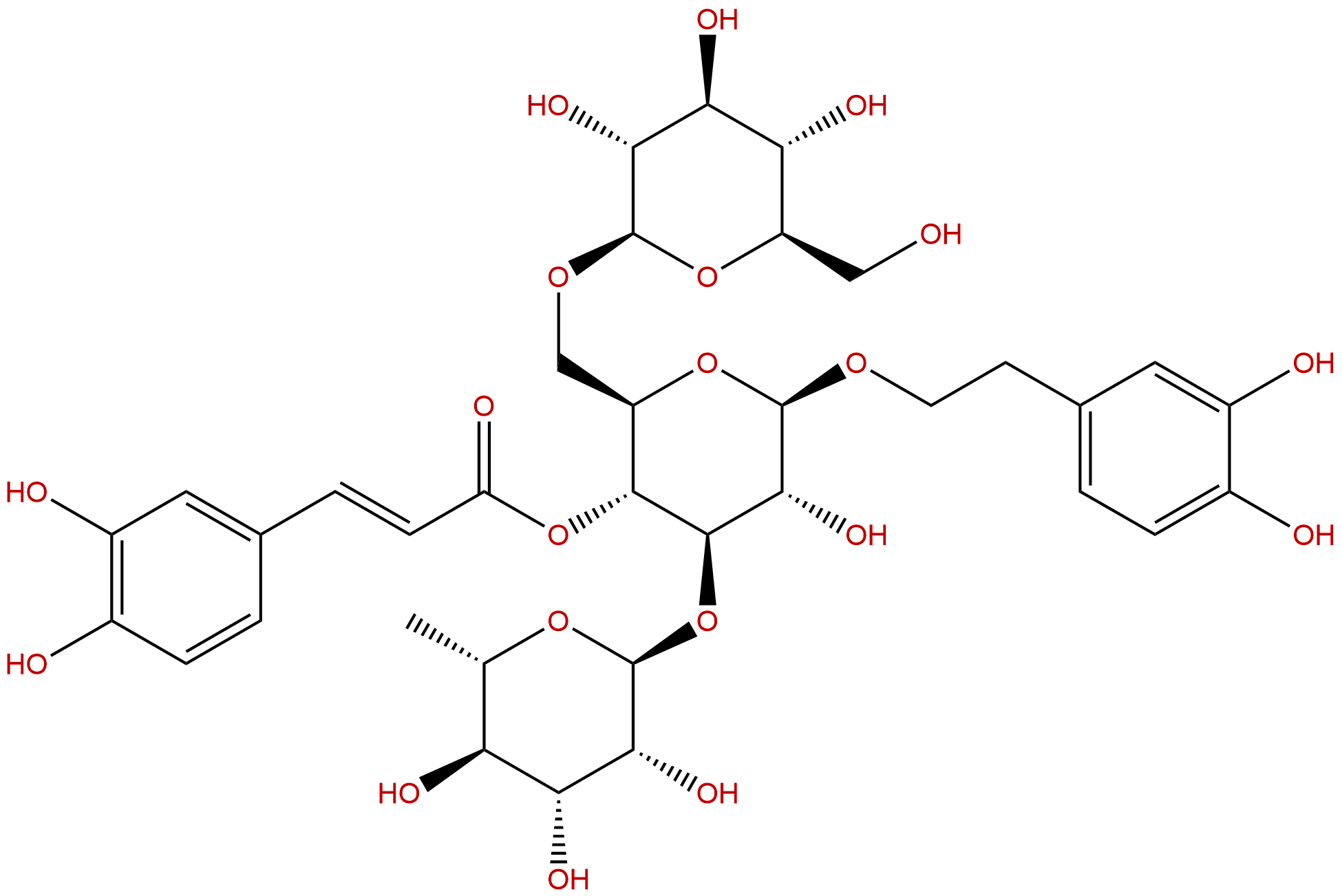
EchinacosideCAS No.:82854-37-3
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0520 |
| Formula: | C35H46O20 |
| Mol Weight: | 786.733 |
Product name: Echinacoside
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP0520
Cas No.: 82854-37-3
Formula: C35H46O20
Mol Weight: 786.733
Botanical Source: Cistanches herba
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Phenols
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Echinacoside is a natural polyphenolic compound, has various kinds of pharmacological activities, such as anti-senescence, anti-hypoxia, anti-cancer, anti-osteoporosis, antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, hepatoprotective, nitric oxide radical-scavenging and vasodilative ones. Echinacoside can improve the hematopoietic function of bone marrow in 5-FU-induced myelosuppression mice, it induces apoptotic cancer cell death by inhibiting the nucleotide pool sanitizing enzyme MTH1. Echinacoside inhibits cytochrome c release and caspase-3 activation caused by ensuing rotenone exposure via activating Trk-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway in neuronal cells.
References:
Int J Biol Macromol. 2015 Jan;72:243-53.
Echinacoside inhibits amyloid fibrillization of HEWL and protects against Aβ-induced neurotoxicity.
We investigated the protection provided by Echinacoside against neurotoxicity induced by β-amyloid protein (Aβ). Through spectroscopic analyses, electron microscopy, cell viability assay, and hemolysis assay, we found that Echinacoside dose dependently inhibited HEWL aggregation, and this inhibition occurred in different fiber-forming stages. Echinacoside could also scavenge the DPPH and OH free radicals in a concentration-dependent manner. 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) and 2',7'-dichlorodihydrofluoresceindiacetate (DCFH-DA) fluorescent measurement results indicated that Echinacoside could increase viability of rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells injured by Aβ and suppress the increase in intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) triggered by Aβ. The present study findings facilitate a better understanding of the interaction between Echinacoside and amyloid-forming proteins and also shed light on the protection of Echinacoside against amyloid fibril-induced neuronal cell death.
J Pharmacol Sci. 2014;126(2):155-63.
Antiproliferative effect of echinacoside on rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells under hypoxia.
The main purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of Echinacoside (ECH) on hypoxia-induced proliferation of rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) and the underlying mechanism.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
PASMCs were incubated under normoxia (nor), hypoxia (hyp), hypoxia + 0.35 mM ECH (hyp + ECH0.35), or hypoxia + 0.4 mM ECH (hyp + ECH0.4) for 24 h. Cell viability was assessed by MTS assays. The morphology of apoptosis was observed by DAPI staining, and apoptosis was quantified by flow cytometric analysis. Caspase-3 activity was determined by immunohistochemistry and real-time PCR, and the expressions of HIF-1α, Bax, Bcl-2, and Fas were determined by real-time PCR. Hypoxia induced significant proliferation of PASMCs, which could be inhibited by ECH in a concentration-dependent manner. This was associated with apoptosis of PASMCs. Z-DEVD-FMK could partly reduce the suppression effect of ECH; protein and gene expression of caspase-3 were significantly higher in the hyp + ECH0.4 and hyp + ECH0.35 groups. ECH significantly increased the expressions of Bax and Fas, but decreased the expressions of Bcl-2 and HIF-1α.
CONCLUSIONS:
ECH could inhibit hypoxia-induced proliferation of rat PASMCs, which is associated with apoptosis of PASMCs and improvement of hypoxia. ECH might be a potential agent for prevention and treatment of hypoxia-induced PAH.
Onco Targets Ther. 2015 Dec 8;8:3649-64.
Echinacoside induces apoptotic cancer cell death by inhibiting the nucleotide pool sanitizing enzyme MTH1.
Inhibition of the nucleotide pool sanitizing enzyme MTH1 causes extensive oxidative DNA damages and apoptosis in cancer cells and hence may be used as an anticancer strategy. As natural products have been a rich source of medicinal chemicals, in the present study, we used the MTH1-catalyzed enzymatic reaction as a high-throughput in vitro screening assay to search for natural compounds capable of inhibiting MTH1.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Echinacoside, a compound derived from the medicinal plants Cistanche and Echinacea, effectively inhibited the catalytic activity of MTH1 in an in vitro assay. Treatment of various human cancer cell lines with Echinacoside resulted in a significant increase in the cellular level of oxidized guanine (8-oxoguanine), while cellular reactive oxygen species level remained unchanged, indicating that Echinacoside also inhibited the activity of cellular MTH1. Consequently, Echinacoside treatment induced an immediate and dramatic increase in DNA damage markers and upregulation of the G1/S-CDK inhibitor p21, which were followed by marked apoptotic cell death and cell cycle arrest in cancer but not in noncancer cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these studies identified a natural compound as an MTH1 inhibitor and suggest that natural products can be an important source of anticancer agents.
HPLC of Echinacoside

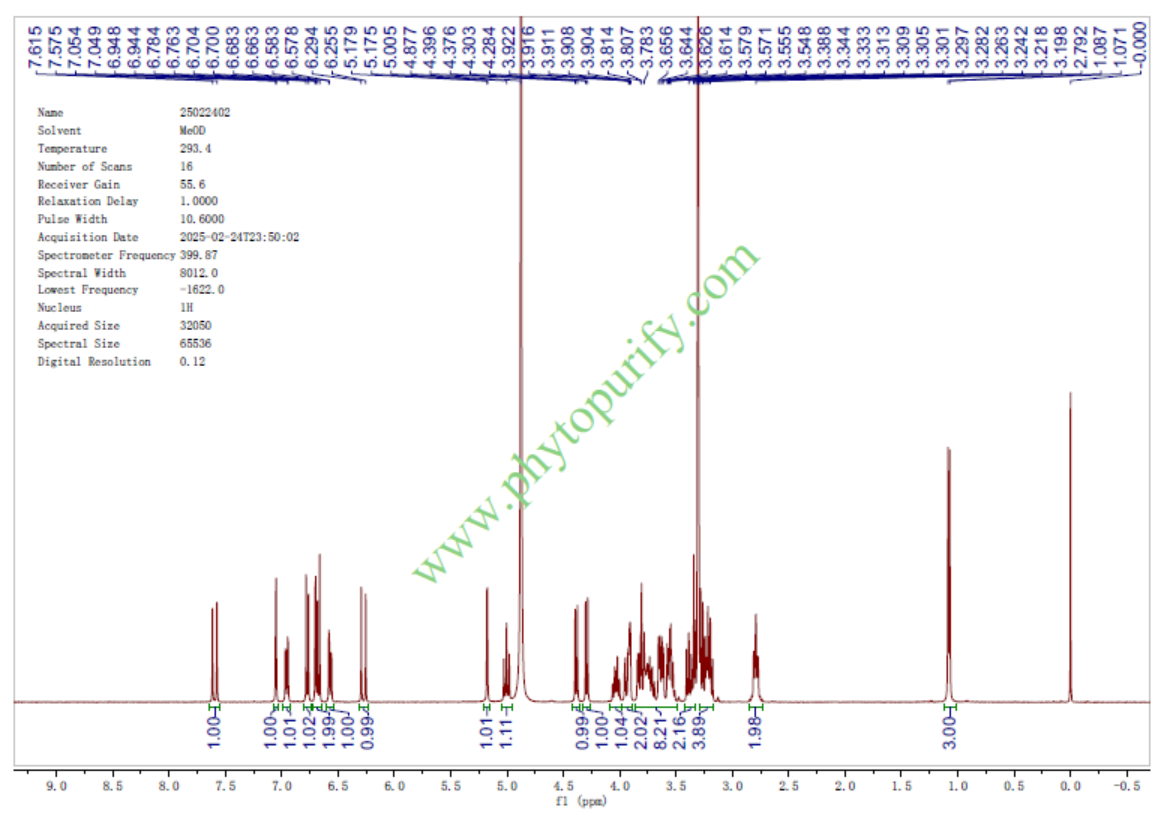
HNMR of Echinacoside