Corosolic acidCAS No.:4547-24-4
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0395 |
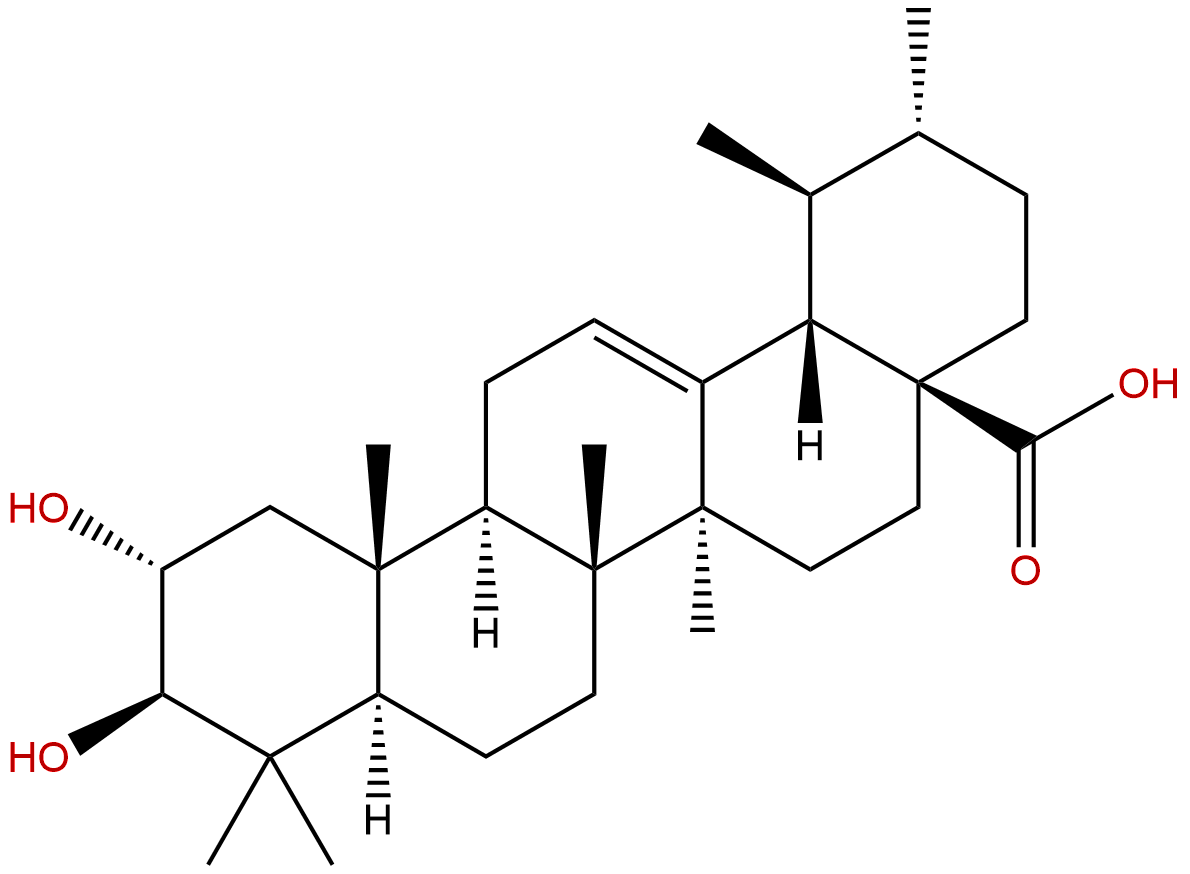
| Formula: | C30H48O4 |
| Mol Weight: | 472.71 |
Product name: Corosolic acid
Synonym name: 2alpha-Hydroxyursolic acid
Catalogue No.: BP0395
Cas No.: 4547-24-4
Formula: C30H48O4
Mol Weight: 472.71
Botanical Source: Chamaenerion angustifolium (preferred genus name Epilobium), Arnebia euchroma, Tripetaleia paniculata and a number of other plants
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Triterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Corosolic acid (CRA), a constituent of banaba leaves, has been reported to have anti-inflammatory and hypoglycemic activities, it can ameliorate hypertension, abnormal lipid metabolism, and oxidative stress as well as the inflammatory state in SHR-cp rats, suggests CRA can be beneficial for preventing atherosclerosis-related diseases.[1]
Corosolic acid significantly inhibits cell viability in both a dose- and a time-dependent manner, induces apoptosis is associated with the activation of caspases via a mitochondrial pathway, suggests it could have strong potentials for clinical application in treating human cervix adenocarcinoma and improving cancer chemotherapy.[2]
Corosolic acid can suppress the M2 polarization of macrophages and tumor cell proliferation by inhibiting both STAT3 and NF-κB activation, thus, it might be a potential new tool for tumor prevention and therapy.[3]
Corosolic acid has antidiabetic effects(especially type 2 diabetes), can improve glucose metabolism by reducing insulin resistance, it inhibits the enzymatic activities of several diabetes-related non-receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) in vitro, such as PTP1B, T-cell-PTP, src homology phosphatase-1 and src homology phosphatase-2.[4,5]
Corosolic acid has antitumor effects in murine sarcoma model through significantly impairing subcutaneous tumor development and lung metastasis and targeting the immunosuppressive activity of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC), and can enhance the antitumor effects of adriamycin and cisplatin in in vitro.[6]
References:
[1] Yu Y, Yamada K, Yoshikawa N, et al. Life Sci, 2006, 79(26):2474-9.
[2] Xu Y, Ge R, Du J, et al. Cancer Lett, 2009, 284(2):229237.
[3] Fujiwara Y, Komohara Y, Ikeda T, et al. Cancer Sci, 2011, 102(1):206-11.
[4] Miura T, Ueda N, Yamada K, et al. Biolo Pharmal Bull, 2006, 29(3):585-7.
[5] Shi L, Zhang W, Zhou Y Y, et al. Eur J Pharmacol, 2008, 584(1):21-9.
[6] Hasita Horlad ?, Yukio Fujiwara ?, Takemura K, et al. Mol Nutr Food Res, 2013, 57(6):1046–54.
[7] Liu B, Yang Y F, He-Zhen W U. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2011, 31(12):2217-9.
HNMR of Corosolic acid
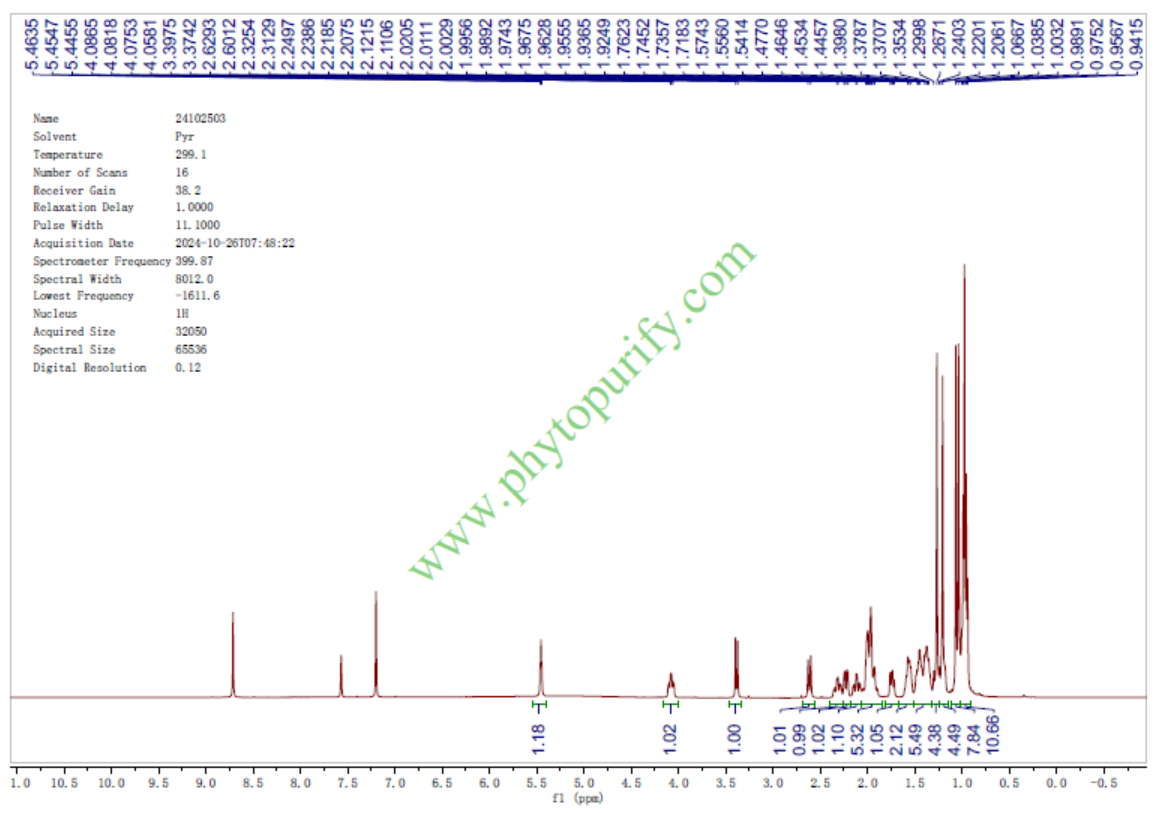
HPLC of Corosolic acid