
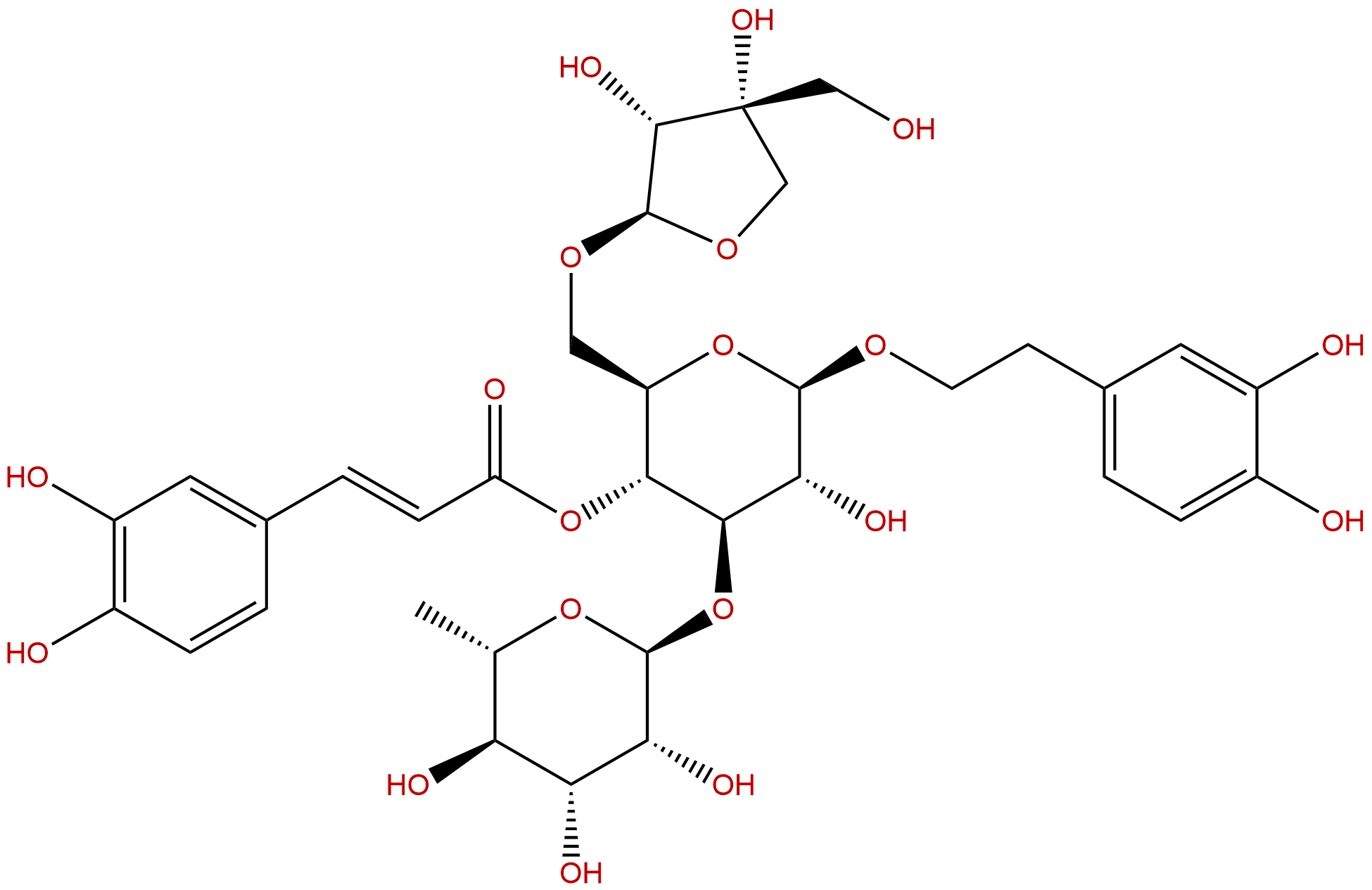
Forsythoside BCAS No.:81525-13-5
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0595 |
| Formula: | C34H44O19 |
| Mol Weight: | 756.707 |
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP0595
Cas No.: 81525-13-5
Formula: C34H44O19
Mol Weight: 756.707
Botanical Source: Phtheirospermum japonicum, Forsythia koreana, Phlomis armeniaca, Scutellaria salviifolia, Marrubium vulgare and Forsythia viridissima
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Forsythoside B inhibits inflammatory response, has antioxidant, antisepsis properties, and also has potent neuroprotective effects with a favorable therapeutic time-window, reduce of cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury degree, attenuating blood-brain barrier (BBB) breakdown. Forsythoside B could inhibit TNF-alpha, IL-6, IκB and modulate NF-κB.
References:
Phytother Res. 2012 Jul;26(7):981-7.
Forsythoside B protects against experimental sepsis by modulating inflammatory factors.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study investigated the effects of Forsythoside B on an experimental model of sepsis induced by caecal ligation and puncture (CLP) in rats and elucidated the potential mechanism in cultured RAW 264.7 cells. Results showed that Forsythoside B concentration-dependently down-regulated the levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and high-mobility group-box 1 protein (HMGB1) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 cells, inhibited the IκB kinase (IKK) pathway and modulated nuclear factor (NF)- κB. Intravenous injection (i.v.) of Forsythoside B alone or plus Imipenem reduced serum levels of TNF-α, IL-6, HMGB1, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells (TREM-1) and endotoxin, while the serum level of IL-10 was up-regulated and myeloperoxidase (MPO) in lung, liver and small intestine was reduced. Meanwhile, i.v. of Forsythoside B alone or plus Imipenem reduced CLP-induced lethality in rats. These data indicated that the antisepsis effect of Forsythoside B is mediated by decreasing local and systemic levels of a wide spectrum of inflammatory mediators. Its antisepsis mechanism may be that Forsythoside Bbinds to LPS and reduces the biological activity of serum LPS, and inhibits NF-κB activition.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our studies enhance the case for the use of Forsythoside B in sepsis. Forsythoside B itself has promise as a therapy for the treatment of sepsis in humans.
Phytomedicine. 2010 Jul;17(8-9):635-9.
Cardioprotection with forsythoside B in rat myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: relation to inflammation response.
The present study was undertaken to examine the effect of Forsythoside B (FB) on rat myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) model and elucidate the potential mechanism.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Left ventricular systolic pressure (LVSP) and +/-dp/dt(max) were detected. Blood samples were collected to determine serum levels of troponin T (Tn-T), TNF-alpha and IL-6. Hearts were harvested to assess histopathological change and infarct size, determine content of MDA, myeloperoxidase (MPO), SOD and GPx activities, analyze expression of high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), phosphor-I kappaB-alpha and phosphor-nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) in ischemic myocardial tissue by Western blot. Compared with control group, rats treatment with FB showed a significant recovery in myocardial function with improvement of LVSP and +/-dp/dt(max). The myocardial infarct volume, serum levels of Tn-T, TNF-alpha and IL-6, content of MDA and MPO activity in myocardial tissue were all reduced, protein expression of HMGB1, phosphor-I kappaB-alpha and phosphor-NF-kappaB were down-regulated, while attenuated the decrease of SOD and GPx activities. Besides, the infiltration of polymorph nuclear leukocytes (PMNs) and histopathological damages in myocardium were decreased in FB treated groups.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggested that FB rescued cardiac function from I/R injury by limiting inflammation response and its antioxidant properties.
HPLC of Forsythoside B
