
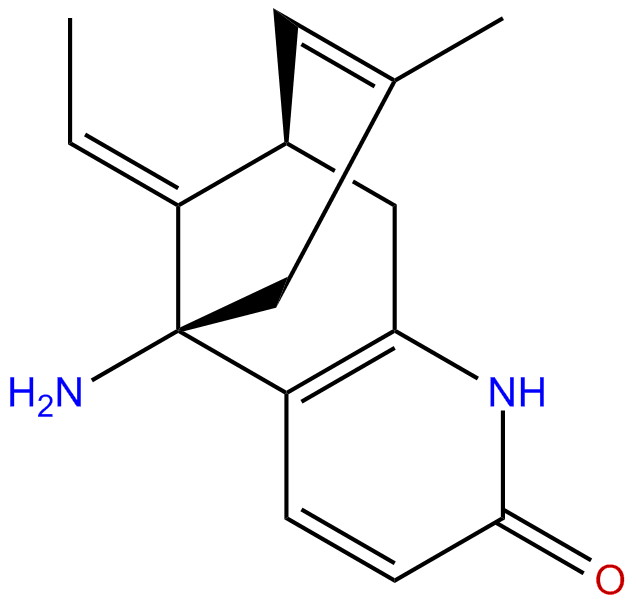
Huperzine ACAS No.:102518-79-6
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0740 |
| Formula: | C15H18N2O |
| Mol Weight: | 242.322 |
Product name: Huperzine A
Synonym name: Selagine; Fordine; Isoselagine
Catalogue No.: BP0740
Cas No.: 102518-79-6
Formula: C15H18N2O
Mol Weight: 242.322
Botanical Source: Lycopodium serratum Thunb.
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Alkaloids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
(-)-Huperzine A is a naturally occurring potent reversible AChE inhibitor that penetrates the blood-brain barrier, it also has several neuroprotective effects including modification of beta-amyloid peptide, reduction of oxidative stress, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic and induction and regulation of nerve growth factor.
References:
Chem Biol Interact. 2013 Mar 25;203(1):120-4.
A combination of [+] and [-]-Huperzine A improves protection against soman toxicity compared to [+]-Huperzine A in guinea pigs.
The neuropathologic mechanisms after exposure to lethal doses of nerve agent are complex and involve multiple biochemical pathways. Effective treatment requires drugs that can simultaneously protect by reversible binding to the acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and blocking cascades of seizure related brain damage, inflammation, neuronal degeneration as well as promoting induction of neuroregeneration. (-)-Huperzine A ([-]-Hup A), is a naturally occurring potent reversible AChE inhibitor that penetrates the blood-brain barrier. It also has several neuroprotective effects including modification of beta-amyloid peptide, reduction of oxidative stress, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic and induction and regulation of nerve growth factor.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Toxicities at higher doses restrict the neuroporotective ability of (-)-Huperzine A for treatment. The synthetic stereoisomer, [+]-Hup A, is less toxic due to poor AChE inhibition and is suitable for both pre-/post-exposure treatments of nerve agent toxicity. [+]-Hup A block the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-induced seizure in rats, reduce excitatory amino acid induced neurotoxicity and also prevent soman induced toxicity with minimum performance decrement. Unique combinations of two stereo-isomers of Hup A may provide an excellent pre/post-treatment drug for the nerve agent induced seizure/status epilepticus. We investigated a combination of [+]-Hup A with a small dose of (-)-Huperzine A ([+] and (-)-Huperzine A) against soman toxicity. Our data showed that pretreatment with a combination [+] and (-)-Huperzine A significantly increased the survival rate and reduced behavioral abnormalities after exposure to 1.2 × LD(50) soman compared to [+]-Hup A in guinea pigs. In addition, [+] and (-)-Huperzine A pretreatment inhibited the development of high power of EEG better than [+]-Hup A pretreatment alone.
CONCLUSIONS:
These data suggest that a combination of [+] and (-)-Huperzine A offers better protection than [+]-Hup A and serves as a potent medical countermeasure against lethal dose nerve agent toxicity in guinea pigs.
HPLC of Huperzine A
