
KavainCAS No.:500-64-1
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0829 |
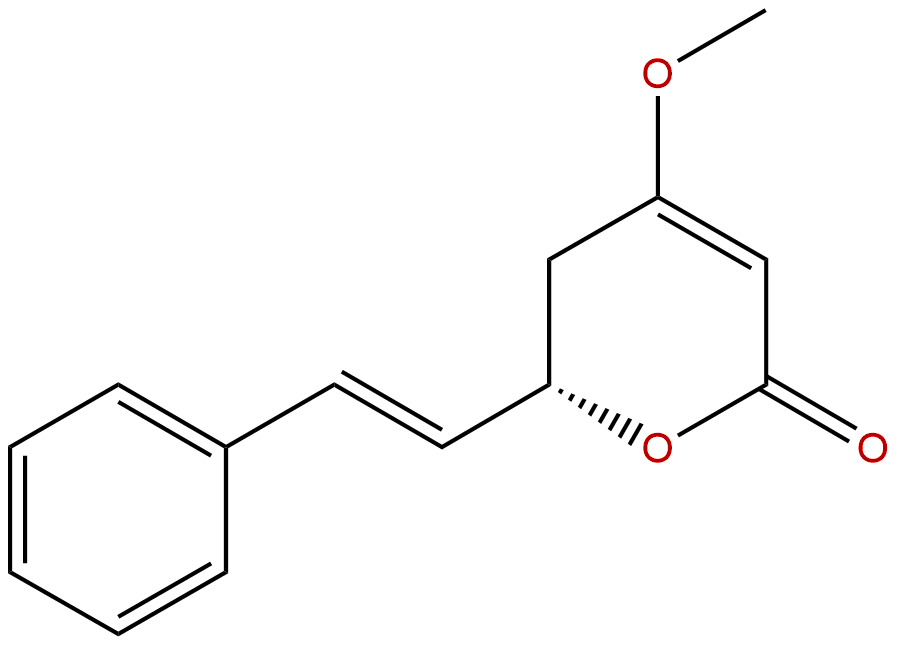
| Formula: | C14H14O3 |
| Mol Weight: | 230.263 |
Synonym name: Kawain
Catalogue No.: BP0829
Cas No.: 500-64-1
Formula: C14H14O3
Mol Weight: 230.263
Botanical Source: Occurs in Root of Piper methysticum
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Kavain has anticonvulsive properties, attenuating vascular smooth muscle contraction through interactions with voltage-dependent Na+ and Ca2+ channels. Kawain is advanced glycation endproduct inhibitors, can increase the mean life span of Caenorhabditis elegans exposed to high glucose.
References:
Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1997 May;21(4):697-706.
Effects of kawain and dihydromethysticin on field potential changes in the hippocampus.
1. The kava-pyrones Kawain and dihydromethysticin are constituents of Piper methysticum which exert anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
3. Kawain and dihydromethysticin reduced reversibly the frequency of occurrence of fp in a concentration range from 5 to 40 mumol/l and 10 to 40 mumol/l, respectively. 4. Reduction of the fp frequency after addition of subthreshold concentrations of 5 mumol/l Kawain and 10 mumol/l dihydromethysticin indicated additive actions of both drugs. 5. Since the serotonin-1A agonist ipsapirone also exerts anxiolytic effects, subthreshold concentrations of Kawain or dihydromethysticin were combined with a subthreshold concentration of ipsapirone in another set of experiments. Combining Kawain and ipsapirone or dihydromethysticin and ipsapirone caused a reduction of the rate of fp to 0.76 and 0.81 of the baseline value, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
6. The findings suggest that (i) single constituents of Piper methysticum may have additive actions, (ii) that the two components Kawain and dihydromethysticin may enhance the effects of the anxiolytic serotonin-1A agonist ipsapirone and (iii) that activation of NMDA receptors and/or voltage dependent calcium channels may be involved in the elementary mechanism of action of some kava-pyrones.
Drug Metab Dispos. 2005 Oct;33(10):1555-63.
Pharmacokinetics and disposition of the kavalactone kawain: interaction with kava extract and kavalactones in vivo and in vitro.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The oral pharmacokinetics of the kavalactone, Kawain (100 mg/kg), were determined in rats with and without coadministration of kava extract (256 mg/kg) to study the effect of the extract on drug disposition. Kawain was well absorbed, with >90% of the dose eliminated within 72 h, chiefly in urine. Compared with Kawain alone, coadministration with kava extract caused a tripling of KawainAUC(0-8 h) and a doubling of C(max). However, a 7-day pretreatment with kava extract (256 mg /kg/day) had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of Kawain administered on day 8.
CONCLUSIONS:
The 7-day pretreatment with kava extract only modestly induced hepatic P450 activities.
HPLC of Kavain

HNMR of Kawain
