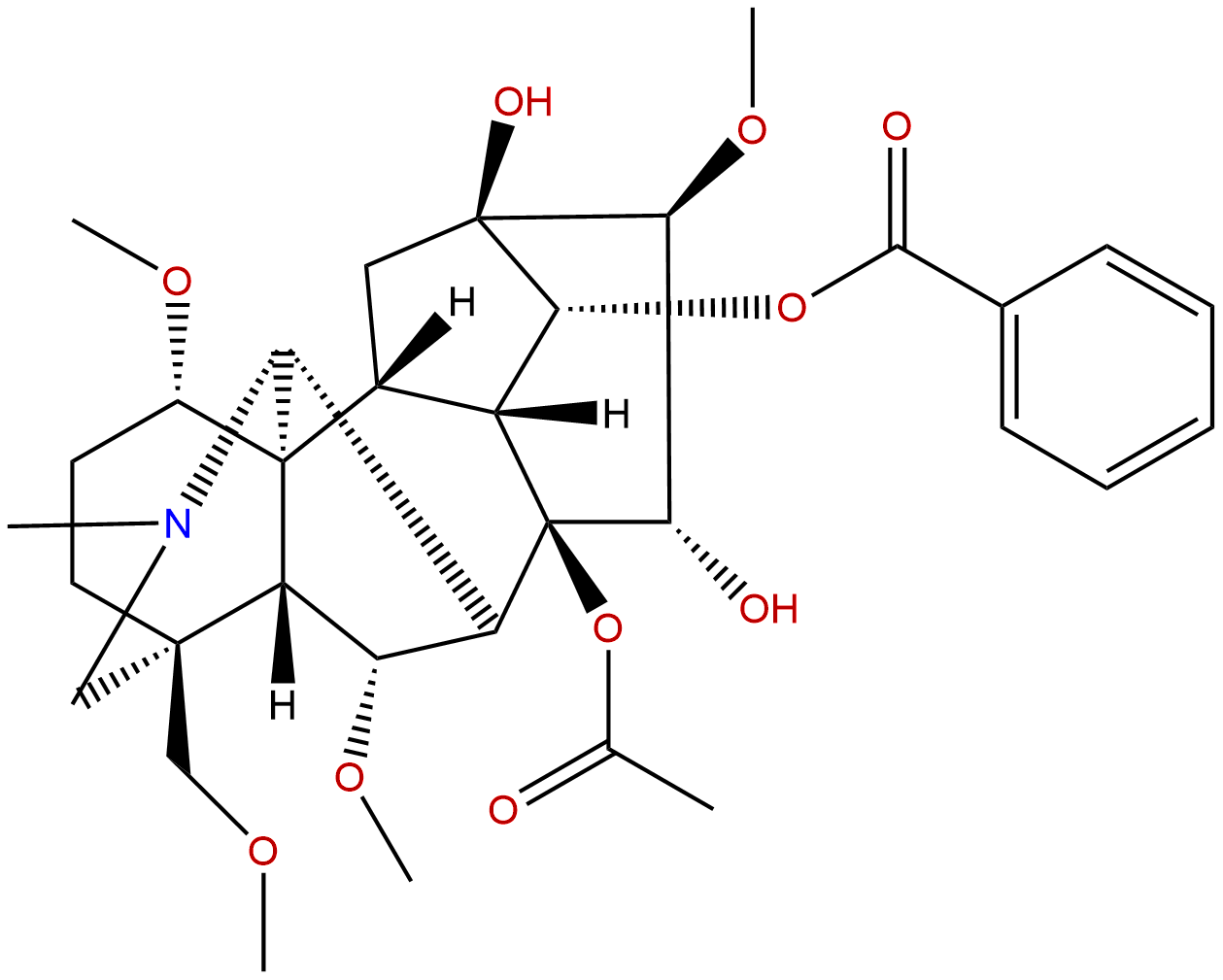
Hypaconitine Descrtption
Product name: Hypaconitine
Synonym name: Deoxymesaconitine; Japaconitine B1; Japaconitine C; Japaconitine C1
Catalogue No.: BP0750
Cas No.: 6900-87-4
Formula: C33H45NO10
Mol Weight: 615.72
Botanical Source: Alkaloid from Aconitum senanense, Aconitum carmichaeli, Aconitum koreanum, Aconitum bullatifolium var. homotrichum, Aconitum callianthum, Aconitum ibukiense, Aconitum tortuosum, Aconitum hakusanense and many other Aconitum spp. (Ranunculaceae)
Physical Description: White powder
Type of Compound: Alkaloids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Hypaconitine (HA), an active and highly toxic constituent derived from Aconitum species, is widely used to treat rheumatism, the hepatic cytochrome P450-catalyzed metabolism of HA. [1]
Hypaconitine, aconitine (AC) and mesaconitine(MA) are aconitum alkaloids, have highly toxic, however, their hydrolysates are considerably less toxic; the intracellular amounts in the presence of inhibitors, P-gp and BCRP were involved in the transport of AC, MA and HA; and MRP2 might transport AC, MA, and HA.[2]
Hypaconitine and aconitine produce neuromuscular blockade by reducing the evoked quantal release, the mechanism of this effect was attributed mainly to blocking of the nerve compound action potential.[3]
Hypaconitine induces QT prolongation, mediated through inhibition of KCNH2 (hERG) potassium channels in conscious dogs.[4]
Hypaconitine can inhibit CaM expression and Cx43 (Ser368) phosphorylation, and liquiritin can interfere with this kind of effect by synergistically inhibiting CaM expression and by antagonizing Cx43 (Ser368) dephosphorylation induced by hypaconitine.[5]
References:
[1] Ye L, Wang T, Yang C, et al. Toxicol Lett, 2011, 204(1):81-91.
[2] Ling Y, Yang X, Zhen Y, et al. Toxicol Lett, 2013, 216(2-3):86-99.
[3] Muroi M, Kimura I, Kimura M. Neuropharmacology, 1990, 29(6):567-72.
[4] Xie S, Ying J, Liu A, et al. J Ethnopharmacol, 2015, 166:375-9.
[5] Yi M, Peng W, Chen X, et al. J Pharm Pharmacol, 2012, 64(11):1654-8.
[6] Zheng H S, Feng N P. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2005, 25(1):34-6.