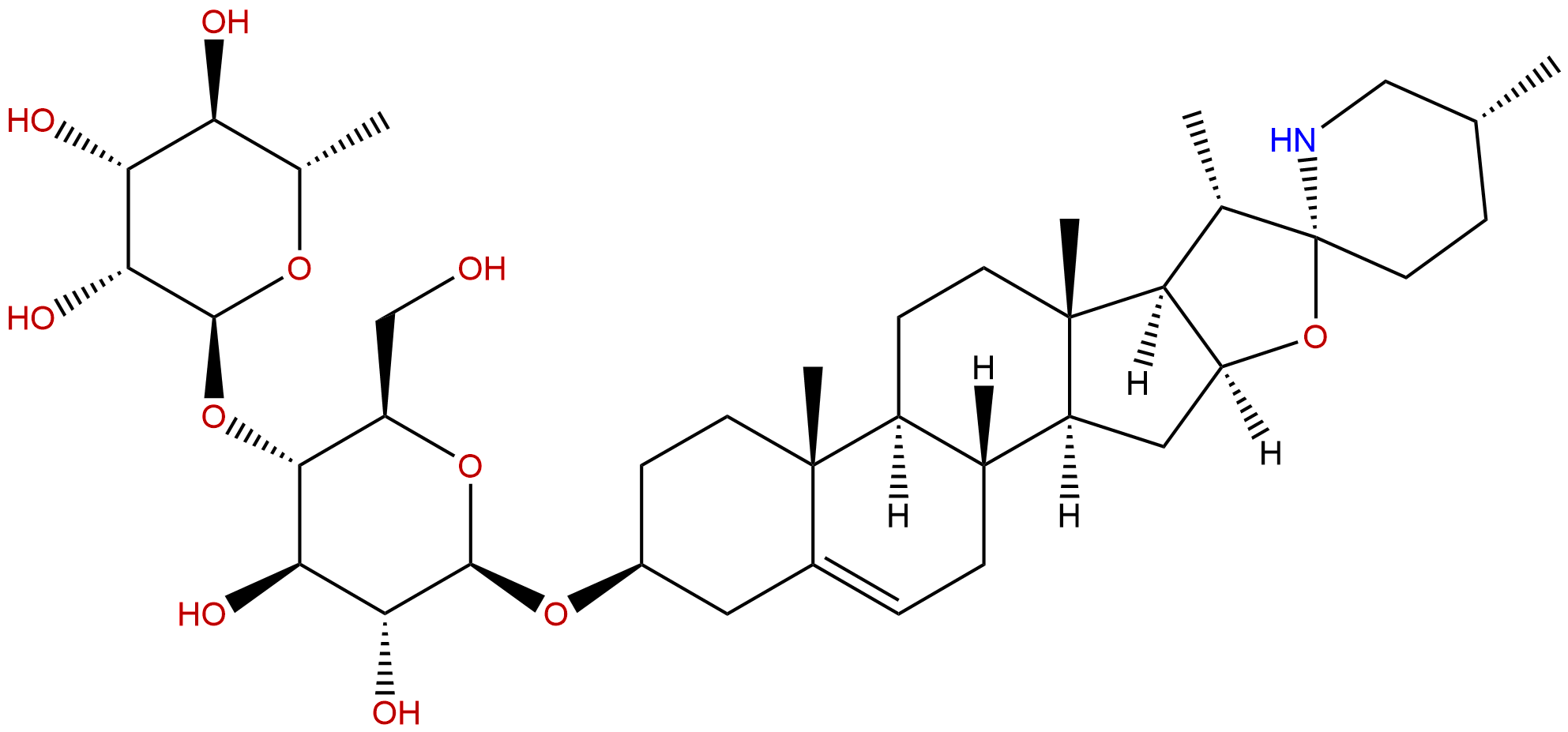
KhasianineCAS No.:32449-98-2
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0830 |
| Formula: | C39H63NO11 |
| Mol Weight: | 721.929 |
Synonym name: Beta2-Solamargine
Catalogue No.: BP0830
Cas No.: 32449-98-2
Formula: C39H63NO11
Mol Weight: 721.929
Botanical Source: Alkaloid from Solanum khasianum and Solanum incanum (Solanaceae)
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Khasianine exhibits strong activity against liver damage induced by CCl4.
References:
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998 Jan 6;242(1):21-5.
The rhamnose moiety of solamargine plays a crucial role in triggering cell death by apoptosis.
Solamargine, solasodine and Khasianine steroidal alkaloids are utilized to determine the role of carbohydrate moiety in the mechanism of apoptosis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The C3 side chain of solamargine, Khasianine and solasodine contains 4'Rha-Glc-Rha2', 4'Rha-Glc and H, respectively. Solamargine possessed potent cytotoxicity to human hepatoma cells, while the cytotoxicity of Khasianine was greatly diminished. Nevertheless, only solamargine could induced "sub-G1" of apoptotic feature in flowcytometry. Thus, the 2'Rha moiety of solamargine may play a crucial role in triggering cell death by apoptosis. In addition, the molecular modeling of solamargine indicated that the 2'Rha moiety was adjacent to the rigid steroid structure, and drastically changed the dihedral angle of the glycosidic bond.
CONCLUSIONS:
The regulations of TNFR I and II expression by different carbohydrate moieties were also distinct. It implied that the carbohydrate moieties of steroidal alkaloids might alter the binding specificity to steroid receptors and consequently regulate the gene expression in different manners.
J Nat Prod. 1993 Jan;56(1):15-21.
Cytotoxic principles and their derivatives of Formosan Solanum plants.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The new steroidal alkaloid capsimine-3-O-beta-D-glucoside [1] was isolated from the root bark of Solanum capsicastrum, and carpesterol [2], 3 beta-(p-hydroxy)-benzoyloxy-22 alpha-hydroxy-4 alpha-methyl-5 alpha-stigmast-7-en-6-one [3], and a new steroidal glycoside named indioside A [4] were isolated from the fruit of Solanum indicum. Indioside A was characterized as 3 beta-O-[alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->2), beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->4), beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)-]alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(-->2)]-beta-D- glucopyranosyl]-diosgenin. Khasianine, dihydrosolasodine, capsimine, and capsimine-3-O-beta-D-glucoside exhibited strong activity against liver damage induced by CCl4.
CONCLUSIONS:
Capsimine and narigenin exhibited significant cytotoxic effect against human PLC/PRF/5 and KB cells in vitro, and capsicastrine and etioline exhibited significant cytotoxicity against human PLC/PRF/5 cells in vitro.
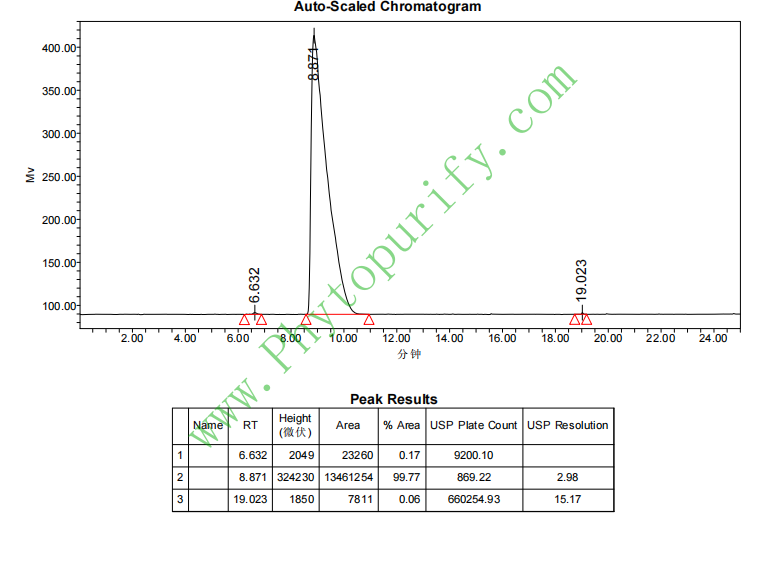
HPLC of Khasianine