
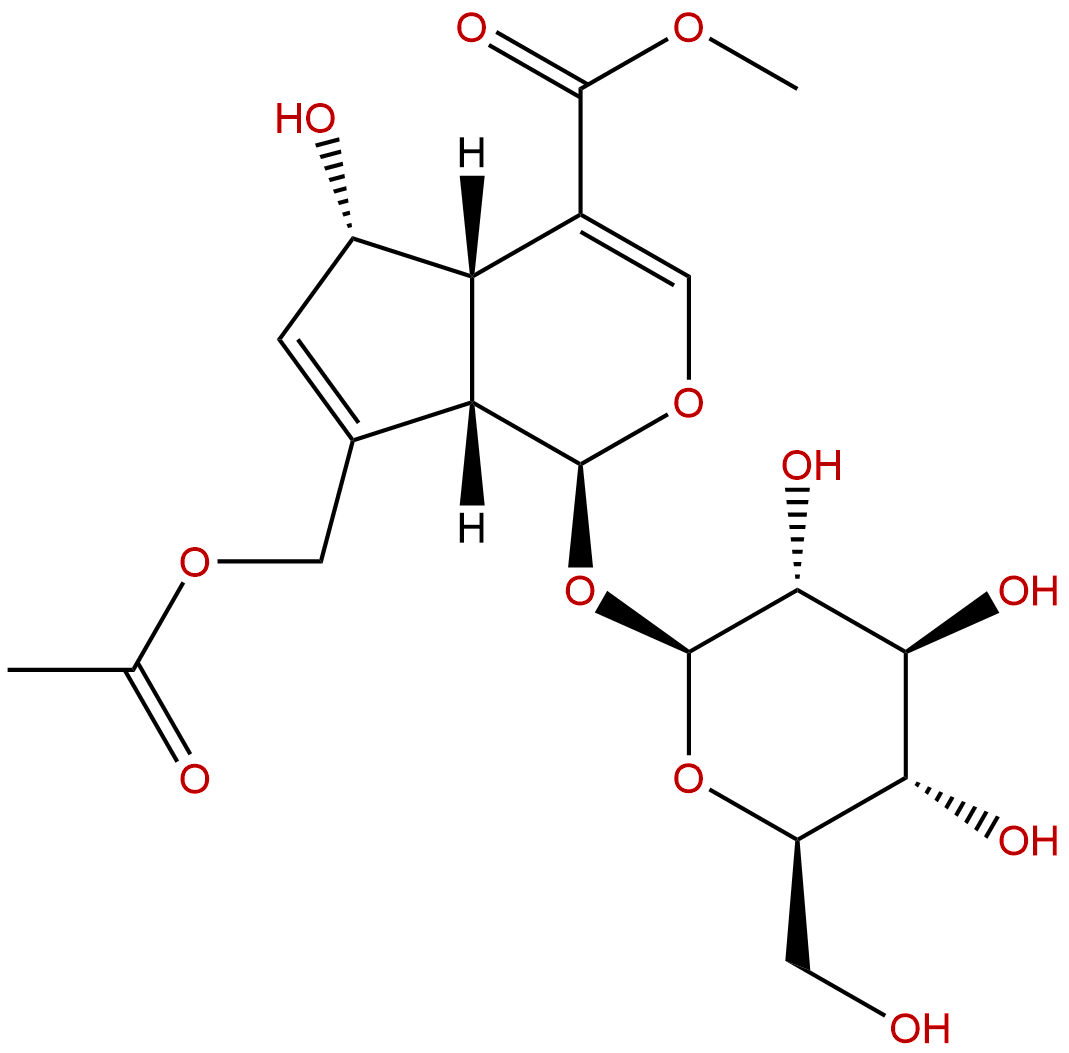
DaphyllosideCAS No.:14260-99-2
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1666 |
| Formula: | C19H26O12 |
| Mol Weight: | 446.405 |
Product name: Daphylloside
Synonym name: Methyl asperulosidic acid
Catalogue No.: BP1666
Cas No.: 14260-99-2
Formula: C19H26O12
Mol Weight: 446.405
Botanical Source: "Daphniphyllum macropodum; Gardenia jasminoides, Plantago lagopus and Mussaenda pubescens. Component of Zhi Zi"
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Iridoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams. Inquire for bulk scale.
We provide solution to improve the water-solubility of compounds, thereby facilitating the variety of activity tests and clinic uses.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Description:
Daphylloside, and asperuloside can be suggested as endoplasmic reticulum stress regulators.
References:
Vietnam Journal of Chemistry, 2015, 53(2e).
Iridoid glycosides from Morinda tomentosa and their endoplasmic reticulum stress modulation activity
Three iridoids 1 - 3, asperulosidic acid, Daphylloside, and asperuloside, were isolated from the methanol extract of the leaves of Morinda tomentosa.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Their chemical structures were elucidated by 1D- and 2D-NMR spectra and in comparison with those reported in the literature. The effects of these compounds on the endoplasmic reticulum stress in XBP1-eGFP-transfected the 293 T cells were measured. Compound 3 significantly reduced the ER-stress both in DMSO-treated and thapsigargin-treated cells. Unlike this compound, compound 3 selectively reduced thapsigargin-induced ER-stress without any effect on the level of XBP1 splicing in DMSO-treated cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggested that compounds 2 and 3 can be suggested as new ER stress regulators.