
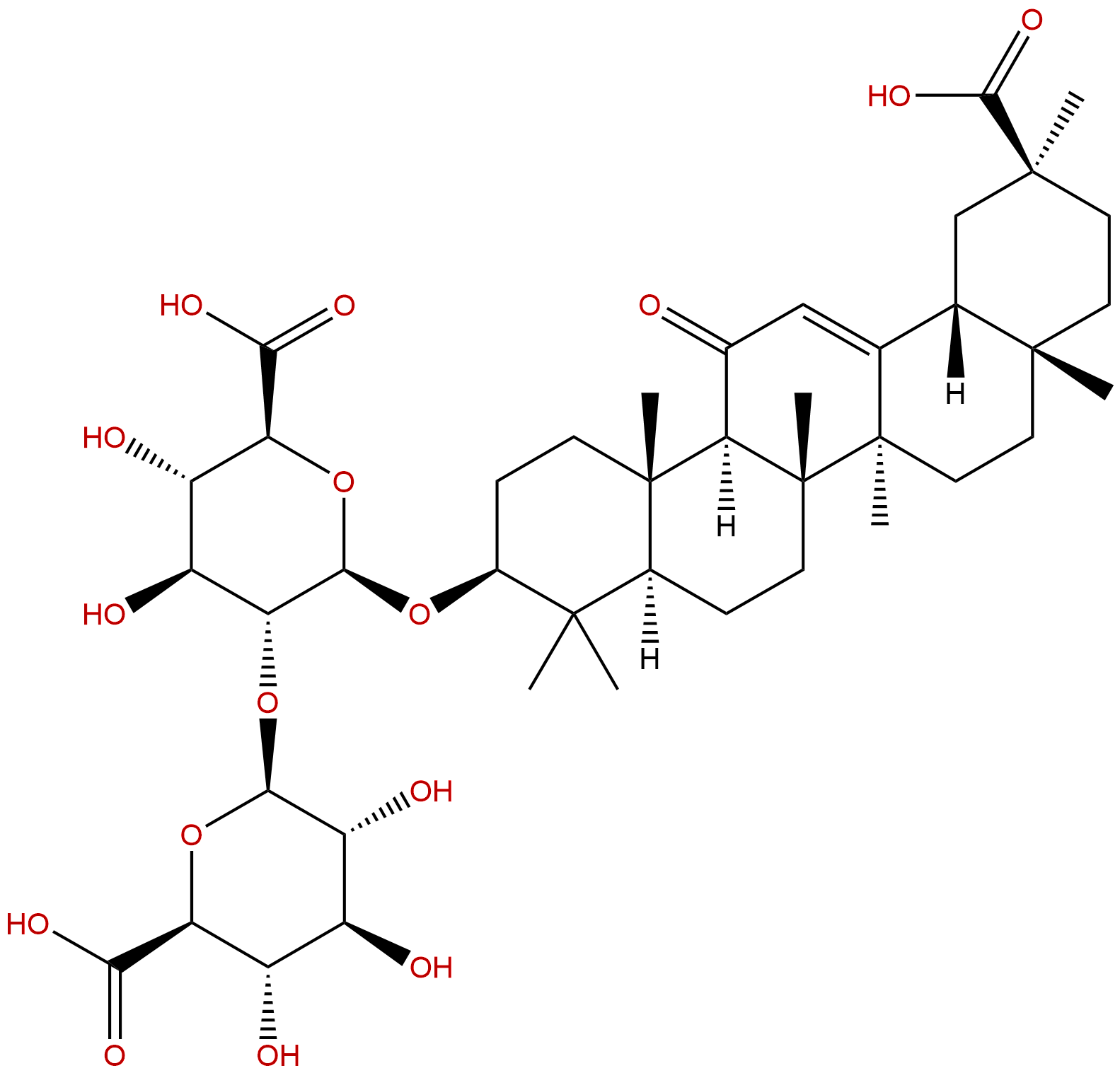
Glycyrrhizic acidCAS No.:1405-86-3
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0682 |
| Formula: | C42H62O16 |
| Mol Weight: | 822.942 |
Product name: Glycyrrhizic acid
Synonym name: Glycyrrhizinic acid; Dermacrin; Glycyrrhitin; Glycyrrhizin
Catalogue No.: BP0682
Cas No.: 1405-86-3
Formula: C42H62O16
Mol Weight: 822.942
Botanical Source: Glycyrrhiza glabra (liquorice), also from Polypodium vulgare, Pradosia and Periandra spp.
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Triterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Glycyrrhizic acid has immunoregulatory function,it(up to 100 mg/ml) can inhibit interleukin-6 and elevate interleukin-10 production in lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages, and significantly inhibit proliferation of spleen lymphocytes; rectally administered glycyrrhizic acid has significant protective effects against TNBS-induced colitis in rats.[1]
Glycyrrhizic acid and 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid may provide an anti-inflammatory effect by attenuating the generation of excessive NO, PGE(2), and ROS and by suppressing the expression of pro-inflammatory genes through the inhibition of NF-κB and PI3K activity, might serve as potential agents for the treatment of inflammatory-mediated diseases.[2]
Glycyrrhizic acid offers radioprotection by scavenging free radicals.[3]
Glycyrrhizic acid is the antiviral component of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. against coxsackievirus A16 and enterovirus 71 of hand foot and mouth disease with distinct mechanisms.[4]
References:
[1] Liu Y, Xiang J, Liu M, et al. Lat Am J Pharm , 2011, 63(3):439-46.
[2] Wang CY, Kao TC, Lo WH, et al.Journal of Agricultural & food Chemistry, 2011, 59(14):7726-33.
[3] Wang D, Pang Y X, Wang W Q, et al. Biochem Syst Ecol, 2013, 50(7):93-100.
[4] Wang J, Chen X, Wei W, et al. J Ethnopharmacol, 2013, 147(1):114-21.
[5] Miao H, Qian Y, Xue L, et al. Primary Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2000,(5):17-18.
HNMR of Glycyrrhizic acid

HPLC of Glycyrrhizic acid
