
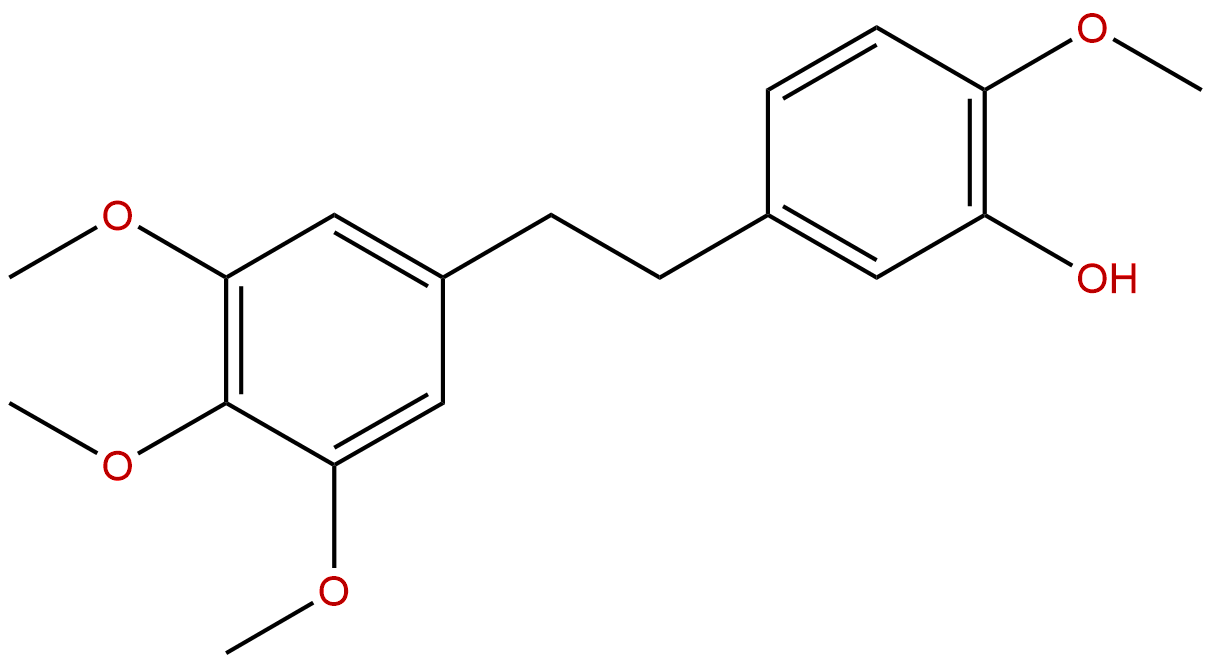
ErianinCAS No.:95041-90-0
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0550 |
| Formula: | C18H22O5 |
| Mol Weight: | 318.369 |
Synonym name: 3'-Hydroxy-3,4,4',5-tetramethoxybibenzyl
Catalogue No.: BP0550
Cas No.: 95041-90-0
Formula: C18H22O5
Mol Weight: 318.369
Botanical Source: Eria carinata
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Erianin, often used as an antipyretic and analgesic agent, it also has antiangiogenic action by inhibiting endothelial metabolism in a JNK/SAPK-dependent manner and inducing endothelial cytoskeletal disorganisation.
References:
Invest New Drugs. 2012 Oct;30(5):1899-907.
ZJU-6, a novel derivative of Erianin, shows potent anti-tubulin polymerisation and anti-angiogenic activities.
ZJU-6 was designed to enhance anti-angiogenesis and anti-tumour activity of its parent compound Erianin, a clinic anti-tumour agent. This study investigated the detailed biological mechanism of ZJU-6 in comparison with that of Erianin.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Both ZJU-6 and Erianin substantially reduced cell viability and induced apoptosis in human cancer cell lines. Profound G2/M cell arrest was observed 24 h after treatment of MCF-7 cells with ZJU-6 (≥ 2.5 μM) or Erianin (≥ 0.1 μM); being consistent with mitotic collapse. 0.5 μM of Erianin or ZJU-6 failed to stabilise tubulin. Pre-G1 MCF-7 cell accumulating 24 h post treatment indicated apoptosis. Caspase-3 activity, PARP cleavage and Annexin V + ve /PI -ve populations correlate the apoptotic destiny of cells exposed to either ZJU-6 or Erianin. Furthermore ZJU-6 showed potent anti-angiogenetic property and demonstrated radical scavenging capacity.
CONCLUSIONS:
Due to its potent anti-proliferative, pro-apoptotic and anti-angiogenic activities ZJU-6 is an attractive chemotherapeutic agent to be developed.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2001 Nov;22(11):1018-22.
Erianin induces apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 cells.
To investigate the effect of Erianin on human HL-60 cell line and explore its mechanism of apoptosis in vitro.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Inhibition of proliferation was measured with colorimetric MTT assay. The morphologic changes were observed by fluorescence and electron microscopes. DNA fragmentation was visualized by agarose gel electrophoresis, and the DNA degradation was determined by flow cytometry. Immunohistochemical analysis was used to identify the expression of bcl-2 and bax genes. The growth of human HL-60 cells was significantly inhibited by Erianin 20-81.9 nmol/L during 72 h treatment (P < 0.01). The IC50 value was 38 nmol/L after a 24-h exposure to Erianin, while that of vincristine, the positive control, was 101 nmol/L. The typical morphologic changes were observed and the nuclear DNA fragmentation exhibited "ladder" pattern. The cell cycle of HL-60 cells was arrested in G2/M phase, and expression of bcl-2 gene was decreased while that of bax was increased.
CONCLUSIONS:
Erianin showed potent inhibitory activity on the proliferation of HL-60 cells. The inhibition might be relative to the apoptosis induced by Erianin and the altered expression of bcl-2 and bax genes in HL-60 cells.
Eur J Cancer. 2004 Jul;40(10):1554-65.
In vivo and in vitro evaluation of erianin, a novel anti-angiogenic agent.
This study evaluated the anti-angiogenic activities of Erianin in vivo and in vitro.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Erianin, a natural product from Dendrobium chrysotoxum, caused moderate growth delay in xenografted human hepatoma Bel7402 and melanoma A375 and induced significant vascular shutdown within 4 h of administering 100 mg/kg of the drug. Erianin also displayed potent anti-angiogenic activities in vitro: it abrogated spontaneous or basic fibroblast growth factor-induced neovascularisation in chick embryo; it inhibited proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (EC(50) 34.1+/-12.7 nM), disrupted endothelial tube formation, and abolished migration across collagen and adhesion to fibronectin. Erianin also exerted selective inhibition toward endothelial cells, and quiescent endothelium showed more resistance than in proliferative and tumour conditions. In a cytoskeletal study, Erianin depolymerised both F-actin and beta-tubulin, more significantly in proliferating endothelial cells than in confluent cells. In conclusion, Erianin caused extensive tumour necrosis, growth delay and rapid vascular shutdown in hepatoma and melanoma models; it inhibited angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro and induced endothelial cytoskeletal disorganisation.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggest that Erianin has the therapeutic potential to inhibit angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro.
HPLC of Erianin
