
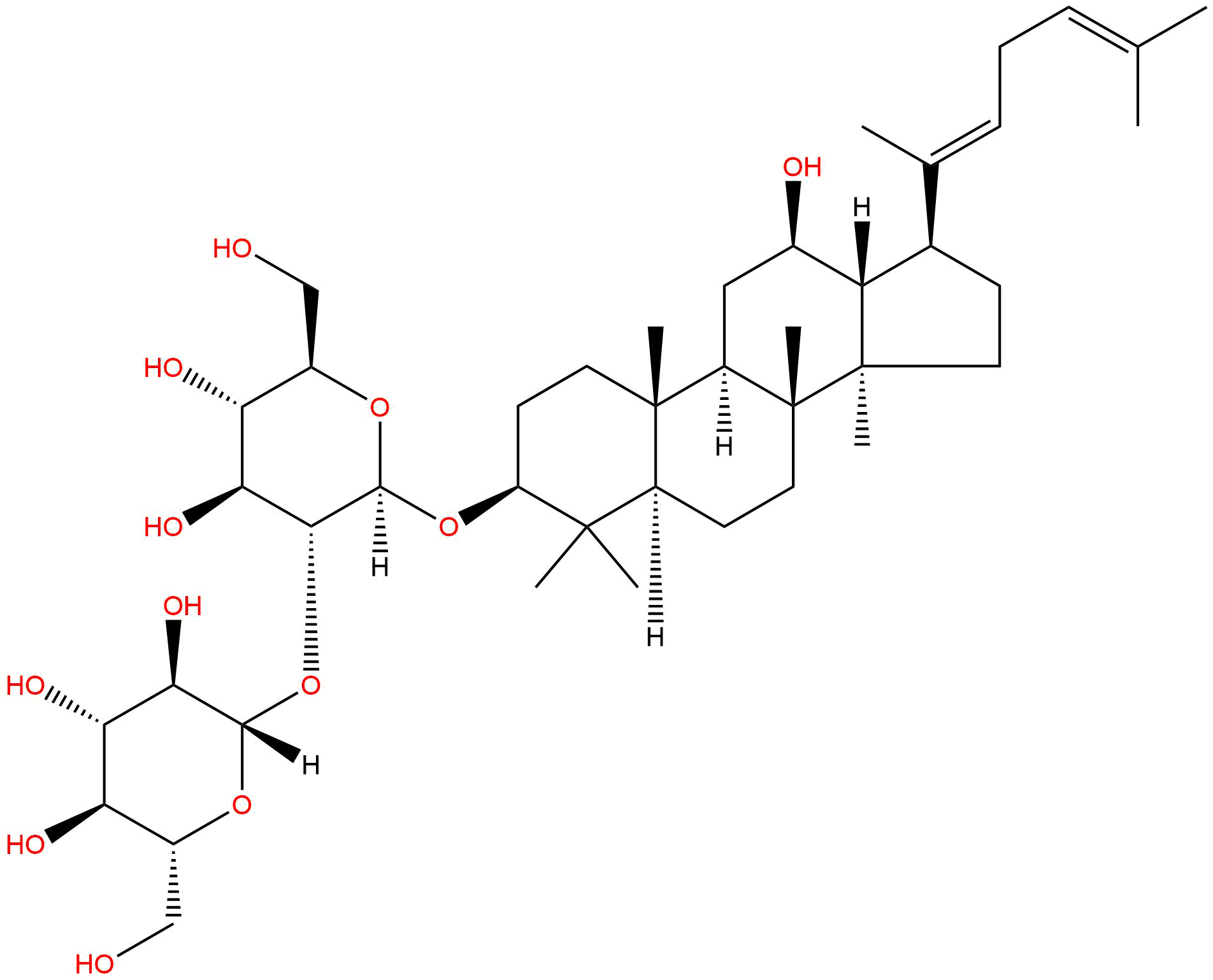
Ginsenoside Rg5CAS No.:186763-78-0
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1651 |
| Formula: | C42H70O12 |
| Mol Weight: | 767.01 |
Product name: Ginsenoside Rg5
Synonym name: Ginsenoside Rg5E
Catalogue No.: BP1651
Cas No.: 186763-78-0
Formula: C42H70O12
Mol Weight: 767.01
Botanical Source:
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Triterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams. Inquire for bulk scale.
We provide solution to improve the water-solubility of compounds, thereby facilitating the variety of activity tests and clinic uses.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Description:
Ginsenoside Rg5 plays a novel role as an IGF-1R agonist, promoting therapeutic angiogenesis and improving hypertension without adverse effects in the vasculature, it can ameliorate lung inflammation possibly by inhibiting the binding of LPS to toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 on macrophages. Ginsenoside Rg5 blocks cell cycle of SK-HEP-1 cells at the Gl/S transition phase by down-regulating cyclin E-dependent kinase activity and that the down-regulation of cyclin E-dependent kinase activity is caused mainly by induced CDK2 inhibitor, p21Cip/WAF1 and decreased levels of cyclin E.
References:
Int Immunopharmacol. 2012 Jan;12(1):110-6.
Ginsenoside Rg5 ameliorates lung inflammation in mice by inhibiting the binding of LPS to toll-like receptor-4 on macrophages.
Heating and steaming processes have been applied to various natural medicines for either enhancing or altering their pharmacological activities, and the chemical compositions of the active components. While ginsenoside Rb1, which is the major constituent of raw ginseng, has been studied extensively for its anti-inflammatory effect, the biological activity of Ginsenoside Rg5, a major constituent of steamed ginseng, remains to be explored.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we isolated Rg5 and examined anti-inflammatory effect in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated macrophages and on LPS-induced lung inflammation. Rg5 inhibited the expression of proinflammatory cytokines, IL-1β and TNF-α, as well as inflammatory enzymes, COX-2 and iNOS in LPS-stimulated alveolar macrophages. Rg5 also reduced LPS-induced phosphorylation of IL-1 receptor-associated kinases (IRAK)-1 and IKK-β, as well as the degradation of IRAK-1 and IRAK-4. Rg5 inhibited the phosphorylation of NF-κB as well as the translocation of p65 into the nucleus. When macrophages were treated with Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated LPS in the presence of Rg5, the fluorescence intensity of LPS observed outside the cell membrane was lower than that in LPS-stimulated alveolar macrophages alone. Rg5, inhibited the levels of protein and neutrophils in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of LPS-stimulated mice, as well as pro-inflammatory cytokines, TNF-α and IL-1β. Rg5 also inhibited iNOS and COX expressions, and NF-κB activation in LPS-stimulated lung inflammation of mice. The inhibitory effect of Rg5 (10 mg/kg) was comparable to that of dexamethasone (5 mg/kg).
CONCLUSIONS:
Based on these findings, Rg5 can ameliorate lung inflammation possibly by inhibiting the binding of LPS to toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 on macrophages.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Apr;19(2):317-26.
Ginsenoside Rg5 improves cognitive dysfunction and beta-amyloid deposition in STZ-induced memory impaired rats via attenuating neuroinflammatory responses.
Neuroinflammatory responses play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Ginsenoside Rg5 (Rg5), an abundant natural compound in Panax ginseng, has been found to be beneficial in treating AD.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we demonstrated that Ginsenoside Rg5 improved cognitive dysfunction and attenuated neuroinflammatory responses in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced memory impaired rats. Cognitive deficits were ameliorated with Ginsenoside Rg5 (5, 10 and 20mg/kg) treatment in a dose-dependent manner together with decreased levels of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β (P<0.05) in brains of STZ rats. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity was also significantly reduced by Ginsenoside Rg5 whereas choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) activity was remarkably increased in the cortex and hippocampus of STZ-induced AD rats (P<0.05). Western blot analysis also demonstrated that Ginsenoside Rg5 increased remarkably BDNF and IGF-1 expressions whereas decreased significantly Aβ deposits (P<0.05). Furthermore, it was observed that the expressions of COX-2 and iNOS were significantly up-regulated in STZ-induced AD rats and down-regulated strongly (P<0.05) by Ginsenoside Rg5 compared with control rats. These data demonstrated that STZ-induced learning and memory impairments in rats could be improved by Ginsenoside Rg5, which was associated with attenuating neuroinflammatory responses.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our findings suggested that Ginsenoside Rg5 could be a beneficial agent for the treatment of AD.
J Biol Chem. 2015 Jan 2;290(1):467-77.
Specific activation of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor by ginsenoside Rg5 promotes angiogenesis and vasorelaxation.
Ginsenoside Rg5 is a compound newly synthesized during the steaming process of ginseng; however, its biological activity has not been elucidated with regard to endothelial function.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We found that Rg5 stimulated in vitro angiogenesis of human endothelial cells, consistent with increased neovascularization and blood perfusion in a mouse hind limb ischemia model. Rg5 also evoked vasorelaxation in aortic rings isolated from wild type and high cholesterol-fed ApoE(-/-) mice but not from endothelial nitric-oxide synthase (eNOS) knock-out mice. Angiogenic activity of Rg5 was highly associated with a specific increase in insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) phosphorylation and subsequent activation of multiple angiogenic signals, including ERK, FAK, Akt/eNOS/NO, and Gi-mediated phospholipase C/Ca(2+)/eNOS dimerization pathways. The vasodilative activity of Rg5 was mediated by the eNOS/NO/cGMP axis. IGF-1R knockdown suppressed Rg5-induced angiogenesis and vasorelaxation by inhibiting key angiogenic signaling and NO/cGMP pathways. In silico docking analysis showed that Rg5 bound with high affinity to IGF-1R at the same binding site of IGF. Rg5 blocked binding of IGF-1 to its receptor with an IC50 of ∼90 nmol/liter. However, Rg5 did not induce vascular inflammation and permeability.
CONCLUSIONS:
These data suggest that Rg5 plays a novel role as an IGF-1R agonist, promoting therapeutic angiogenesis and improving hypertension without adverse effects in the vasculature.
HPLC of Ginsenoside Rg5

HNMR of Ginsenoside Rg5
