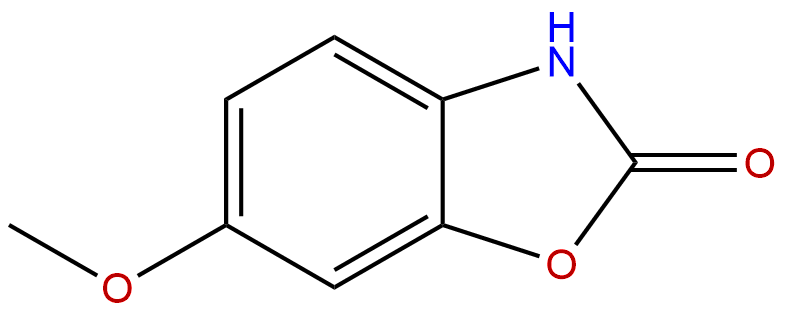
CoixolCAS No.:532-91-2
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP3451 |
| Formula: | C8H7NO3 |
| Mol Weight: | 165.148 |
Product name: Coixol
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP3451
Cas No.: 532-91-2
Formula: C8H7NO3
Mol Weight: 165.148
Botanical Source:
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Alkaloids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams. Inquire for bulk scale.
We provide solution to improve the water-solubility of compounds, thereby facilitating the variety of activity tests and clinic uses.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
References:
Arch Pharm Res. 2015 May;38(5):620-7.
Suppressive effects of coixol, glyceryl trilinoleate and natural products derived from Coix Lachryma-Jobi var. ma-yuen on gene expression, production and secretion of airway MUC5AC mucin.
In this study, we investigated whether natural products including Coixol derived from Coix Lachryma-Jobi var. ma-yuen affect MUC5AC mucin gene expression, production and secretion from airway epithelial cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Confluent NCI-H292 cells were pretreated with oleic acid, linoleic acid, glyceryl trilinoleate, beta-stigmasterol or Coixol for 30 min and then stimulated with PMA (phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate), EGF (epidermal growth factor) or TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-α) for 24 h. The MUC5AC mucin gene expression, mucin protein production and secretion were measured by RT-PCR and ELISA. The results were as follows: (1) Oleic acid, linoleic acid, glyceryl trilinoleate, beta-stigmasterol and Coixol inhibited the expression of MUC5AC mucin gene induced by PMA from NCI-H292 cells; (2) Oleic acid, linoleic acid, glyceryl trilinoleate, beta-stigmasterol and Coixol also inhibited the production of MUC5AC mucin protein induced by the same inducers from NCI-H292 cells; (3) Coixolinhibited the expression of MUC5AC mucin gene and production of MUC5AC mucin protein, induced by EGF or TNF-α from NCI-H292 cells; (4) Coixol decreased PMA-induced MUC5AC mucin secretion from NCI-H292 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
This result suggests that Coixol, the characteristic component among the examined five natural products derived from C. Lachryma-Jobi var. ma-yuen, can regulate gene expression, production and secretion of mucin, by directly acting on airway epithelial cells.
Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1981 Mar;77(3):245-59.
Behavioral and EEG effects of coixol (6-methoxybenzoxazolone), one of the components in Coix Lachryma-Jobi L. var. ma-yuen Stapf.
Coixol (6-methoxybenzoxazolone) contained in Coix Lachryma-Jobi L. var. ma-yuen Stapf was compared with chlorzoxazone with respect to behavioral and EEG effects in mice and rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Coixol 50-100 mg/kg, i.p. decreased locomotor activities of both species and produced hypothermia in rats. These effects of Coixol were the same in potency as chlorzoxazone given in the same dose. Coixol was approximately twice as potent as chlorzoxazone in potentiating thiopental-induced sleep. This compound attenuated the writhing syndrome induced by 1% acetic acid and increased the threshold to jumping response induced by foot shock, to the same degree as seen with chlorzoxazone. Coixol was equipotent to chlorzoxazone in preventing convulsions induced by maximal electro-shock, while it was about 1.5 times more potent than chlorzoxazone in suppressing pentylenetetrazol-induced convulsion. Coixol 20-100 mg/kg inhibited the lever pressing response of hypothalamic self-stimulation in rats. In rats with chronically implanted electrodes, Coixol 50-100 mg/kg induced drowsy patterns on the spontaneous EEG. The EEG arousal response to the external auditory stimulation was inhibited by the same doses of Coixol, whereas it failed to suppress the arousal response to the midbrain reticular stimulation.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that Coixol has pharmacological properties qualitatively similar to chlorzoxazone and acts as a central muscle relaxant with an anti-convulsant effect.
Biol Reprod. 1988 Sep;39(2):465-71.
The plant metabolite 6-methoxybenzoxazolinone interacts with follicle-stimulating hormone to enhance ovarian growth.
6-Methoxybenzoxazolinone (6-MBOA) is a novel plant metabolite that enhances reproductive status in vertebrate consumers while it inhibits insect, fungal, and bacterial infestation of the plant. Ovaries of prepubertal rats show a dose response to increasing amounts of 6-MBOA.administered in Silastic capsule implants.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Ovaries increased in size in response to capsules with 0.5-3.0 cm exposed surface area of 6-MBOA, whereas larger capsules (6 cm 6-MBOA) had no effect. Removal of the pituitary in both prepubertal and mature rats eliminated the stimulatory influence of 6-MBOA. In hypophysectomized animals treated with diethylstibestrol implants, 6-MBOA did not affect ovarian weight and no animals ovulated. Administration of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) increased ovarian weight and stimulated production of ova, and FSH combined with 6-MBOA resulted in larger ovaries that released more ova. 6-MBOA also enhanced ovarian growth in intact prepubertal animals treated with pregnant mare's serum gonadotropin.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results show that 6-MBOA has the ability to interact with FSH to stimulate follicular development and increase ovulation. Non-steroidal plant compounds may have a significant impact on the reproductive patterns of wild animal populations.
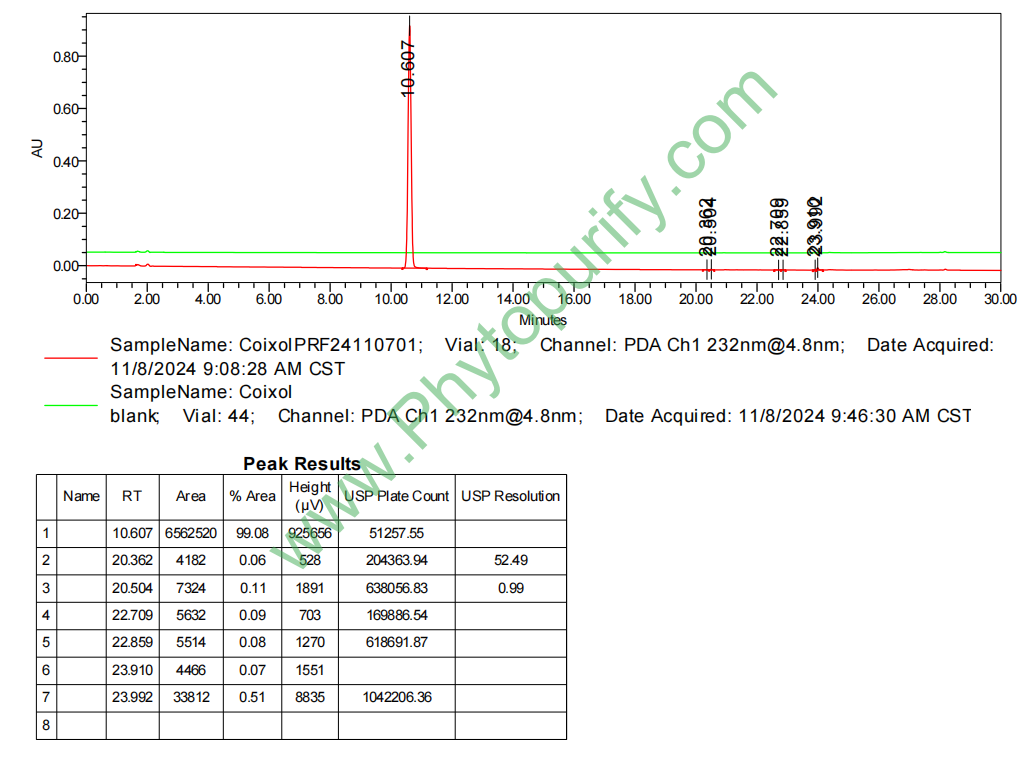
HPLC of Coixol
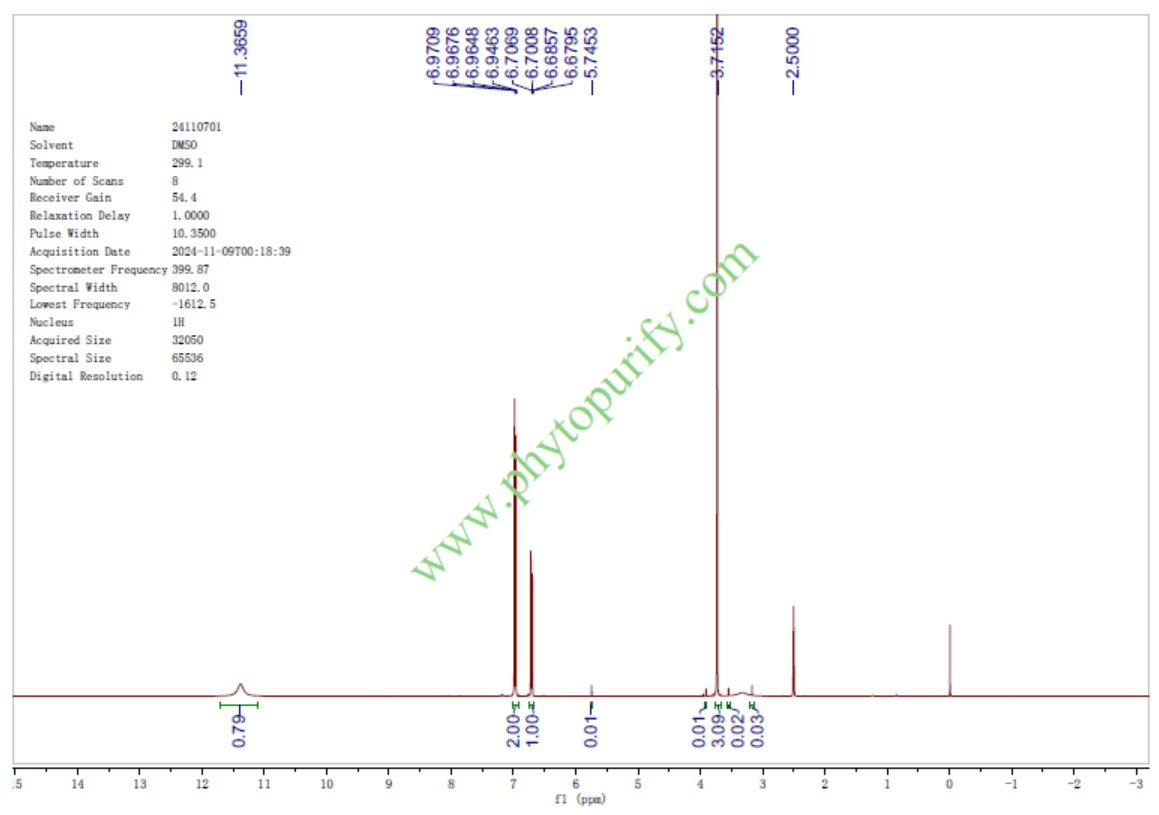
HNMR of Coixol