Kinsenoside Descrtption
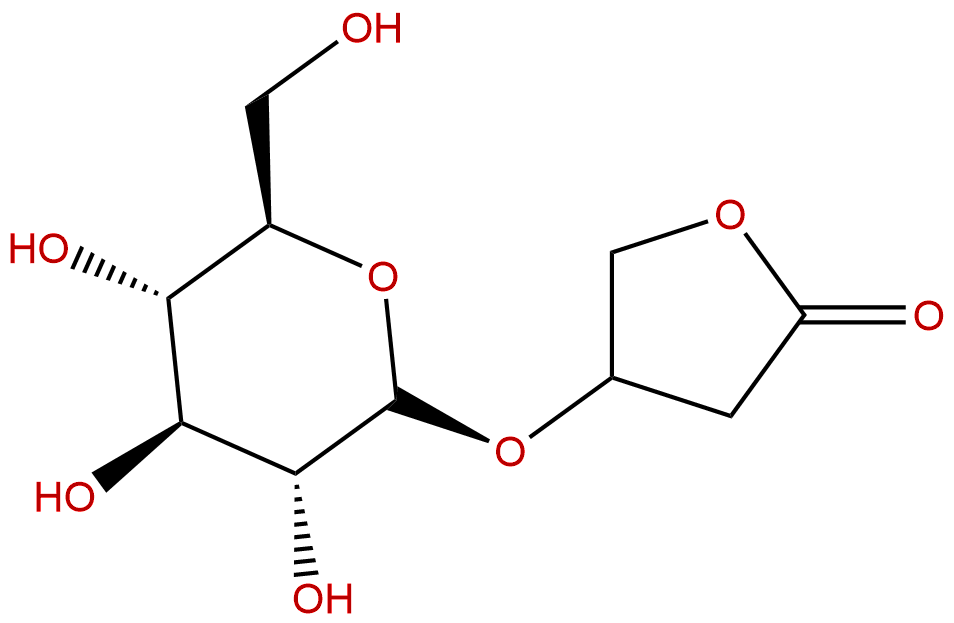
Product name: Kinsenoside
Synonym name: (+)-Kinsenoside
Catalogue No.: BP1705
Cas No.: 151870-74-5
Formula: C10H16O8
Mol Weight: 264.23
Botanical Source:
Physical Description:
Type of Compound:
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams. Inquire for bulk scale.
We provide solution to improve the water-solubility of compounds, thereby facilitating the variety of activity tests and clinic uses.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Description:
Kinsenoside shows significant antihepatotoxic, and anti-inflammatory activities. Kinsenoside could be useful for repairing beta cells in pancreatic islet injury as well as improving its function, it could promote the glucose tolerance of acute glucose increase in both diabetic and normal healthy rats. Kinsenoside inhibits osteoclastogenesis from macrophages by attenuating RANKL-induced NF-κB and NFATc1 activities, which in turn, prevents bone loss from OVX mice.
References:
J Ethnopharmacol. 2007 Nov 1;114(2):141-5.
Antihyperglycemic activity of kinsenoside, a high yielding constituent from Anoectochilus roxburghii in streptozotocin diabetic rats.
Different doses of Kinsenoside, a high yielding constituent from Anoectochilus roxburghii, was orally administered to further investigate its biological activity and pharmacological mechanisms that involve in the hypoglycemic effect on streptozotocin (STZ) diabetic rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Our study showed that this compound exhibited significantly antihyperglycemic activity at the dose of 15mg/kg body weight, which is speculated to be partially attributed to modulating the activity of enzymatic antioxidants, scavenging free radicals, and reducing the content of factor NO. Much more intact beta cells in the islets of Langerhans with denser insulin in Kinsenoside-treated groups than the negative control were observed, which greatly supported the morphological and functional elucidation.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results displayed that Kinsenoside could be useful for repairing beta cells in pancreatic islet injury as well as improving its function. The OGTT evidenced that this compound could promote the glucose tolerance of acute glucose increase in both diabetic and normal healthy rats.
Phytother Res. 2007 Jan;21(1):58-61.
The hepatoprotective activity of kinsenoside from Anoectochilus formosanus.
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl(4)) causes chronic hepatitis, featuring an increase in hepatic hydroxyproline, spleen weight and serum GPT levels and a decrease in plasma albumin levels.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Crude extracts of fresh whole plants of Anoectochilus formosanus showed inhibition of chronic hepatitis induced by CCl(4) in mice. Bioactivity-guided fractionation and spectroscopic analysis revealed that Kinsenoside was the most active compound. In an in vitro study, the LD(50) values for H(2)O(2)-induced cytotoxicity in BALB/c normal liver cells were significantly higher after Kinsenoside pretreatment than after vehicle alone, further confirming that Kinsenoside shows significant antihepatotoxic activity.
HPLC of Kinsenoside