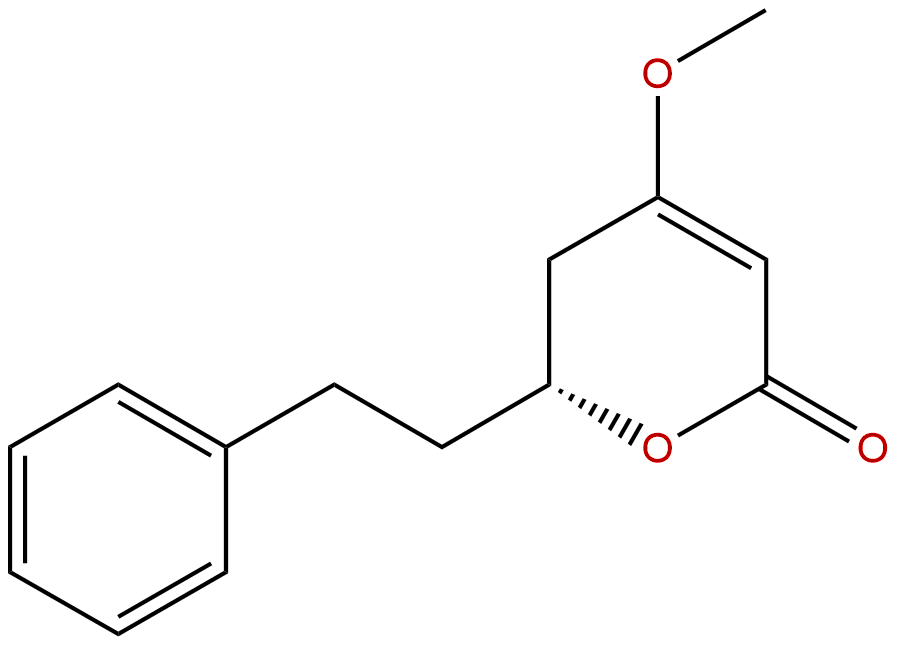
DihydrokawainCAS No.:587-63-3
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0495 |
| Formula: | C14H16O3 |
| Mol Weight: | 232.279 |
Synonym name: Marindinin
Catalogue No.: BP0495
Cas No.: 587-63-3
Formula: C14H16O3
Mol Weight: 232.279
Botanical Source: Root of Piper methysticum and Aniba gigantifolia
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Dihydrokavain may play an important role in regulation of GABAergic neurotransmission, it non-competitively inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-batrachotoxinin-A 20-alpha-benzoate to receptor site 2 of voltage-gated Na+ channels. Dihydrokavain may treat sleep disturbances, as well as stress and anxiety.
References:
Planta Med. 2002 Dec;68(12):1092-6.
Kavalactones and dihydrokavain modulate GABAergic activity in a rat gastric-brainstem preparation.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Using an in vitro neonatal rat gastric-brainstem preparation, the activity of majority neurons recorded in the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) of the brainstem were significantly inhibited by GABA A receptor agonist, muscimol (30 microM), and this inhibition was reversed by selective GABA A receptor antagonist, bicuculline (10 microM). Application of kavalactones (300 microg/ml) and Dihydrokavain (300 microM) into the brainstem compartment of the preparation also significantly reduced the discharge rate of these NTS neurons (39 % and 32 %, respectively, compared to the control level), and this reduction was partially reversed by bicuculline (10 microM). Kavalactones or Dihydrokavain induced inhibitory effects were not reduced after co-application of saclofen (10 microM; a selective GABA B receptor antagonist) or naloxone (100 nM; an opioid receptor antagonist). Pretreatment with kavalactones (300 microg/ml) or Dihydrokavain (300 microM) significantly decreased the NTS inhibitory effects induced by muscimol (30 microM), approximately from 51 % to 36 %.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results demonstrated modulation of brainstem GABAergic mechanism by kavalactones and Dihydrokavain, and suggested that these compounds may play an important role in regulation of GABAergic neurotransmission.
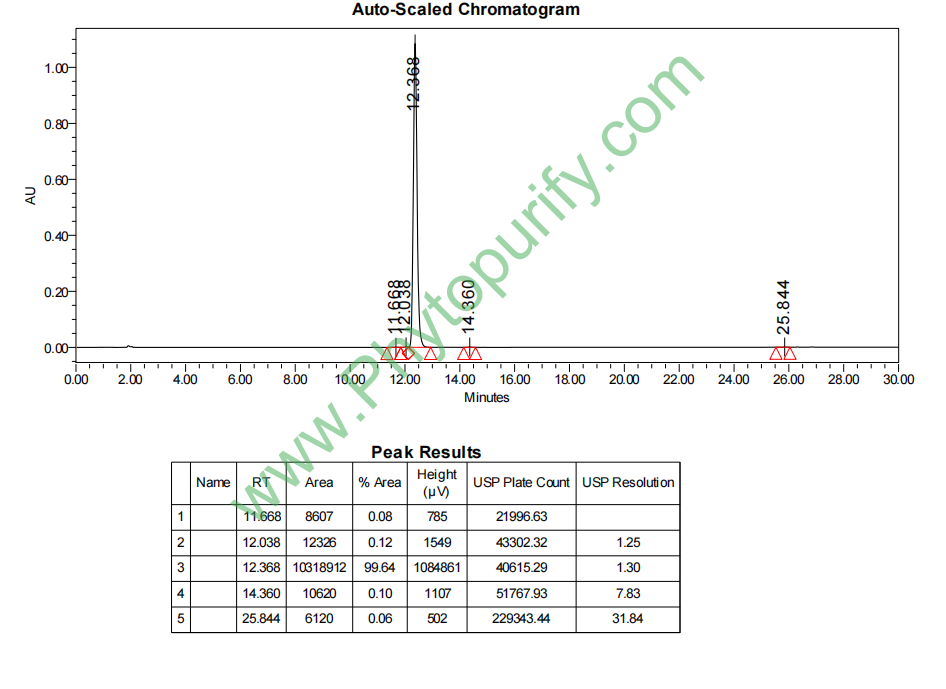
HPLC of Dihydrokawain