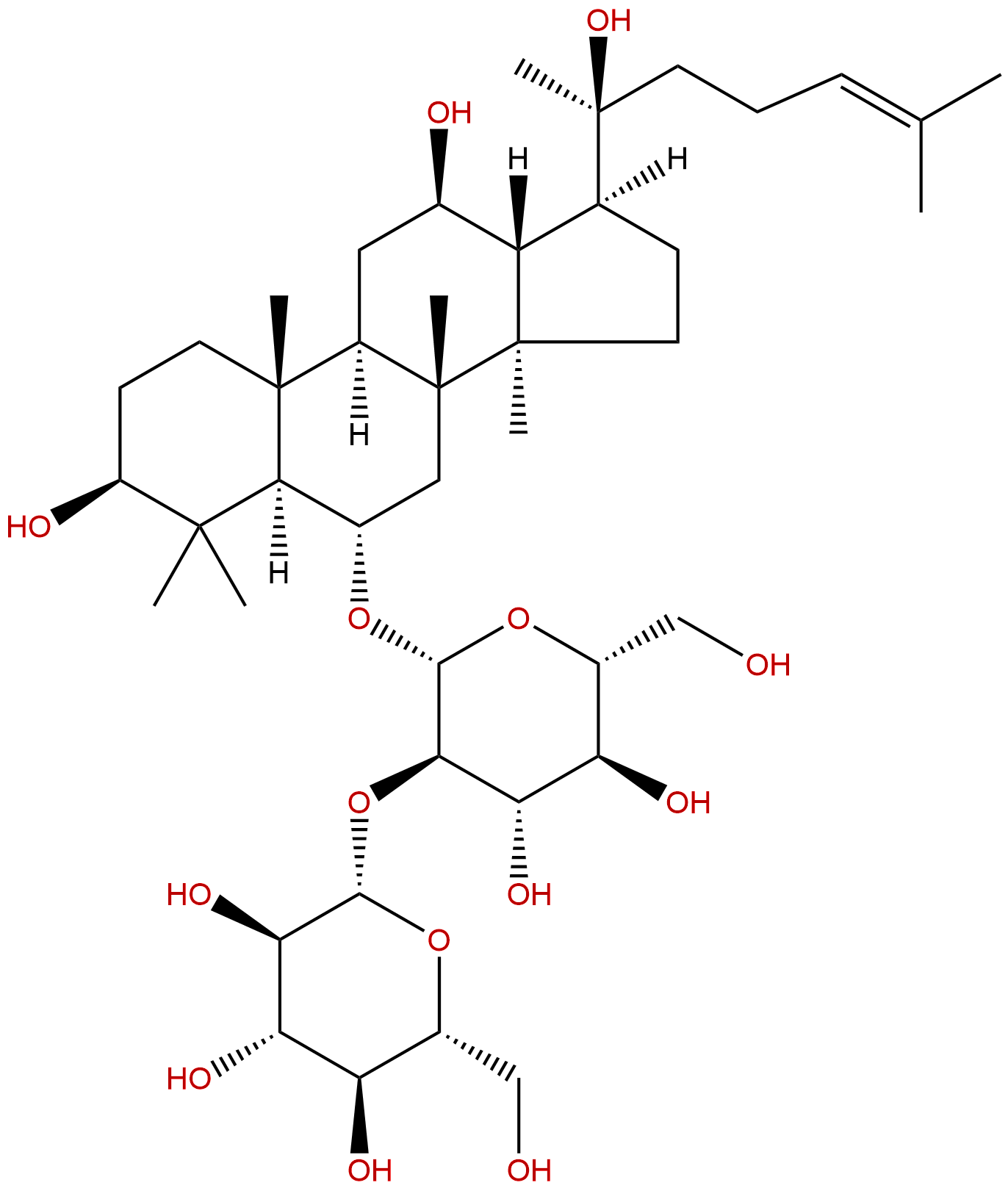
Ginsenoside Rf Descrtption
Product name: Ginsenoside Rf
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP0663
Cas No.: 52286-58-5
Formula: C42H72O14
Mol Weight: 801.024
Botanical Source: Panax ginseng (ginseng)
Physical Description: White powder
Type of Compound: Triterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
GinsenosideRf, as an effective natural product, induces G2/Mphase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human osteosarcoma MG-63 cells through the mitochondrial pathway, suggests that it may have a therapeutic effect on human osteosarcoma.[1]
Ginsenoside Rf(Rf) , a trace component of ginseng root, produces antinociception in mice; Ginsenoside Rf potentiates U-50,488H-induced analgesia and inhibits tolerance to its analgesia in mice.[2,3]
Ginsenoside Rf regulates voltage-dependent Ca(2+) channels through pertussis toxin (PTX)-sensitive G proteins in rat sensory neurons, suggests that Rf can act through a novel G protein-linked receptor in the nervous system. [4]
Ginsenoside Rf induces CYP3A4 and MDR1 gene expression through constitutive androstane receptor- and pregnane X receptor-mediated pathways. [5]
Ginsenoside Rf significantly reduces the production of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, NO, and ROS, which are most highly activated in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and suppresses TNF-α/LPS-induced NF-κB transcriptional activity; suggests that ginsenoside Rf has potent intestinal anti-inflammatory effects that could be used to treat diseases such as IBD.[6]
References:
[1] Shangguan W J, Li H, Zhang Y H. Oncol Rep, 2014, 31(1):305-13.
[2] Mogil J S, Shin Y H, Mccleskey E W, et al. Brain Res, 1998, 792(2):218-28.
[3] Nemmani K V S, Ramarao P. Life Sci, 2003, 72(7):759-68.
[4] Choi S, Jung S Y, Ko Y S, et al. Mol Pharmacol, 2002, 61(4):928-35.
[5] Li Y, Wang Q, Yao X, et al. Eur J Pharmacol, 2010, 640(1-3):46-54.
[6] Ahn S, Siddiqi M H, Aceituno V C, et al. Immunl Invest, 2016,45(5):439-49.
[7] Zang P, Zhang P, Gao Y, et al. J Med Plant Res, 2011, 5(23):5513-6.