. Nut Res Pract, 2013, 7(6):423-9.
[5] Jin M, Son K H, Chang H W. Biol Pharm Bull, 2011, 34(7):1032-6.
[6] Ling-Yun M A, Yao L W, Shuang-Cheng M A, et al. Chinese J Pharm Anal, 2009,29(9):1469-500.
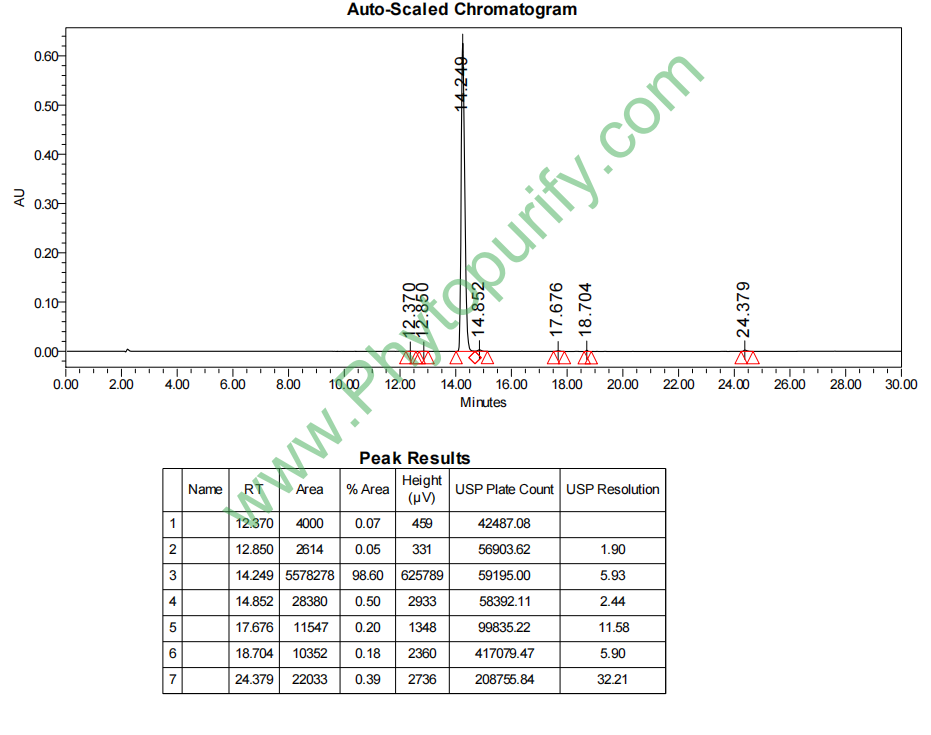
HPLC of Luteoloside