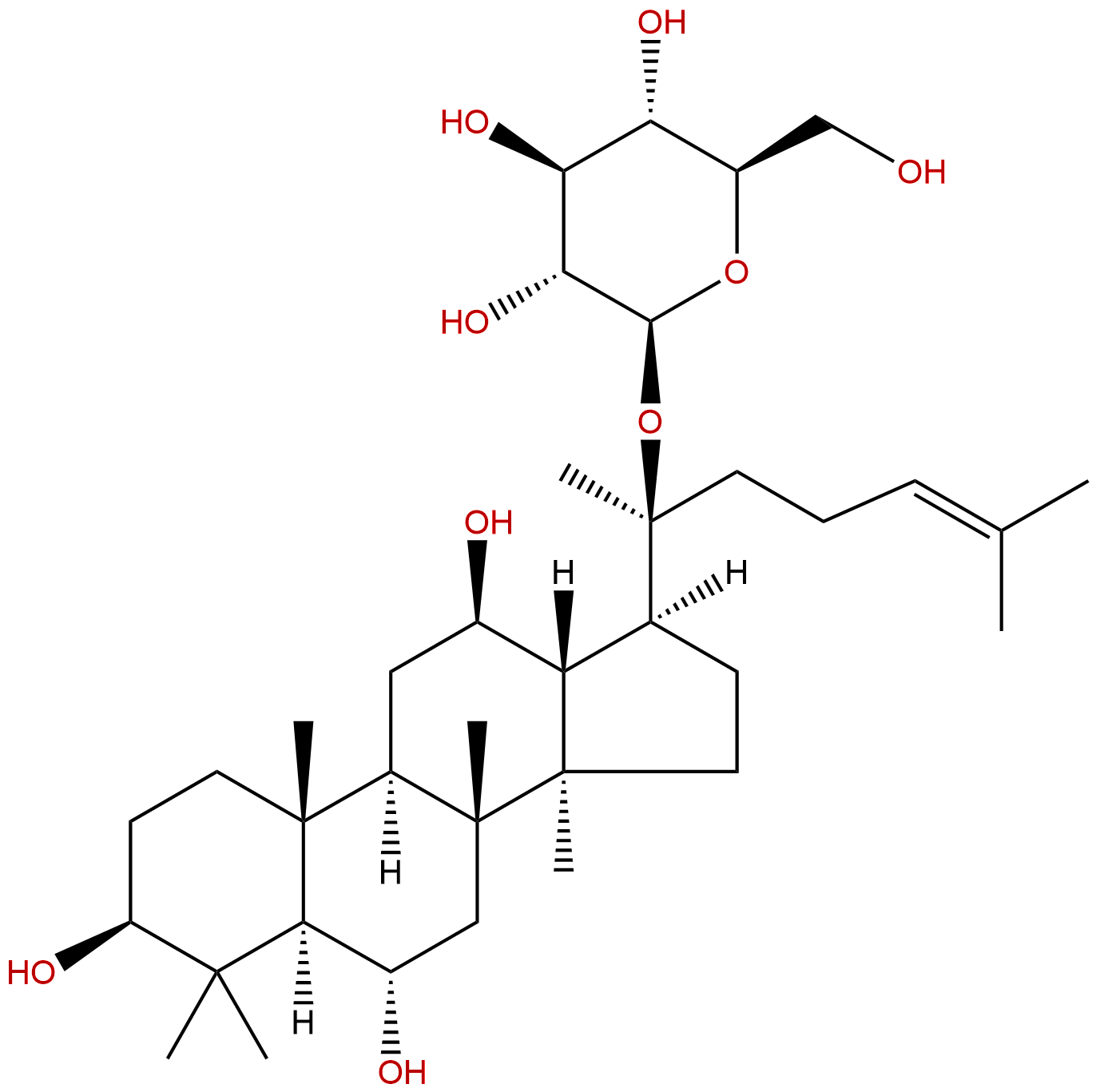
Ginsenoside F1CAS No.:53963-43-2
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0652 |
| Formula: | C36H62O9 |
| Mol Weight: | 638.883 |
Product name: Ginsenoside F1
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP0652
Cas No.: 53963-43-2
Formula: C36H62O9
Mol Weight: 638.883
Botanical Source: Panax spp.
Physical Description: White powder
Type of Compound: Triterpenoids
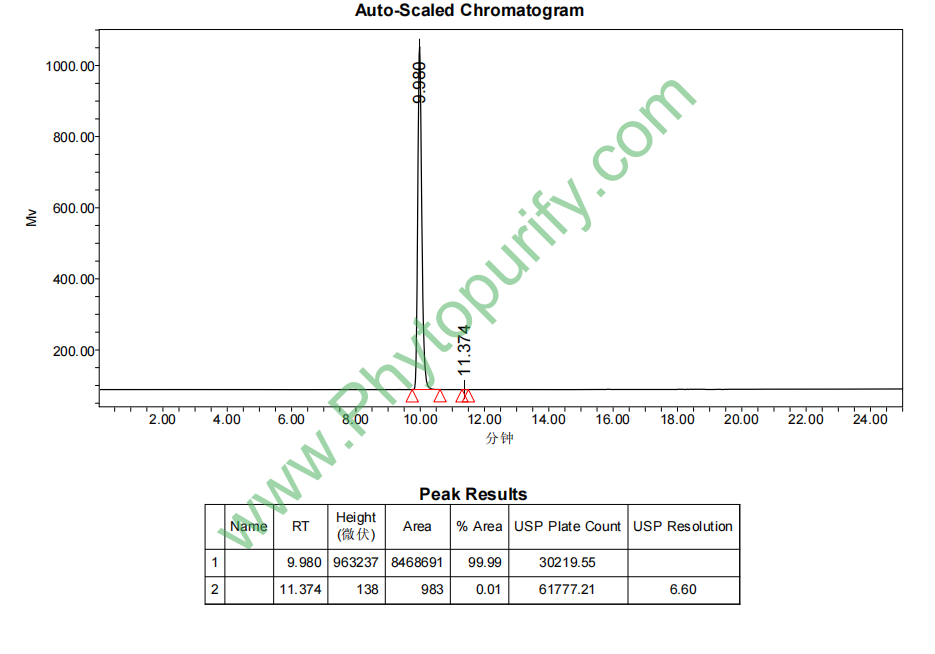
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Ginsenoside (G)-F1 is an enzymatic metabolite generated from G-Rg1, it has been reported to suppress platelet aggregation and to reduce gap junction-mediated intercellular communication, also as a novel anti-skin cancer drug with anti-proliferative and anti-migration features.[1]
Ginsenoside F1 significantly reduces ultraviolet-B-induced cell death by maintaining constant levels of Bcl-2 and protects HaCaT cells from apoptosis caused by ultraviolet B irradiation. [2]
Ginsenoside F1(GF1) has beneficial effects on skin, it reduces α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-induced melanin secretion in B16F10 cell culture media by 60%, but does not suppress intracellular melanin levels, tyrosinase activity and expression; it primarily modulates the Rho family GTPases resulting in dendrite retraction, suggests that GF1 could act as a potent skin-whitening agent.[3]
Ginsenoside F1 has inhibitory effect of elastase and tyrosinase, indicates that ginsenoside F1 have a potential for industrial cosmetic materials.[4]
References:
[1] Yoo D S, Rho H S, Yong G L, et al. J Ginseng Res, 2011, 35(1):86-91.
[2] Lee E H, Cho S Y, Kim SJShin E S, et al.J Invest Dermatol, 2003, 121(3):607-13.
[3] Ji H K, Baek E J, Lee E J, et al. Exp Dermatol, 2014, 24(2):150-2.
[4] Hong, S.C., Korean J Pharm, 2013, 44(1):10-5.
[5] Chong G, Gao Y G, Pu Z, et al. Chinese Trad Herbal Drugs, 2014, 45(14):2009-13.
HPLC of Ginsenoside F1