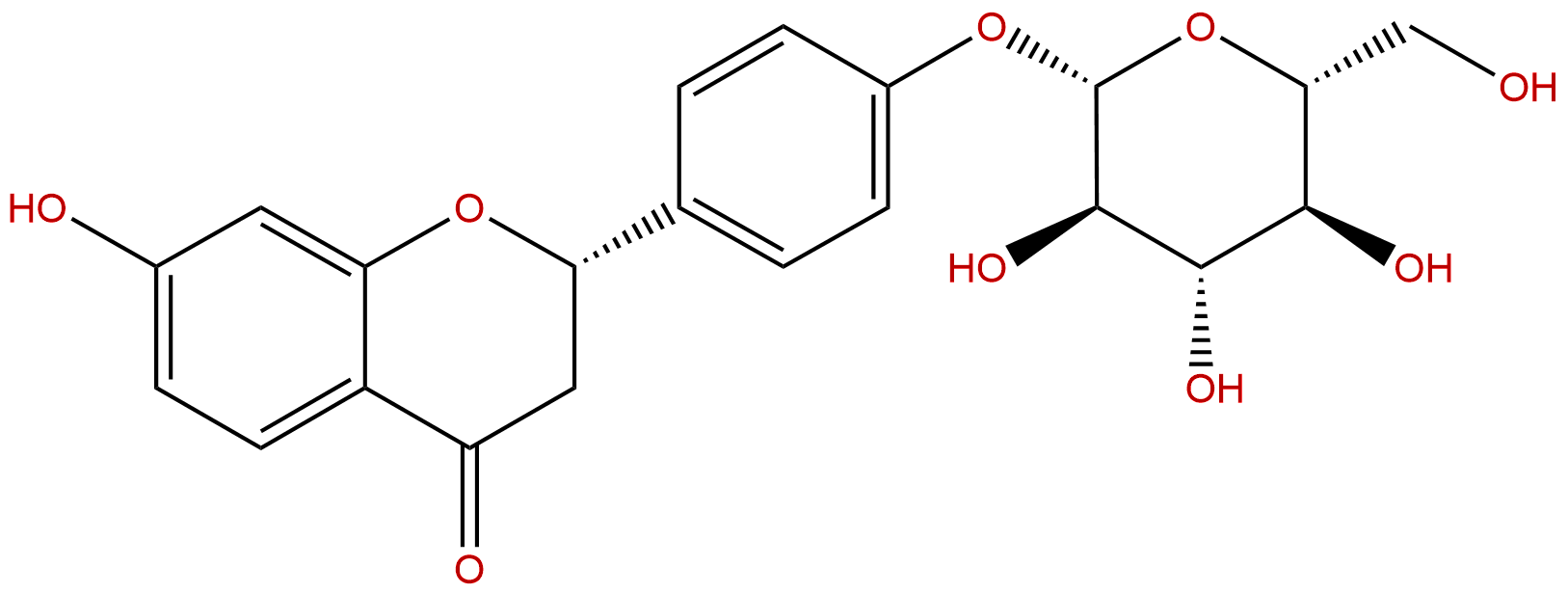
LiquiritinCAS No.:551-15-5
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0874 |
| Formula: | C21H22O9 |
| Mol Weight: | 418.398 |
Product name: Liquiritin
Synonym name: Liquiritoside
Catalogue No.: BP0874
Cas No.: 551-15-5
Formula: C21H22O9
Mol Weight: 418.398
Botanical Source: Glycyrrhiza glabra (licorice) and Glycyrrhiza uralensis (Chinese licorice)
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Flavonoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Liquiritin, a flavone compound derived from Glycyrrhiza uralensis, it can effectively reverse alteration in immobility time and sucrose consumption, can increase SOD activity, inhibit lipid peroxidation, and lessen production of MDA, demonstrates that a potential antidepressant-like effect of liquiritin treatment on chronic variable stress can induce depression model rats, which might be related to defense of liquiritin against oxidative stress.[1]
Liquiritin has neuroprotective effect against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in mice via its antioxidant and antiapoptosis properties, it might be a potential agent against cerebral I/R injury in mice.[2]
Liquiritin significantly promotes the neurite outgrowth stimulated by NGF in PC12 cells in dose dependant manners whereas the liquiritin alone did not induce neurite outgrowth, and it has the neurotrophic effect on the overexpression of neural related genes such as neurogenin 3, neurofibromatosis 1, notch gene homolog 2, neuromedin U receptor 2 and neurotrophin 5; liquiritin also modulate ERK? and AKT/GSK?3β?dependent pathways to protect against glutamate?induced cell damage in differentiated PC12 cells,thus, liquiritin may be a good candidate for treatment of various neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease or Parkinson’s disease.[3,4]
Liquiritin can attenuate advanced glycation end products-induced endothelial dysfunction via RAGE/NF-κB pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells, it may be a promising agent for the treatment of vasculopathy in diabetic patients.[5]
References:
[1] Zhao Z, Wang W, Guo H, et al. Behal Brain Res, 2008, 194(194):108-13.
[2] YaXuan Sun, Yue Tang, AiLi Wu, et al.J Asian Nat Prod Res, 2010, 12(12):1051-60.
[3] Chen Z A, Wang J L, Liu R T, et al. Cytotechnol, 2009, 60(60):125-32.
[4] Teng L, Meng Q, Lu J, et al. Mol Med Rep, 2014, 10(2):818-24.
[5] Zhang X, Song Y, Han X, et al. Mol Cell Biochem, 2013, 374(1-2):191-201.
[6] Seo C S, Kim J H, Shin H K. Pak J Pharm Sci, 2014, 27(4):819-24.
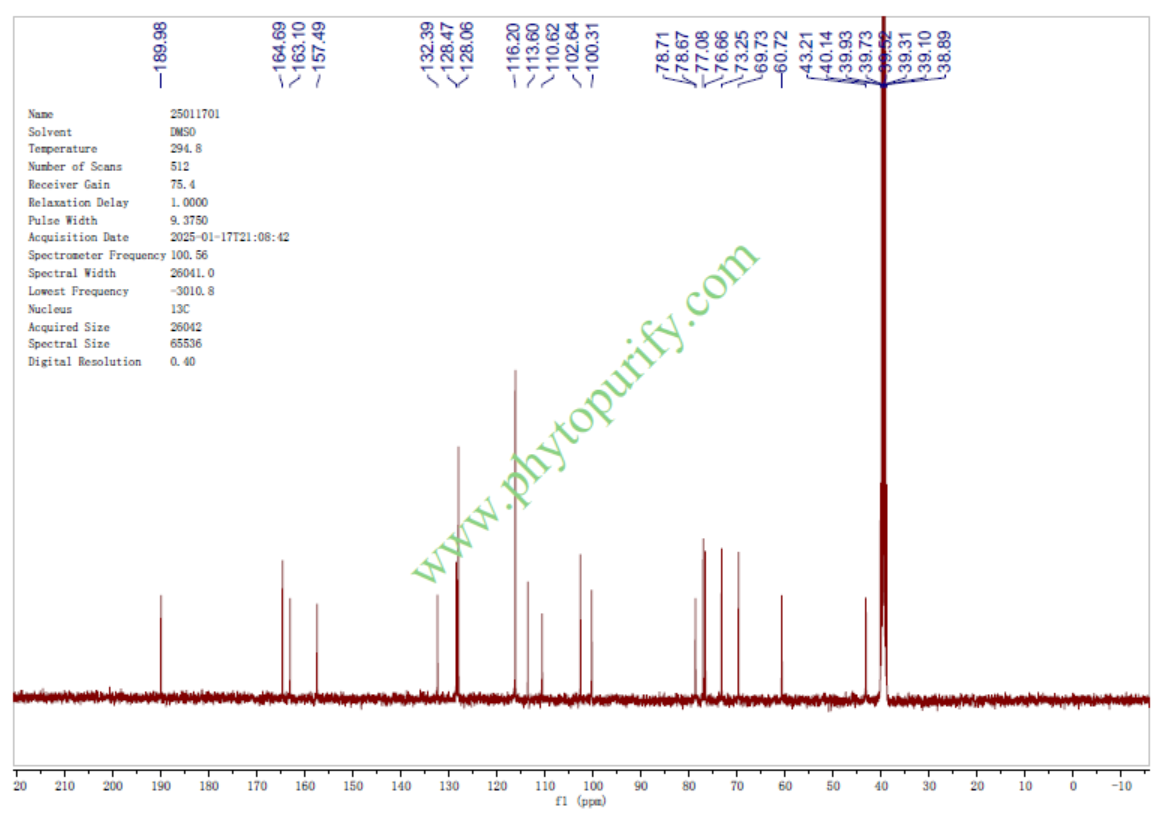
HPLC of Liquiritin
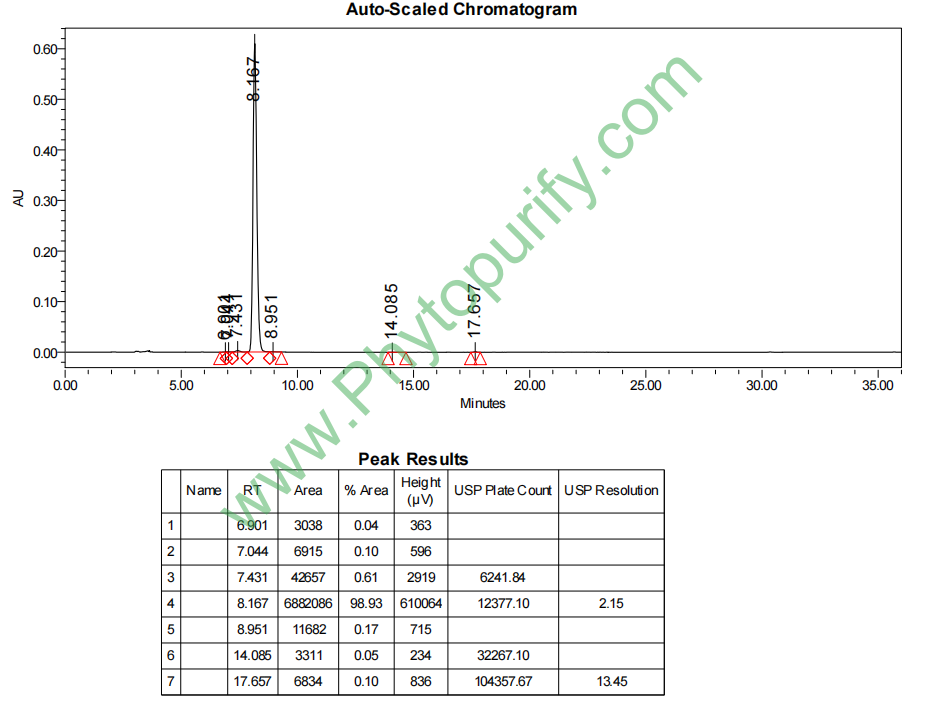
NMR of Liquiritin