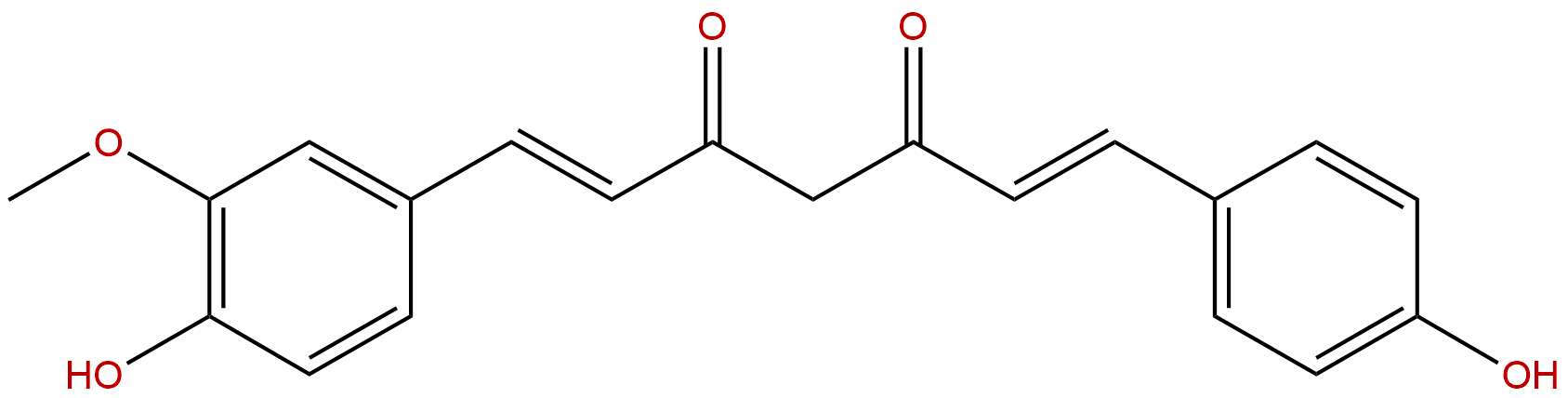
Demethoxycurcumin Descrtption
Product name: Demethoxycurcumin
Synonym name: p-Hydroxycinnamoylferuloylmethane;7789-33-5
Catalogue No.: BP0472
Cas No.: 22608-11-3
Formula: C20H18O5
Mol Weight: 338.359
Botanical Source: Curcuma zedoaria, Curcuma longa and Curcuma xanthorrhiza
Physical Description: Yellow powder
Type of Compound: Phenols
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Demethoxycurcumin (DMC) is one of the main active compounds of curcuminoids found in turmeric powder, which is used as a spice in Asian cooking and traditional medicine, has anti-inflammation and anti-cancer activities, the mechanism of DMC-mediated anti-invasive activity involves modulation of the expression of invasion-associated proteins, possibly by targeting NF-κB in MDA-MB-231 cells.[1]
Demethoxycurcumin has the relative potency for suppression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced nuclear factor-B (NF-B) activation, the relative potency is curcumin > demethoxycurcumin> bisdemethoxycurcumin, they also exhibit variable anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative activities, which do not correlate with their ability to modulate the ROS status.[2]
Demethoxycurcumin, curcumin and bisdemethoxycurcumin have pro-oxidant, anti-oxidant and cleavage activities on DNA .[3]
Demethoxycurcumin (DMC) has differential potency for inhibition of cancer cell invasion, the differential potency is BDMC> or =DMC>Cur, whereas the cell migration is not affected, shows higher antimetastasis potency than curcumin by the differentially down-regulation of ECM degradation enzymes.[4]
Demethoxycurcumin exerts its in vitro anti-inflammatory effect in LPS-activated N9 microglial cells by blocking nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and MAPKs activation, which may be partly due to its potent down-regulation of the NADPH-derived iROS production.[5]
Demethoxycurcumin can induce the apoptosis of human lung cancer NCI-H460 cells through the mitochondrial-dependent pathway, it may be used as a novel anticancer agent for the treatment of lung cancer in the future.[6]
References:
[1] Yodkeeree S, Ampasavate C, Sung B, et al. Eur J Pharmacol, 2009, 627(1-3):8-15.
[2] Sandur SK, Pandey MK, Sung B,et al. Carcinogenesis, 2007, 28(8):1765-73.
[3] Jayaprakasha G K, Rao L J, Sakariah K K. Food Chem, 2006, 98(4):720-4.
[4] Ahsan H, Parveen N, Khan N U, et al. Chem-biol interact, 1999, 121(2):161-75.
[5] Yodkeeree S, Chaiwangyen W, Garbisa S, et al. J Nutr Biochem, 2009, 20(20):87-95.
[6] Zhang L, Wu C, Zhao S, et al. Int Immunopharmacol, 2010, 10(3):331-8.
[7] Jadhav B K, Mahadik K R, Paradkar A R. Chromato, 2007, 65(7):483-8.