
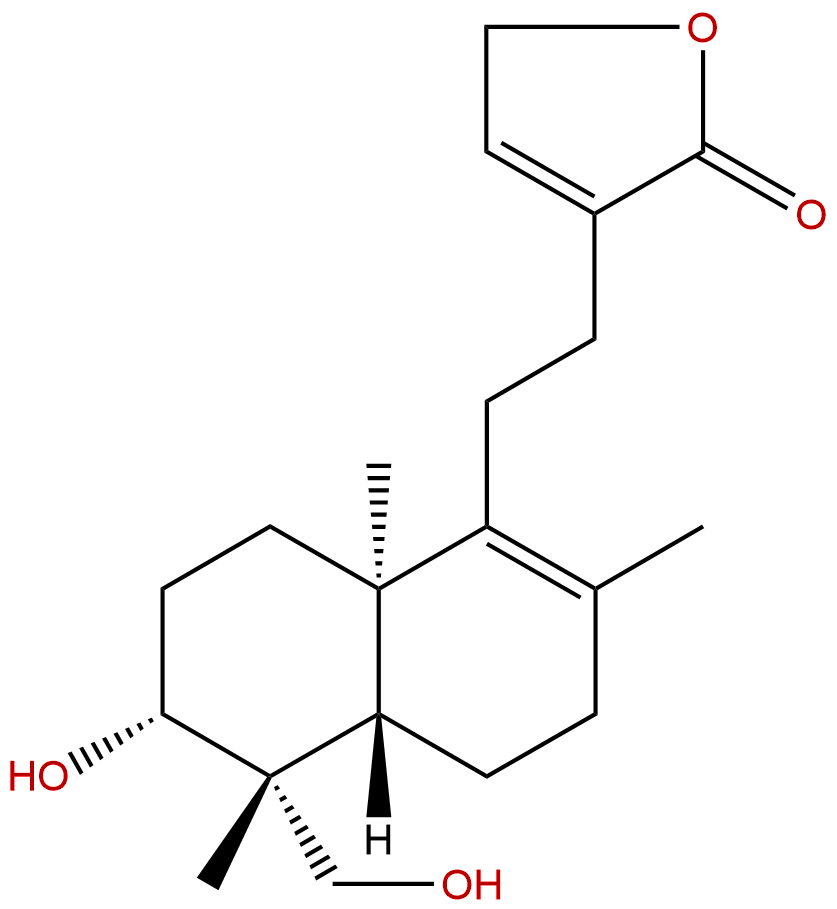
DeoxyandrographolideCAS No.:79233-15-1
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP3118 |
| Formula: | C20H30O4 |
| Mol Weight: | 334.456 |
Product name: Deoxyandrographolide
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP3118
Cas No.: 79233-15-1
Formula: C20H30O4
Mol Weight: 334.456
Botanical Source:
Physical Description: Cryst.
Type of Compound: Diterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams. Inquire for bulk scale.
We provide solution to improve the water-solubility of compounds, thereby facilitating the variety of activity tests and clinic uses.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Description:
Deoxyandrographolide promotes glucose uptake through glucose transporter-4 translocation to plasma membrane in L6 myotubes and exerts antihyperglycemic effect in vivo.
References:
Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Dec 5;768:207-16.
Deoxyandrographolide promotes glucose uptake through glucose transporter-4 translocation to plasma membrane in L6 myotubes and exerts antihyperglycemic effect in vivo.
Skeletal muscle is the principal site for postprandial glucose utilization and augmenting the rate of glucose utilization in this tissue may help to control hyperglycemia associated with diabetes mellitus.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we explored the effect of Deoxyandrographolide (DeoAn) isolated from the Andrographis paniculata Nees on glucose utilization in skeletal muscle and investigated its antihyperglycemic effect in vivo in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats and genetically diabetic db/db mice. In L6 myotubes, DeoAn dose-dependently stimulated glucose uptake by enhancing the translocation of glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) to cell surface, without affecting the total cellular GLUT4 and GLUT1 content. These effects of DeoAn were additive to insulin. Further analysis revealed that DeoAn activated PI-3-K- and AMPK-dependent signaling pathways, account for the augmented glucose transport in L6 myotubes. Furthermore, DeoAn lowered postprandial blood glucose levels in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats and also suppressed the rises in the fasting blood glucose, serum insulin, triglycerides and LDL-Cholesterol levels of db/db mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggest the therapeutic efficacy of the DeoAn for type 2 diabetes mellitus and can be potential phytochemical for its management.