
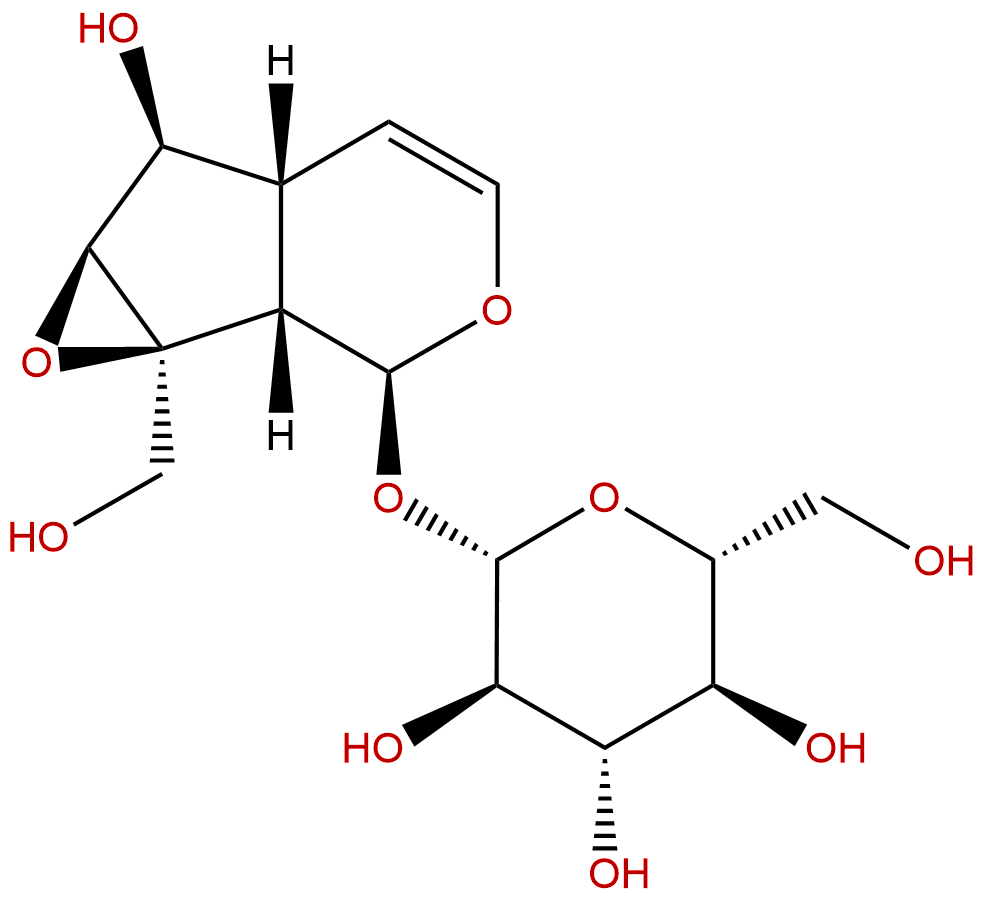
CatalpolCAS No.:2415-24-9
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0321 |
| Formula: | C15H22O10 |
| Mol Weight: | 362.331 |
Product name: Catalpol
Synonym name: Catalpinoside
Catalogue No.: BP0321
Cas No.: 2415-24-9
Formula: C15H22O10
Mol Weight: 362.331
Botanical Source: Plantago lanceolata, Buddleia globosa, Buddleia variabilis and Lagotis brevituba
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Iridoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Catalpol, an iridoid glucoside, has been reported to inhibit apoptosis of neuron and endothelial cells; the pretreatment of H9c2 cells with catalpol can be against H 2 O 2 -induced apoptosis, and the protective effect of catalpol involves the mitochondrial-dependent caspase pathway and is associated with increased Bcl-2 and decreased Bax expression.[1]
Catalpol has the neuroprotective effects of in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory models, it can prevent mesencephalic neuron death and ameliorate cognitive ability animals; catalpol can exert inhibitory effects on the inflammatory reaction in astrocytes and that inactivation of NF-κB could be the major determinant for its anti-inflammatory mechanism, therefore, it may potentially be a highly effective therapeutic agent in treating neurodegenerative diseases associated with inflammation.[2]
Catalpol exerts the most significant cytoprotective effect on astrocytes by suppressing the production of free radicals and elevating antioxidant capacity.[3]
Catalpol can increase presynaptic proteins and up-regulate relative signaling molecules in the hippocampus of the aged rats, it seems to indicate that catalpol might ameliorate age-related neuroplasticity loss by “normalizing” presynaptic proteins and their relative signaling pathways in the aged rats.[4]
References:
[1] Hu L A, Sun Y K, Zhang H S, et al. Bioscience Reports, 2016,36(3).
[2] Bi J, Jiang B, Zorn A, et al. Toxicol in Vitro, 2013, 27(2):543-50.
[3] Li Y, Bao Y, Bo J, et al. Int J Dev Neurosci, 2008, 26(3–4):309-17.
[4] Liu J, He Q J, Zou W, et al. Brain Res, 2006, 1123(1):68-79.
[5] Sun L L, Ren Y H, Chen H L, et al. China Pharmacy, 2013(04):374-5.
HPLC of Catalpol
